Designing 🌧️ Stormwater Drainage systems is essential to ensure the efficient collection and disposal of surface runoff from rainfall. Proper pipe sizing ensures that the stormwater is carried safely without causing flooding, ponding, or structural damage.
📘 1. Key Formula: Rational Method
The Rational Method is widely used for stormwater pipe sizing in small urban drainage systems: Q=C ⋅ i ⋅ A
Where:
- Q = Peak runoff (m³/s or cfs)
- C = Runoff coefficient (depends on surface type)
- i = Rainfall intensity (mm/hr or in/hr)
- A = Catchment area (hectares or acres)
📐 2. Step-by-Step Pipe Sizing Procedure
🔹 Step 1: Define Catchment Area
Measure the area contributing runoff to the pipe. Use site drawings or GIS tools.
- Units: hectares (ha) or square meters (m²)
🔹 Step 2: Assign Runoff Coefficient (C)
Based on surface type:
| Surface | C value |
|---|---|
| Paved / Asphalt | 0.85–0.95 |
| Roof surface | 0.75–0.95 |
| Lawn / grass area | 0.10–0.35 |
| Concrete surface | 0.90–0.95 |
🔹 Step 3: Determine Rainfall Intensity (i)
Use local IDF curves or rainfall data for the required return period (e.g., 10-year, 25-year storm).
- Units: mm/hr or in/hr
🔹 Step 4: Calculate Peak Flow (Q)
Q = (C⋅i⋅A) / 360
- Result in m³/s if using mm/hr and hectares
- Adjust for multiple catchments if needed
🔹 Step 5: Select Pipe Diameter
Use Manning’s Formula for flow in pipes: Q = 1/ n ⋅ A ⋅ R ^ 2/3 ⋅ S ^1/2
Where:
- n = Manning’s roughness coefficient (typically 0.013 for concrete, 0.011 for PVC)
- A = Cross-sectional area of pipe
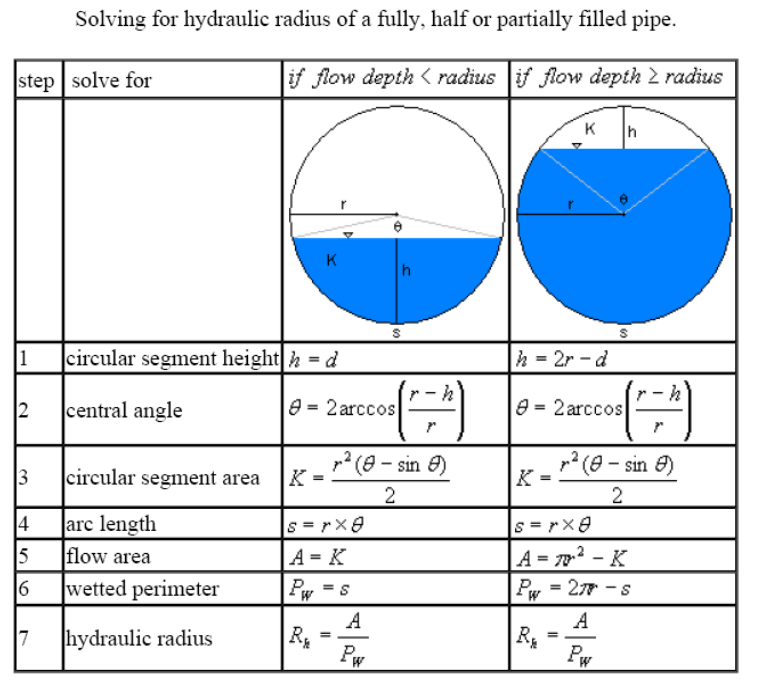
- R = Hydraulic radius = A / P (P = wetted perimeter)
- S = Slope of pipe
🧰 Example Calculation
- Catchment Area (A) = 0.5 ha
- Surface = Pavement ⇒ C = 0.90`
- Rainfall Intensity (i) = 75 mm/hr
- Pipe Slope (S) = 0.005 (0.5%)
- Manning’s n = 0.013
Q = 0.9 ⋅ 75 ⋅ 0.5 / 360 = 0.094 m3/s
Use Manning’s formula to back-calculate required pipe diameter that will carry 0.094 m³/s.

f = arc sin (0.4r/r) = 0.412 radians = 23.578 degrees
q = 180+2*f = 3.965 radians = 227.156 degrees
Sample Calculation for an 8″ (0.203mm) pipe. D = 0.203
FLOW AREA
Method 1

= 0.102^2*(227.156*pi/180-SIN(227.156))/2
= 0.024 m2
Method 2

= 0.102^2*(3.965/2+COS(0.412)*SIN(0.412)
= 0.024 m2
WETTED PERIMETER

= 0.102*3.965
= 0.402 m
B. CALCULATION OF DISCHARGE CAPACITY, Qc
Manning’s Formula
Assume flow depth equal to 0.7 times the pipe diameter for the max. design flow rate.
Qc = 3600 * A * R2/3 * S 1/2 / n
Where,
D = Pipe Diameter, m
A = Flow Area, m2
P = Wetted Perimeter, m
S = Bed Gradient
n = Roughness Coefficient
R = Hydraulic Radius, m
= A/P
C.CALCULATION OF VELOCITIES
Qc = V * A
Where ,
v = velocity, m/s
A = Flow Area, m2
vmax ≤ 3 m/s
vmin ≥ 0.75 m/s Qcmin = 0.2 x Qcmax

✅ Design Tips
- Always check full flow capacity (pipe not surcharged)
- Include minimum self-cleansing velocity (≥ 0.6 m/s)
- Consider future expansion (use 25–50% extra capacity)
- Provide manholes and catchpits at changes in slope or direction
📚 Codes & References
- IS 1172, IS 2065, IS 3370, and SP 35
- US EPA SWMM software
- StormCAD / Civil 3D for advanced modeling
- Local municipal design manuals
- Rain Water Gutter and Down Take SystemsTypical Gutter and Downpipe Systems: An Overview Understanding Rain Water… Read more: Rain Water Gutter and Down Take Systems
- Stormwater Drainage CalculationDesigning 🌧️ Stormwater Drainage systems is essential to ensure the… Read more: Stormwater Drainage Calculation
- Structural Engineering Design Criteria – American Codes and StandardsIn the United States, structural engineering design is governed by… Read more: Structural Engineering Design Criteria – American Codes and Standards
- Insert Plate Details & Drawing – Embedded in Concrete StructuresInsert plates are embedded steel plates installed in concrete elements… Read more: Insert Plate Details & Drawing – Embedded in Concrete Structures
- Anchor Bolt Details and Drawing – Embedded in ConcreteAnchor bolts are crucial elements in structural and foundation systems,… Read more: Anchor Bolt Details and Drawing – Embedded in Concrete
- Staircase Layout and DetailsA staircase is an essential architectural element that provides vertical… Read more: Staircase Layout and Details
- Guard House Layout and DetailsA guard house, also known as a security cabin or… Read more: Guard House Layout and Details
- Pump Shed Structural Steel DrawingA pump shed is a small but critical structure designed… Read more: Pump Shed Structural Steel Drawing
- Column BucklingIntroduction Structural dynamics problems deal with structures in motion. Examples… Read more: Column Buckling
- Moody Chart | Moment Reactions for Rectangular Plates |Introduction to Moody’s Chart for Slab Design Moody’s Chart is… Read more: Moody Chart | Moment Reactions for Rectangular Plates |
- Standard Road DetailsRigid & Flexible Road Details – Drawings & Requirements Road… Read more: Standard Road Details
- DG Building Architectural Plan & Finishing ScheduleA DG (Diesel Generator) building is a dedicated structure designed… Read more: DG Building Architectural Plan & Finishing Schedule
- Technical Details for Wash Basin Section and ElevationA wash basin is an essential plumbing fixture used in… Read more: Technical Details for Wash Basin Section and Elevation
- Tender Technical Specification for Plumbing and Sanitary worksTender Technical Specification for Factory buildings – Plumbing and Sanitary… Read more: Tender Technical Specification for Plumbing and Sanitary works
- Fencing Gate Details and RequirementsA fencing gate is an essential component of any secure… Read more: Fencing Gate Details and Requirements
- Fencing Layout and Details For Transformer AreaTransformer fencing is an essential safety requirement to protect electrical… Read more: Fencing Layout and Details For Transformer Area
- Fencing with Angle Post and Pipe Post Details & ArrangementsFencing using angle posts and pipe (dia) posts is widely… Read more: Fencing with Angle Post and Pipe Post Details & Arrangements
- Civil Engineering Formula Book | Pocket Guide pdf Free download |Civil Engineering Formula Book – Essential Reference for Engineers Civil… Read more: Civil Engineering Formula Book | Pocket Guide pdf Free download |
- Transformer Foundation with Soak Pit Layout and DetailsA transformer foundation with a soak pit is designed to… Read more: Transformer Foundation with Soak Pit Layout and Details
- Grating Standard Details and SpecificationsGrating Details and Requirements Gratings are open-grid flooring systems made… Read more: Grating Standard Details and Specifications
- Chequered Plate Standard DetailsChequered Plate Standard Details A chequered plate (also known as… Read more: Chequered Plate Standard Details
- Handrail Details for Steel Structural FloorsDetails and Requirements of Handrails for Steel Structural Floors Handrails… Read more: Handrail Details for Steel Structural Floors
- Cable Pull Pit Requirements and DetailsCable Pull Pit Requirements and Details A cable pull pit… Read more: Cable Pull Pit Requirements and Details
- Laboratory Building Plan and Architecture DetailsLaboratory Building Plan Requirements for Industries Designing an industrial laboratory… Read more: Laboratory Building Plan and Architecture Details
- Structural Bolt Details Types Grades and ApplicationsStructural Bolt Details: Types, Grades, and Applications Structural bolts are… Read more: Structural Bolt Details Types Grades and Applications
- Finishing Schedule Drawing for Doors, Windows, and Rolling ShuttersHow to Prepare a Finishing Schedule Drawing for Doors, Windows,… Read more: Finishing Schedule Drawing for Doors, Windows, and Rolling Shutters
- Workshop Building Architectural LayoutHow to Prepare an Architectural Layout for a Workshop Building… Read more: Workshop Building Architectural Layout
- Calculation of Foundation Bearing Capacity as per IS 6403 – 1981The IS 6403:1981 standard provides guidelines for calculating the bearing… Read more: Calculation of Foundation Bearing Capacity as per IS 6403 – 1981
- Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity Calculation For FoundationsHow to Calculate Bearing Capacity of a Foundation The bearing… Read more: Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity Calculation For Foundations
- DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHOD OF MULTISTORY CONCRETE BUILDINGSThe recommendations which should be taken into account in designing… Read more: DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHOD OF MULTISTORY CONCRETE BUILDINGS
- Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions pdf Free DownloadAre you preparing for a Civil or Structural Engineering job… Read more: Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions pdf Free Download
- Civil Structural Engineering Interview QuestionsCivil & Structural Engineering Interview Questions Here’s a comprehensive list… Read more: Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions
- SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAMS WITH FORMULAIntroduction Figures 1 through 32 provides a series of shear… Read more: SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAMS WITH FORMULA
- Weathering Course in RCC RoofProcedure for Weathering Course in RCC Roof A weathering course… Read more: Weathering Course in RCC Roof
- Rolling Shutter Fixing Detail with RCC BeamRolling Shutter Fixing Detail with RCC Beam Rolling shutters are… Read more: Rolling Shutter Fixing Detail with RCC Beam
- Duct Bank Details and Pipe Sleeves DetailsDuct Bank Details and Pipe Sleeves Details A duct bank… Read more: Duct Bank Details and Pipe Sleeves Details
- Handrail Details | Construction Methods and Types of Handrail |Methods of Typical Handrail Construction in RCC Structures Handrails in… Read more: Handrail Details | Construction Methods and Types of Handrail |
- Details of RampMethods and Details of Ramp Construction Ramps are inclined surfaces… Read more: Details of Ramp
- Design Calculation of Steel Shelter – AISC 360PURPOSE AND SCOPE The scope of this document is to… Read more: Design Calculation of Steel Shelter – AISC 360
- Cage Ladder Specification and Detail DrawingDetailed Specification for Steel Cage Ladders Steel cage ladders are… Read more: Cage Ladder Specification and Detail Drawing
- Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19)Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19) The… Read more: Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19)
- Fencing Detail DrawingFencing Detail Drawing Requirements To create a comprehensive fencing detail… Read more: Fencing Detail Drawing
- RCC Fencing Post DetailsRequirements for RCC Fence Posts RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) posts… Read more: RCC Fencing Post Details
- Gypsum Board False Ceiling InstallationGypsum board false ceiling installation layout and details Installing a… Read more: Gypsum Board False Ceiling Installation
- Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete PedestalsDesign of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals Pedestal rebars parallel… Read more: Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals
- Wind Load Calculation as per IS 875 Part 3 2015Wind Load Calculation Wind speed -33m/sec From Ground floor to… Read more: Wind Load Calculation as per IS 875 Part 3 2015
- DESIGN BASIS FOR CIVIL AND STRUCTURALDesign Basis for Civil and Structural SPECIFIC DESIGN REQUIREMENTS [CIVIL]… Read more: DESIGN BASIS FOR CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL
- General Specification for Civil and Structural WorksCONTENTS CLAUSE NO. DESCRIPTION PAGE NO. 1.00.00 INTRODUCTION 1 2.00.00… Read more: General Specification for Civil and Structural Works
- Green BuildingA green building is a structure designed, constructed, and operated… Read more: Green Building
- Fireproofing DetailsFireproofing, also known as fire-resistive protection, is crucial for structural… Read more: Fireproofing Details
- Response Spectrum Analysis in STAAD proIn STAAD.Pro, combining loads using the SRSS (Square Root of… Read more: Response Spectrum Analysis in STAAD pro
- SHELTER WITH 25T CRANE DRAWING | PEB SHED |Designing a shelter with a 25-ton capacity crane involves structural… Read more: SHELTER WITH 25T CRANE DRAWING | PEB SHED |
- MONORAIL DETAILSTo create a monorail drawing connected to a concrete beam,… Read more: MONORAIL DETAILS
- Lifting Padeye DesignPadeye is a plate or attachment point commonly used in… Read more: Lifting Padeye Design
- Corbel Design and DetailsDESIGN OF CORBEL A corbel is a short cantilever used… Read more: Corbel Design and Details
- BEHAVIOUR OF STEEL CHIMNEY UNDER DYNAMIC LOADINGSIntroducing Steel Chimneys or Stack The behavior of steel chimneys… Read more: BEHAVIOUR OF STEEL CHIMNEY UNDER DYNAMIC LOADINGS
- DESIGN OF WIND PRESSURE AS PER EN 1991-1-4The calculation for wind load as per EN 1991-1-4 for a gas plant located in a terrain category I includes parameters such as a fundamental basic wind velocity of 32.30 m/s, a directional factor and season factor of 1.00 each, and various terrain factors and roughness lengths. Wind turbulence intensity and peak velocity pressure vary with height.
- Grade Slab DetailsPaving or Grade slab Details A grade slab, also known… Read more: Grade Slab Details
- Resort Cottage PlanDesigning a cottage plan involves creating a cozy, functional, and… Read more: Resort Cottage Plan
- CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT ARRANGEMENTA well-designed batching plant arrangement ensures efficient concrete production, safety,… Read more: CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT ARRANGEMENT
- LOAD COMBINATIONS NBCC 2023LOAD COMBINATIONS CANADIAN CODE NBCC 2023 The National Building Code… Read more: LOAD COMBINATIONS NBCC 2023
- STEEL SHED DRAWING1. Plan View (Top View): Outline of the Shed: Show… Read more: STEEL SHED DRAWING
- Plumbing DrawingCreating a plumbing scheme drawing involves outlining the entire plumbing… Read more: Plumbing Drawing
- Pre Engineered Building Design Specification IS CodePre-Engineered Building PEB PEB stands for Pre-Engineered Building. It refers… Read more: Pre Engineered Building Design Specification IS Code
- BATHROOM FIXTURES AND FITTINGS – European Closet, Urinal & Wash BasinBATHROOM FIXTURES AND FITTINGS European Closet – fitting dimensions For… Read more: BATHROOM FIXTURES AND FITTINGS – European Closet, Urinal & Wash Basin
- Design of Pipe Support Foundation CalculationDesign of Pipe Support Foundation Calculation Piping Input: GA and… Read more: Design of Pipe Support Foundation Calculation
- Design of Concrete Anchor BlocksSTATIC ANALYSIS & DESIGN OF PIPE ANCHOR BLOCK FOUNDATION DESIGN… Read more: Design of Concrete Anchor Blocks
- PEB Shed DrawingPEB – Industrial standard architectural drawing with all details.





































































Leave a Reply