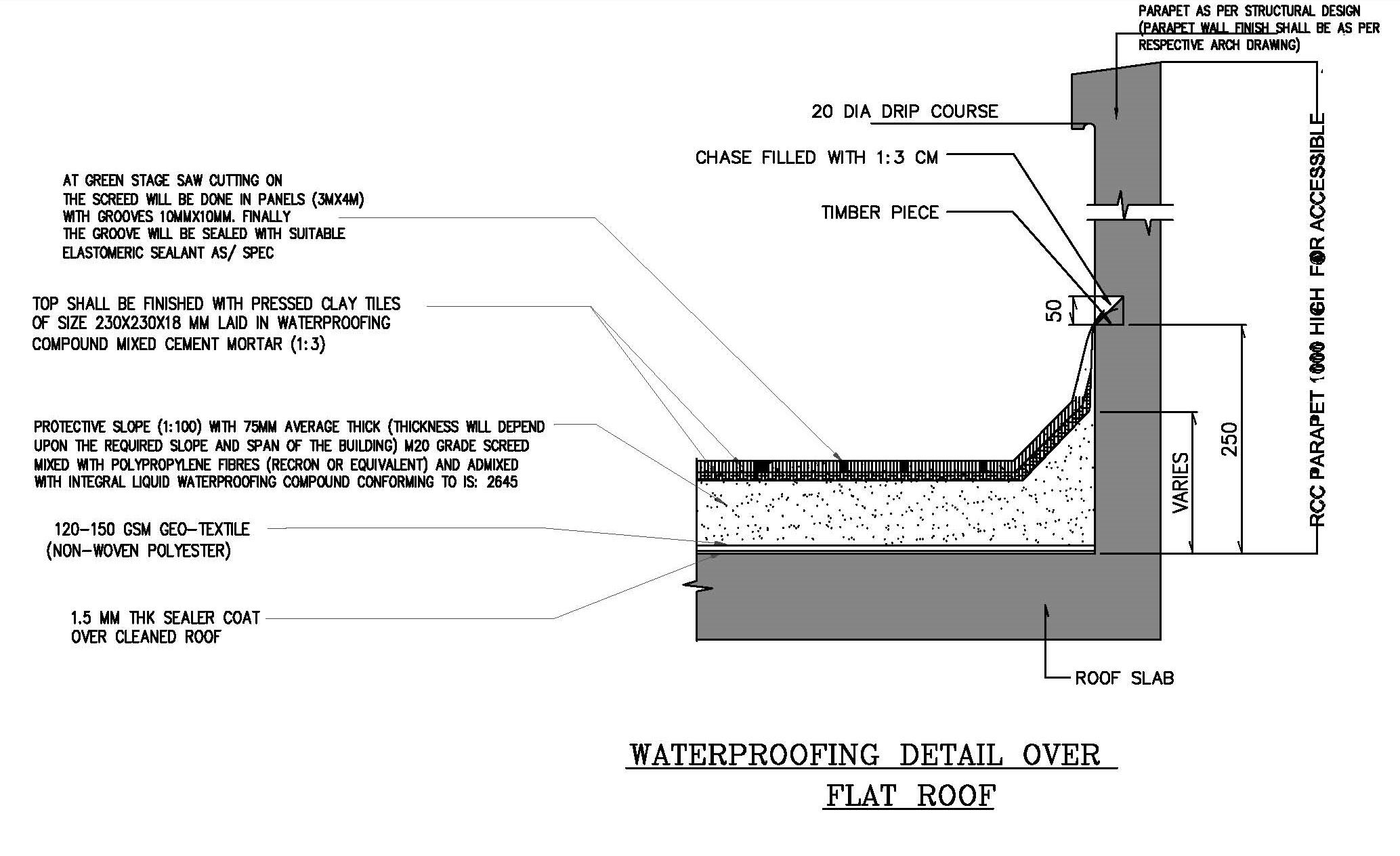
Procedure for Weathering Course in RCC Roof
A weathering course is a protective layer applied on RCC roofs to prevent water seepage, thermal stresses, and enhance the durability of the structure. It is particularly important in areas with high rainfall and temperature variations.
1. Purpose of Weathering Course
- Prevent water leakage into the roof slab.
- Protect the RCC slab from thermal expansion and contraction.
- Improve insulation against heat.
- Increase the lifespan of the roof.
2. Materials Required
- Brick Jelly or Clay Brick Aggregate:
- Crushed brick aggregates (sizes 20–40 mm).
- Lightweight and thermally resistant.
- Lime Mortar:
- Mixture of slaked lime and fine sand (ratio: 1:2 or 1:3).
- Acts as a binding material and insulator.
- Waterproofing Compound (optional):
- Additives to enhance water resistance.
- Tiles or Finishing Layer:
- Terracotta tiles, weatherproof clay tiles, or ceramic tiles.
- Bitumen or Waterproof Membrane (optional):
- For extra waterproofing in severe conditions.


3. Procedure for Laying Weathering Course
Step 1: Surface Preparation
- Clean the RCC Slab:
- Remove dust, loose particles, oil, or grease from the roof slab.
- Wash the surface with water.
- Repair Damages:
- Fill cracks or holes in the RCC slab using a cementitious repair mortar.
- Provide Slope:
- Ensure the roof slab has a minimum slope of 1:100 to facilitate drainage.
- Apply a screed layer if needed to achieve the slope.
- Mix Lime Mortar:
- Prepare a lime mortar with lime and sand in a ratio of 1:3.
- Add a small quantity of water to achieve a workable consistency.
- Spread Brick Jelly:
- Spread brick aggregates or brick jelly evenly over the roof slab.
- Compact the layer using wooden rammers.
- Embed in Lime Mortar:
- Pour the lime mortar onto the brick jelly layer.
- Fill all voids between aggregates by tamping the mixture.
- Level and Compact:
- Level the surface and compact it well using a wooden float.
Step 2: Laying the Brick Jelly Layer
Step 3: Curing
- Water Curing:
- Start curing the weathering course after 24 hours.
- Keep the surface moist by sprinkling water for at least 7–14 days.

Step 4: Finishing
- Optional Waterproofing Layer:
- Apply a bitumen coating or waterproofing membrane for additional protection.
- Lay Tiles:
- Place weatherproof tiles or terracotta tiles on the compacted layer.
- Fix tiles with a cement mortar (1:3) for stability.
- Fill joints with waterproof grout.
- Final Slope Check:
- Ensure the tile layer also maintains the drainage slope towards rainwater outlets.
4. Design Considerations
- Thickness:
- Brick jelly layer: 75–100 mm.
- Tile or finishing layer: 20–30 mm.
- Slope:
- Provide a slope of 1:100 or 1:50 towards the water drainage points.
- Drainage Points:
- Ensure rainwater pipes are positioned at the lowest points on the roof.

5. Maintenance Tips
- Regular Cleaning:
- Keep the roof free from debris and stagnant water.
- Inspect for Cracks:
- Repair cracks or damage in the weathering course promptly.
- Recoat Waterproofing:
- Reapply waterproof coatings every 5–7 years for added durability.
6. Advantages of Weathering Course
- Provides thermal insulation to reduce heat ingress.
- Prevents structural deterioration caused by water seepage.
- Reduces roof maintenance costs.
7. Standards and Codes
- IS 456:2000 – General RCC design guidelines.
- NBC (National Building Code of India) – Roofing and drainage specifications.
- Technical Details for Wash Basin Section and ElevationA wash basin is an essential plumbing fixture used in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.… Read more: Technical Details for Wash Basin Section and Elevation
- Tender Technical Specification for Plumbing and Sanitary worksTender Technical Specification for Factory buildings – Plumbing and Sanitary works PART-1: GENERAL ✔ Piping… Read more: Tender Technical Specification for Plumbing and Sanitary works
- Fencing Gate Details and RequirementsA fencing gate is an essential component of any secure enclosure, allowing controlled access while… Read more: Fencing Gate Details and Requirements
- Fencing Layout and Details For Transformer AreaTransformer fencing is an essential safety requirement to protect electrical transformers from unauthorized access, vandalism,… Read more: Fencing Layout and Details For Transformer Area
- Fencing with Angle Post and Pipe Post Details & ArrangementsFencing using angle posts and pipe (dia) posts is widely used for boundary protection, security… Read more: Fencing with Angle Post and Pipe Post Details & Arrangements
- Civil Engineering Formula Book | Pocket Guide pdf Free download |Civil Engineering Formula Book – Essential Reference for Engineers Civil engineering is a vast field… Read more: Civil Engineering Formula Book | Pocket Guide pdf Free download |
- Transformer Foundation with Soak Pit Layout and DetailsA transformer foundation with a soak pit is designed to support the weight of the… Read more: Transformer Foundation with Soak Pit Layout and Details
- Grating Standard Details and SpecificationsGrating Details and Requirements Gratings are open-grid flooring systems made from metal or fiberglass used… Read more: Grating Standard Details and Specifications
- Chequered Plate Standard DetailsChequered Plate Standard Details A chequered plate (also known as a checker plate, tread plate,… Read more: Chequered Plate Standard Details
- Handrail Details for Steel Structural FloorsDetails and Requirements of Handrails for Steel Structural Floors Handrails are essential for safety and… Read more: Handrail Details for Steel Structural Floors
- Cable Pull Pit Requirements and DetailsCable Pull Pit Requirements and Details A cable pull pit (also called a cable pulling… Read more: Cable Pull Pit Requirements and Details
- Laboratory Building Plan and Architecture DetailsLaboratory Building Plan Requirements for Industries Designing an industrial laboratory building requires careful planning to… Read more: Laboratory Building Plan and Architecture Details
- Structural Bolt Details Types Grades and ApplicationsStructural Bolt Details: Types, Grades, and Applications Structural bolts are high-strength fasteners used to connect… Read more: Structural Bolt Details Types Grades and Applications
- Finishing Schedule Drawing for Doors, Windows, and Rolling ShuttersHow to Prepare a Finishing Schedule Drawing for Doors, Windows, and Rolling Shutters A finishing… Read more: Finishing Schedule Drawing for Doors, Windows, and Rolling Shutters
- Workshop Building Architectural LayoutHow to Prepare an Architectural Layout for a Workshop Building in Industrial Projects Designing an… Read more: Workshop Building Architectural Layout
- Calculation of Foundation Bearing Capacity as per IS 6403 – 1981The IS 6403:1981 standard provides guidelines for calculating the bearing capacity of shallow foundations, ensuring… Read more: Calculation of Foundation Bearing Capacity as per IS 6403 – 1981
- Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity Calculation For FoundationsHow to Calculate Bearing Capacity of a Foundation The bearing capacity of a foundation is… Read more: Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity Calculation For Foundations
- DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHOD OF MULTISTORY CONCRETE BUILDINGSThe recommendations which should be taken into account in designing the multistoried reinforced concrete buildings… Read more: DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHOD OF MULTISTORY CONCRETE BUILDINGS
- Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions pdf Free DownloadAre you preparing for a Civil or Structural Engineering job interview? Whether you’re a fresh… Read more: Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions pdf Free Download
- Civil Structural Engineering Interview QuestionsCivil & Structural Engineering Interview Questions Here’s a comprehensive list of 100 Civil & Structural… Read more: Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions
- SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAMS WITH FORMULAIntroduction Figures 1 through 32 provides a series of shear and moment diagrams with accompanying… Read more: SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAMS WITH FORMULA
- Weathering Course in RCC RoofProcedure for Weathering Course in RCC Roof A weathering course is a protective layer applied… Read more: Weathering Course in RCC Roof
- Rolling Shutter Fixing Detail with RCC BeamRolling Shutter Fixing Detail with RCC Beam Rolling shutters are often used in commercial, industrial,… Read more: Rolling Shutter Fixing Detail with RCC Beam
- Duct Bank Details and Pipe Sleeves DetailsDuct Bank Details and Pipe Sleeves Details A duct bank is an underground network of… Read more: Duct Bank Details and Pipe Sleeves Details
- Handrail Details | Construction Methods and Types of Handrail |Methods of Typical Handrail Construction in RCC Structures Handrails in RCC structures are important safety… Read more: Handrail Details | Construction Methods and Types of Handrail |
- Details of RampMethods and Details of Ramp Construction Ramps are inclined surfaces designed to provide smooth access… Read more: Details of Ramp
- Design Calculation of Steel Shelter – AISC 360PURPOSE AND SCOPE The scope of this document is to provide the calculations for the… Read more: Design Calculation of Steel Shelter – AISC 360
- Cage Ladder Specification and Detail DrawingDetailed Specification for Steel Cage Ladders Steel cage ladders are robust, durable, and commonly used… Read more: Cage Ladder Specification and Detail Drawing
- Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19)Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19) The design of concrete beams in… Read more: Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19)
- Fencing Detail DrawingFencing Detail Drawing Requirements To create a comprehensive fencing detail drawing, ensure the following components… Read more: Fencing Detail Drawing
- RCC Fencing Post DetailsRequirements for RCC Fence Posts RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) posts are commonly used for durable… Read more: RCC Fencing Post Details
- Gypsum Board False Ceiling InstallationGypsum board false ceiling installation layout and details Installing a false ceiling with gypsum board… Read more: Gypsum Board False Ceiling Installation
- Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete PedestalsDesign of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals Pedestal rebars parallel to anchor bolts have been… Read more: Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals
- Wind Load Calculation as per IS 875 Part 3 2015Wind Load Calculation Wind speed -33m/sec From Ground floor to Slab level – 14.675m SLAB… Read more: Wind Load Calculation as per IS 875 Part 3 2015
- DESIGN BASIS FOR CIVIL AND STRUCTURALDesign Basis for Civil and Structural SPECIFIC DESIGN REQUIREMENTS [CIVIL] CONTENT CLAUSE NO. … Read more: DESIGN BASIS FOR CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL
- General Specification for Civil and Structural WorksCONTENTS CLAUSE NO. DESCRIPTION PAGE NO. 1.00.00 INTRODUCTION 1 2.00.00 CODES AND STANDARDS 1 3.00.00… Read more: General Specification for Civil and Structural Works
- Green BuildingA green building is a structure designed, constructed, and operated to minimize its environmental impact… Read more: Green Building
- Fireproofing DetailsFireproofing, also known as fire-resistive protection, is crucial for structural elements in buildings to prevent… Read more: Fireproofing Details
- Response Spectrum Analysis in STAAD proIn STAAD.Pro, combining loads using the SRSS (Square Root of the Sum of the Squares)… Read more: Response Spectrum Analysis in STAAD pro
- SHELTER WITH 25T CRANE DRAWING | PEB SHED |Designing a shelter with a 25-ton capacity crane involves structural considerations to support the heavy… Read more: SHELTER WITH 25T CRANE DRAWING | PEB SHED |
- MONORAIL DETAILSTo create a monorail drawing connected to a concrete beam, several basic concepts should be… Read more: MONORAIL DETAILS
- Lifting Padeye DesignPadeye is a plate or attachment point commonly used in lifting and rigging operations to… Read more: Lifting Padeye Design
- Corbel Design and DetailsDESIGN OF CORBEL A corbel is a short cantilever used to support structural loads like… Read more: Corbel Design and Details
- BEHAVIOUR OF STEEL CHIMNEY UNDER DYNAMIC LOADINGSIntroducing Steel Chimneys or Stack The behavior of steel chimneys under dynamic loadings, such as… Read more: BEHAVIOUR OF STEEL CHIMNEY UNDER DYNAMIC LOADINGS
- DESIGN OF WIND PRESSURE AS PER EN 1991-1-4The calculation for wind load as per EN 1991-1-4 for a gas plant located in a terrain category I includes parameters such as a fundamental basic wind velocity of 32.30 m/s, a directional factor and season factor of 1.00 each, and various terrain factors and roughness lengths. Wind turbulence intensity and peak velocity pressure vary with height.
- Grade Slab DetailsPaving or Grade slab Details A grade slab, also known as a ground-bearing slab, is… Read more: Grade Slab Details
- Resort Cottage PlanDesigning a cottage plan involves creating a cozy, functional, and aesthetically pleasing layout that maximizes… Read more: Resort Cottage Plan
- CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT ARRANGEMENTA well-designed batching plant arrangement ensures efficient concrete production, safety, and ease of maintenance. The… Read more: CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT ARRANGEMENT
- LOAD COMBINATIONS NBCC 2023LOAD COMBINATIONS CANADIAN CODE NBCC 2023 The National Building Code of Canada (NBCC) 2023 provides… Read more: LOAD COMBINATIONS NBCC 2023
- STEEL SHED DRAWING1. Plan View (Top View): Outline of the Shed: Show the overall dimensions of the… Read more: STEEL SHED DRAWING
- Plumbing DrawingCreating a plumbing scheme drawing involves outlining the entire plumbing system of a building, showing… Read more: Plumbing Drawing
- Pre Engineered Building Design Specification IS CodePre-Engineered Building PEB PEB stands for Pre-Engineered Building. It refers to a building system where… Read more: Pre Engineered Building Design Specification IS Code
- BATHROOM FIXTURES AND FITTINGS – European Closet, Urinal & Wash BasinBATHROOM FIXTURES AND FITTINGS European Closet – fitting dimensions For European closet fixing dimensions, you’ll… Read more: BATHROOM FIXTURES AND FITTINGS – European Closet, Urinal & Wash Basin
- Design of Pipe Support Foundation CalculationDesign of Pipe Support Foundation Calculation Piping Input: GA and Reinforcement Details of Pipe Support… Read more: Design of Pipe Support Foundation Calculation
- Design of Concrete Anchor BlocksSTATIC ANALYSIS & DESIGN OF PIPE ANCHOR BLOCK FOUNDATION DESIGN OF PIPE ANCHOR BLOCK FOUNDATION… Read more: Design of Concrete Anchor Blocks
- PEB Shed DrawingPEB – Industrial standard architectural drawing with all details.
Related Posts: