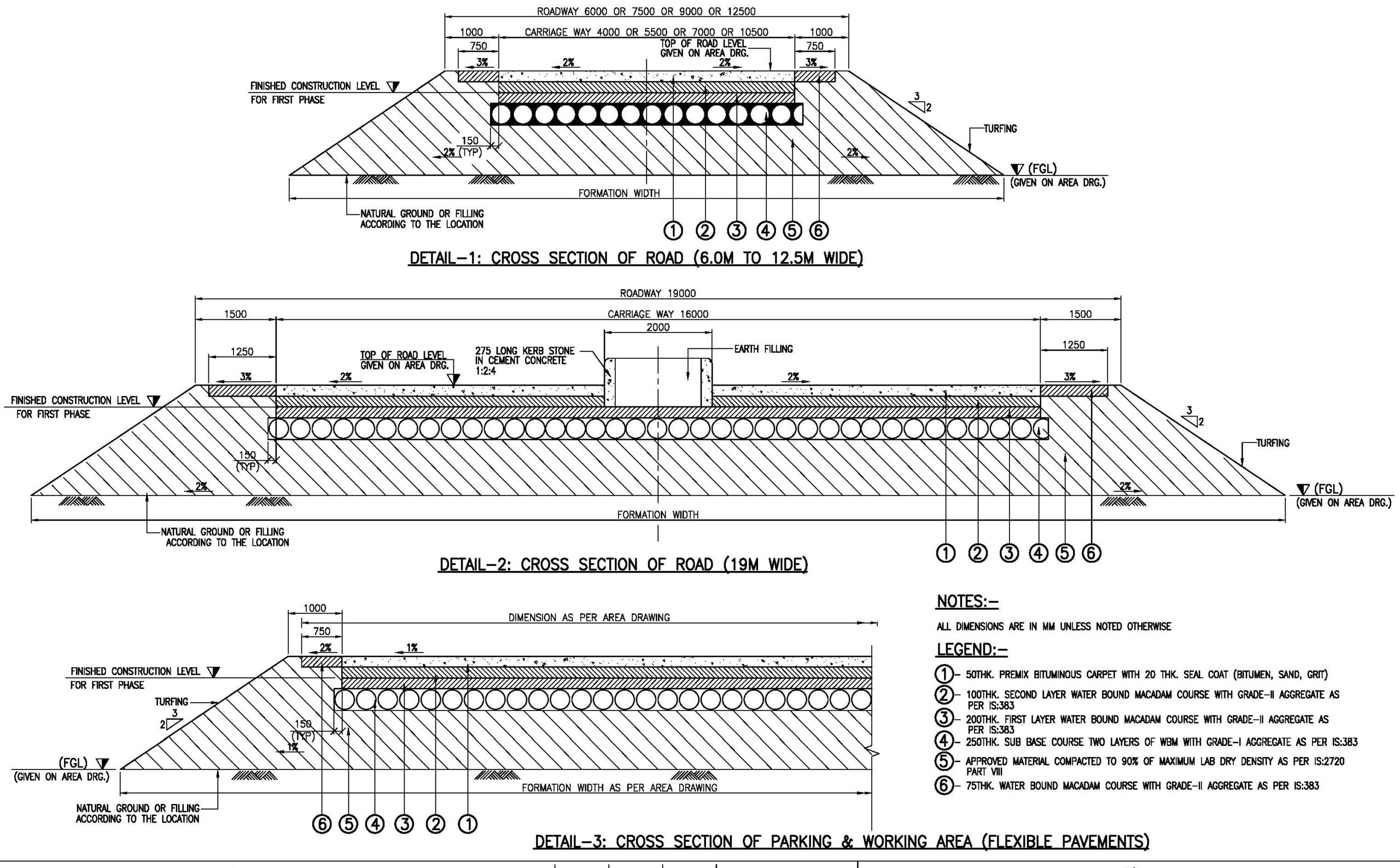
Rigid & Flexible Road Details – Drawings & Requirements
Road construction is broadly classified into rigid pavement and flexible pavement based on the material used and load distribution characteristics. A rigid road consists of concrete pavement, while a flexible road is primarily made of bituminous (asphalt) layers. Both have unique structural designs, materials, and applications.
1. Difference Between Rigid & Flexible Roads
| Feature | Rigid Road (Concrete Pavement) | Flexible Road (Bituminous Pavement) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | PCC (Plain Cement Concrete) or RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) | Bitumen (Asphalt) with Aggregates |
| Load Distribution | Slab action (distributes load over a large area) | Layered system (load transferred gradually) |
| Design Life | 30-50 years | 10-20 years |
| Initial Cost | High | Low |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | High |
| Riding Comfort | Good, smooth | Slightly rough, depends on surface conditions |
| Weather Resistance | High | Susceptible to temperature variations |
| Repair Methods | Difficult (requires concrete breaking) | Easy (overlay with new bituminous layers) |
2. Rigid Road (Concrete Pavement) – Structure & Layers
A rigid pavement consists of the following layers:
1️⃣ Subgrade – Compacted soil base (minimum 150 mm thick).
2️⃣ Subbase Course – Granular layer or dry lean concrete (DLC).
3️⃣ Base Course – PCC or RCC layer (150-300 mm thick).
4️⃣ Surface Course – Concrete slab with joints for expansion/contraction.
5️⃣ Joints & Reinforcements – Includes dowel bars & tie bars to control cracks.
Standard Drawing Details for Rigid Roads
📌 Expansion Joints & Contraction Joints – Placed at intervals to allow movement.
📌 Reinforcement Details – RCC slabs reinforced with steel mesh or rebars.
📌 Drainage System – Curbs and stormwater drains provided along the pavement.
📌 Pavement Thickness Design – Based on traffic load and subgrade strength (e.g., IRC 58:2015).


3. Flexible Road (Bituminous Pavement) – Structure & Layers
A flexible pavement consists of multiple layers designed to absorb stress gradually.
1️⃣ Subgrade – Well-compacted soil or embankment (minimum 300 mm thick).
2️⃣ Subbase Course – Crushed stone or granular layer (150-200 mm thick).
3️⃣ Base Course – Water-bound macadam (WBM) or bituminous macadam (BM).
4️⃣ Binder Course – Bituminous layer for stability and load transfer.
5️⃣ Wearing Course – Top surface layer (hot mix asphalt or dense bituminous macadam).
Standard Drawing Details for Flexible Roads
📌 Layer-by-Layer Cross-Section – Showing thickness of each road layer.
📌 Surface Drainage Details – Side drains and camber slope for water runoff.
📌 Pavement Markings & Signages – As per IRC 35 for road safety.
📌 Flexible Pavement Thickness Design – Based on traffic load & subgrade CBR value (e.g., IRC 37:2018).




4. Key Design & Construction Requirements
✔ Soil Testing for Subgrade Strength – California Bearing Ratio (CBR) method used.
✔ Traffic Load Estimation – Pavement thickness designed as per Equivalent Single Axle Load (ESAL).
✔ Drainage System Integration – Side drains and culverts for stormwater management.
✔ Surface Texture & Skid Resistance – Ensuring safe vehicle movement.
✔ Joint Design (for Rigid Pavements) – Expansion, contraction, and construction joints.
✔ Maintenance Considerations – Crack filling, pothole repairs, and resurfacing schedules.
5. Compliance with Standards & Codes
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| IRC 58:2015 | Design of Rigid Pavements |
| IRC 37:2018 | Design of Flexible Pavements |
| IS 456:2000 | General RCC Design for Rigid Roads |
| IS 73:2013 | Bitumen Specifications for Flexible Pavements |
| MORTH Specifications | Indian Road Construction Guidelines |
6. Download Free Road Construction Drawings & Guides
📥 Rigid Road (Concrete Pavement) Cross-Section Drawing (PDF & DWG)
📥 Flexible Road (Bituminous Pavement) Layer Details (PDF & DWG)
📥 Pavement Design Guide (IRC & IS Code-Based)
📥 Road Drainage & Camber Design Specifications
7. Conclusion
Both rigid and flexible roads play an important role in infrastructure development. A well-designed road ensures durability, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Choosing between concrete (rigid) or bituminous (flexible) pavement depends on traffic load, climate conditions, and budget.
💬 Need professional road design layouts and specifications? Contact us for custom road drawings!
- Catch Basin Types and Details

- Foundation Detail Drawings for Buildings With CAD Files

- Bar Bending Schedule | BBS Calculator For Beam Column and Slab

- Room Paint Calculator | Paint, Primer & Putty Quantity & Cost Estimator

- Brick Wall Construction Calculator | Calculate Bricks & Cost Instantly |

- Unit Converter – Feet, Inches, cm, mm, Yard to Meter and Vice Versa

- Civil Engineering Interview Questions and Important Practical Foundation

- Road Turning Radius as per IS/IRC Codes and International Standards AASHTO BS/DMRB

- Steel Staircase Design

- Steel Shed with Mezzanine Floor

- Structural Masonry Designers Manual

- Water Supply Piping Plan and Plumbing Schematic Diagram

- Sump Pit Drawing

- Cage Ladder Detail Standard Drawing pdf Free Download

- Lintel Slab Layout Details

- PILE CAP Detail Drawing

- Eurocode Load Combinations EN 1990 2002

- Expansion Joint Detail and Specification

- Storm Water Drain Detail Drawing

- Thrust Blocks and Restraints Details

- Octagonal Foundation Reinforcement Details

- Design of Pump Foundation Dynamic and Static Analysis

- Electrical Layout For Residential Building

- Rain Water Gutter and Down Take Systems

- Stormwater Drainage Calculation

- Structural Engineering Design Criteria – American Codes and Standards

- Insert Plate Details & Drawing – Embedded in Concrete Structures

- Anchor Bolt Details and Drawing – Embedded in Concrete

- Staircase Layout and Details

- Guard House Layout and Details

- Pump Shed Structural Steel Drawing

- Column Buckling

- Moody Chart | Moment Reactions for Rectangular Plates |

- Standard Road Details

- DG Building Architectural Plan & Finishing Schedule

- Technical Details for Wash Basin Section and Elevation

- Tender Technical Specification for Plumbing and Sanitary works

- Fencing Gate Details and Requirements

- Fencing Layout and Details For Transformer Area

- Fencing with Angle Post and Pipe Post Details & Arrangements

- Civil Engineering Formula Book | Pocket Guide pdf Free download |

- Transformer Foundation with Soak Pit Layout and Details

- Grating Standard Details and Specifications

- Chequered Plate Standard Details

- Handrail Details for Steel Structural Floors

- Cable Pull Pit Requirements and Details

- Laboratory Building Plan and Architecture Details

- Structural Bolt Details Types Grades and Applications

- Finishing Schedule Drawing for Doors, Windows, and Rolling Shutters

- Workshop Building Architectural Layout

- Calculation of Foundation Bearing Capacity as per IS 6403 – 1981

- Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity Calculation For Foundations

- DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHOD OF MULTISTORY CONCRETE BUILDINGS

- Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions pdf Free Download

- Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions

- SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAMS WITH FORMULA

- Weathering Course in RCC Roof

- Rolling Shutter Fixing Detail with RCC Beam

- Duct Bank Details and Pipe Sleeves Details

- Handrail Details | Construction Methods and Types of Handrail |

- Details of Ramp

- Design Calculation of Steel Shelter – AISC 360

- Cage Ladder Specification and Detail Drawing

- Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19)

- Fencing Detail Drawing

- RCC Fencing Post Details

- Gypsum Board False Ceiling Installation

- Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals

- Wind Load Calculation as Per Indian Code

- DESIGN BASIS FOR CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL

- General Specification for Civil and Structural Works

- Green Building

- Fireproofing Details

- Response Spectrum Analysis in STAAD pro

- SHELTER WITH 25T CRANE DRAWING | PEB SHED |

- MONORAIL DETAILS

- Lifting Padeye Design

- Corbel Design and Details

- BEHAVIOUR OF STEEL CHIMNEY UNDER DYNAMIC LOADINGS

- DESIGN OF WIND PRESSURE AS PER EN 1991-1-4

- Grade Slab Details

- Resort Cottage Plan

- CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT ARRANGEMENT

- LOAD COMBINATIONS NBCC 2023

- STEEL SHED DRAWING

- Plumbing Drawing

- Pre Engineered Building Design Specification IS Code

- BATHROOM FIXTURES AND FITTINGS – European Closet, Urinal & Wash Basin

- Design of Pipe Support Foundation Calculation

- Design of Concrete Anchor Blocks

- PEB Shed Drawing