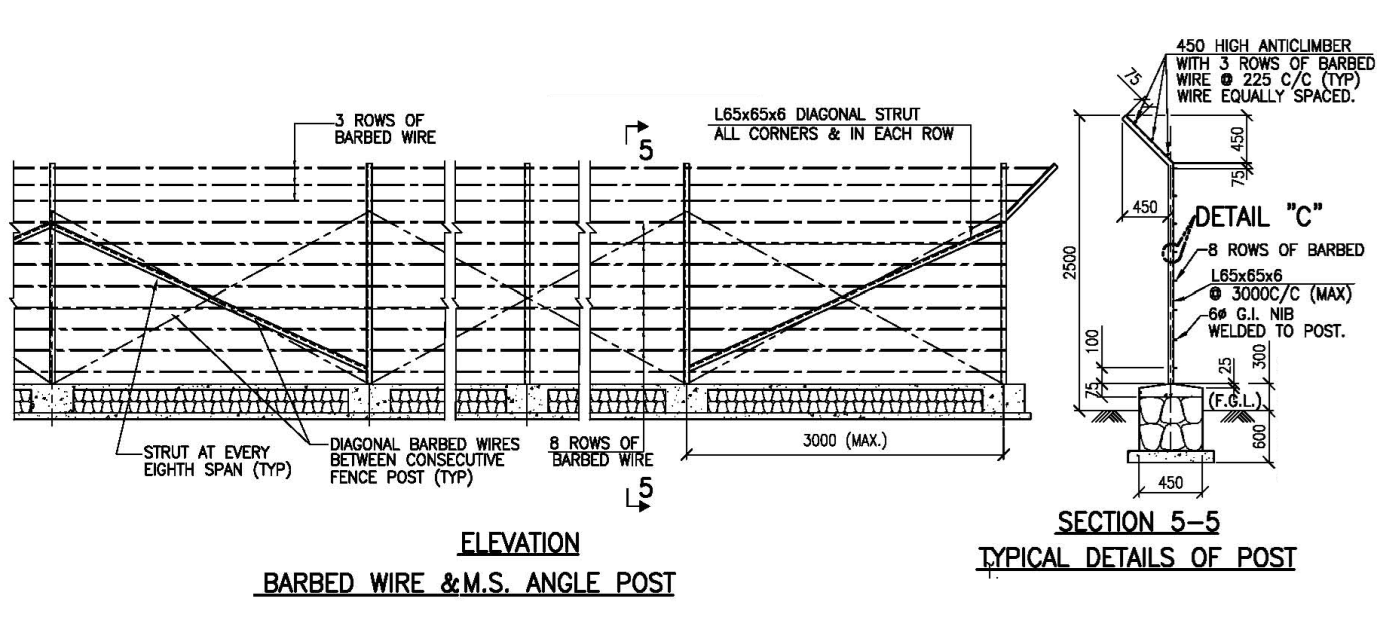
Fencing Detail Drawing Requirements
To create a comprehensive fencing detail drawing, ensure the following components and details are included:
1. Plan View
- Show the layout of the fence, including:
- Total length of the fence.
- Location of posts (spacing, corner posts, and gate posts).
- Alignment with property boundaries or site limits.
- Gate locations and dimensions.

2. Elevation View
- Display the height of the fence above the ground.
- Indicate:
- Fence material (chain link, barbed wire, panels, etc.).
- Number of wires or panels.
- Position of hooks or clamps for wire fixing.
- Post spacing and height distribution.
3. Material Specifications
- Specify materials used, such as:
- Concrete grade (e.g., M20 or M25).
- Steel reinforcement (diameter and type).
- Fencing material (chain link, barbed wire, etc.).
- Protective coatings (paint, galvanization).
4. Connection Details
- Hooks or clamps for attaching the fence material.
- Fastening methods (bolts, welding, or ties).
- Joint details for corner and gate posts.
5. Notes and Standards
- Mention relevant codes and standards, e.g., IS 456, IS 1786.
- Include any additional instructions for installation and curing.

Sample Drawing Description
A drawing that includes:
- RCC fence post elevation with reinforcement details.
- Foundation detail with dimensions.
- Hook positions for fencing wires.
- Plan view of post alignment and spacing.
Steel Fencing with Barbed Wire: Codal Requirements
Below are the general codal requirements for designing and constructing steel fencing with barbed wire as per Indian and international standards:
1. Indian Standards (IS Codes):
- IS 280:2006
- Specifies the requirements for mild steel wire used for barbed wire.
- Minimum tensile strength: 350 MPa for the wire.
- Barbs should be made of galvanized steel wire with sharp edges.
- IS 4826:1979
- Deals with the galvanization requirements for steel fencing materials.
- Minimum zinc coating: 275 g/m² for outdoor fencing in moderate environments.
- IS 1521:1972
- Specifies tensile tests for metallic wires.
- Ensures the strength of barbed wire and fencing wires.
- IS 875 (Part 3):1987
- Covers wind load considerations for fencing in exposed areas.
- IS 16644:2018
- Provides specifications for security fencing with barbed wires.

2. International Standards
- ASTM A121-07
- Covers specifications for barbed wire, including coating and tensile properties.
- ASTM F567-14
- Details the installation guidelines for security fencing, including barbed wire.
- ISO 556:1975
- Specifies barbed wire dimensions and tolerances for standard applications.
3. General Design Requirements
- Post Spacing:
- Typically 2.5–3 meters for standard fencing.
- Height of Fencing:
- Minimum height: 1.5–2.4 meters, depending on security needs.
- Barbed Wire Configuration:
- Number of strands: 3–5.
- Spacing between strands: 150–200 mm.
- Steel Fence Posts:
- Material: Hot-rolled steel, galvanized or painted.
- Dimensions: Circular hollow sections (50 mm diameter) or angular sections (50 mm x 50 mm).
- Concrete Footing:
- Minimum size: 300 mm x 300 mm x 500 mm deep.
4. Codal Installation Guidelines
- Posts should be embedded 0.6–0.9 m below ground level for stability.
- Tensioning devices to maintain taut wires.
- Use corrosion-resistant materials or proper coatings.
Requirements for RCC Fence Posts
RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) posts are commonly used for durable fencing solutions. Below are the key requirements and considerations:
1. Material Requirements
- Cement: Use OPC 43/53 grade cement for strength and durability.
- Aggregate:
- Coarse Aggregate: Crushed stone with a maximum size of 20 mm.
- Fine Aggregate: Clean sand with proper grading.
- Reinforcement Steel:
- Mild steel or HYSD bars of 6 mm to 12 mm diameter depending on the design.
- Ensure rust-free steel bars.
- Water: Clean, potable water for mixing and curing.
2. Design Requirements
- Dimensions:
- Height: Typically 1.8 m to 3.0 m above ground, with 0.5 m below ground for embedding.
- Cross-section: Square (100 mm x 100 mm) or rectangular (100 mm x 150 mm), depending on the load.
- Reinforcement:
- Provide 4 longitudinal bars with lateral ties at 150 mm spacing.
- For higher loads, increase reinforcement diameter or density.
- Concrete Mix: Use M20 or M25 grade concrete for strength and durability.
3. Structural Considerations
- Load Resistance: Posts must resist:
- Wind loads.
- Tension from barbed wire or fencing material.
- Lateral loads from environmental factors.
- Spacing Between Posts: Typically 2.5 to 3.0 m depending on fence material and design.
- Foundation: Embed posts in a concrete base to ensure stability.
- Depth: Minimum 500 mm to 1000 mm depending on soil conditions.
- Width: At least 1.5 times the cross-section of the post.
4. Durability Requirements
- Cover to Reinforcement: Provide at least 20-25 mm cover to avoid corrosion.
- Curing: Cure for at least 7-14 days to achieve full strength.
- Finishing: Apply water-resistant paint or plaster for additional protection.
5. Installation Guidelines
- Alignment: Ensure proper alignment and plumb during installation.
- Foundation Filling: Compact the soil around the post to prevent tilting.
- Fencing Attachment: Use hooks, grooves, or clamps integrated into the post for attaching fencing material.
6. Standards and Codes
- IS Codes:
- IS 456:2000 for concrete design.
- IS 1786 for reinforcement bars.
- Safety: Ensure compliance with local construction regulations and safety guidelines.


- 3D HOUSE DESIGN (10)
- Civil and Structural Design Calculations (32)
- Commercial Plans (5)
- Engineering Concepts – Civil & Structural (91)
- Excel Spreadsheets (16)
- House Plans (39)
- Industrial standards (29)
Cage Ladder Specification and Detail Drawing
Detailed Specification for Steel Cage Ladders Steel cage ladders are robust, durable, and commonly used…
Staircase Ideas 40+
Here are some staircase ideas to inspire designs for residential, commercial, or creative spaces: 1….
Vertical Vessel Foundation Design
Vertical Vessel foundation design The design of a foundation for a vertical vessel involves ensuring…
Effective Length for RCC Columns
In STAAD.Pro, ELY and ELZ are parameters used to define the effective length factors of…
DESIGN OF SLABS AS PER IS456
DESIGN OF SLABS AS PER IS456 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional…
Design of Staircase Waist Slab
Design of Staircase Waist Slab A waist slab is the inclined structural element of a…
Monorail Beam Design
Designing a monorail beam as per IS 800:2007 (General Construction in Steel – Code of…
HOUSE PLAN 35 x 50 | SOUTH FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 35 x 50 | SOUTH FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19)
Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19) The design of concrete beams in…
Wind Load Calculation as per Canadian Code | NBCC 2020 |
To calculate wind load as per the National Building Code of Canada (NBCC) 2020, the…
HOUSE PLAN 40 x 60 | NORTH FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 40 x 60 | NORTH FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
HOUSE PLAN 60 x 30 | SOUTH FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 60 x 30 | SOUTH FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
RCC Fencing Post Details
Requirements for RCC Fence Posts RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) posts are commonly used for durable…
HOUSE PLAN 30 x 40 | NORTH FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 30 x 40 | NORTH FACING | North facing House Plan 30 x…
HOUSE PLAN 45 x 45 | WEST FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 45 x 45 | WEST FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
HOUSE PLAN 40 x 40 | WEST FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 40 x 40| WEST FACING | West facing House Plan 40 x40 ground…
HOUSE PLAN 30 x 50 | SOUTH FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 30 x 50 | SOUTH FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
Modern House Front Elevation Design
Designing a Front Elevation involves creating an attractive and functional exterior view of a building….
Transformer Foundation Design
Designing a transformer foundation involves considering the transformer’s size, weight, dynamic forces, and environmental conditions…
Gypsum Board False Ceiling Installation
Gypsum board false ceiling installation layout and details Installing a false ceiling with gypsum board…
Box Culvert Design
Box culvert design according to IRC 6 (Standard Specifications and Code of Practice for Road…
Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals
Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals Pedestal rebars parallel to anchor bolts have been…
Wind Load Calculation for Pipe Rack
To calculate wind load on Pipe racks, open structures, cable trays and pipes as per ASCE 7-10, use…
Apartment House Plan | West Facing 60 x 60 |
HOUSE PLAN 60 x 60 | WEST FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
kitchen marble design 30+
Here is a modern kitchen design with luxurious marble elements. It showcases a sleek and…
Wind Load Calculation as per IS 875 Part 3 2015
Wind Load Calculation Wind speed -33m/sec From Ground floor to Slab level – 14.675m SLAB…
DESIGN BASIS FOR CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL
Design Basis for Civil and Structural SPECIFIC DESIGN REQUIREMENTS [CIVIL] CONTENT CLAUSE NO. …
General Specification for Civil and Structural Works
CONTENTS CLAUSE NO.DESCRIPTIONPAGE NO.1.00.00INTRODUCTION12.00.00CODES AND STANDARDS13.00.00SCOPE OF CIVIL WORKS124.00.00MAJOR PLANT STRUCTURES/UTILITIES/13 COMPONENTS 5.00.00DOCUMENT SUBMISSION156.00.00LAYOUT167.00.00WORKMANSHIP178.00.00TEMPORARY WORK179.00.00INTERFACE WITH STRUCTURES…
Green Building
A green building is a structure designed, constructed, and operated to minimize its environmental impact…
Fireproofing Details
Fireproofing, also known as fire-resistive protection, is crucial for structural elements in buildings to prevent…
Response Spectrum Analysis in STAAD pro
In STAAD.Pro, combining loads using the SRSS (Square Root of the Sum of the Squares)…
SHELTER WITH 25T CRANE DRAWING | PEB SHED |
Designing a shelter with a 25-ton capacity crane involves structural considerations to support the heavy…
HOUSE PLAN 20 x 60 | WEST FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 20 x 60 | WEST FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
MONORAIL DETAILS
To create a monorail drawing connected to a concrete beam, several basic concepts should be…
WEST FACING HOUSE PLAN 50 x 40 | DUPLEX TYPE |
HOUSE PLAN 50 x 40| WEST FACING | House Plan ground + first floors, the…
Side Face Reinforcement as per ACI & IS code
Side face reinforcement – IS 456:2000 (Indian Standard) The side face reinforcement in structural elements,…
HOUSE PLANS
HOUSE PLAN 40 x 40| SOUTH FACING | DUPLEX HOUSE TYPE | House Plan ground…
HOUSE PLAN 35 x 50 | EAST FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 35 x 50 | EAST FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
HOUSE PLAN 25 x 60 | NORTH FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 25 x 60 | NORTH FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
HOUSE PLAN 35 x 50 | NORTH FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 35 x 50 | NORTH FACING | House Plan ground + first floors,…
Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structures as Per IS 801
www.rcenggstudios.com Shelter Design Using Cold Formed Steel Section ABSTARCT: Cold formed steel section are extensively…
HOUSE PLAN 30 x 40 | EAST FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 30 x 40| EAST FACING | House Plan ground + first floors, the…
HOUSE PLAN 30 x 40| NORTH FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 30 x 40| NORTH FACING | House Plan ground + first floors, the…
HOUSE PLAN 20 x 40 | NORTH FACING |
HOUSE PLAN 20 x 40| NORTH FACING | House Plan ground + first floors, the…
Lifting Padeye Design
Padeye is a plate or attachment point commonly used in lifting and rigging operations to…
Corbel Design and Details
DESIGN OF CORBELA corbel is a short cantilever used to support structural loads like beams…
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS USING RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS
The purpose of this chapter is to summarize the fundamental equations used in the response…
Building Load Calculation
1. INTRODUCTION: The structure is a “Multi-storied building” consisting of Two Basement Floors + Stilts…
Deep Excavations
ABSTRACT All major topics in the design of in-situ retaining systems for deep excavations…
Bathroom Tiles Designs Ideas 50+
Here are some popular bathroom tile design ideas that can inspire a stylish and functional…