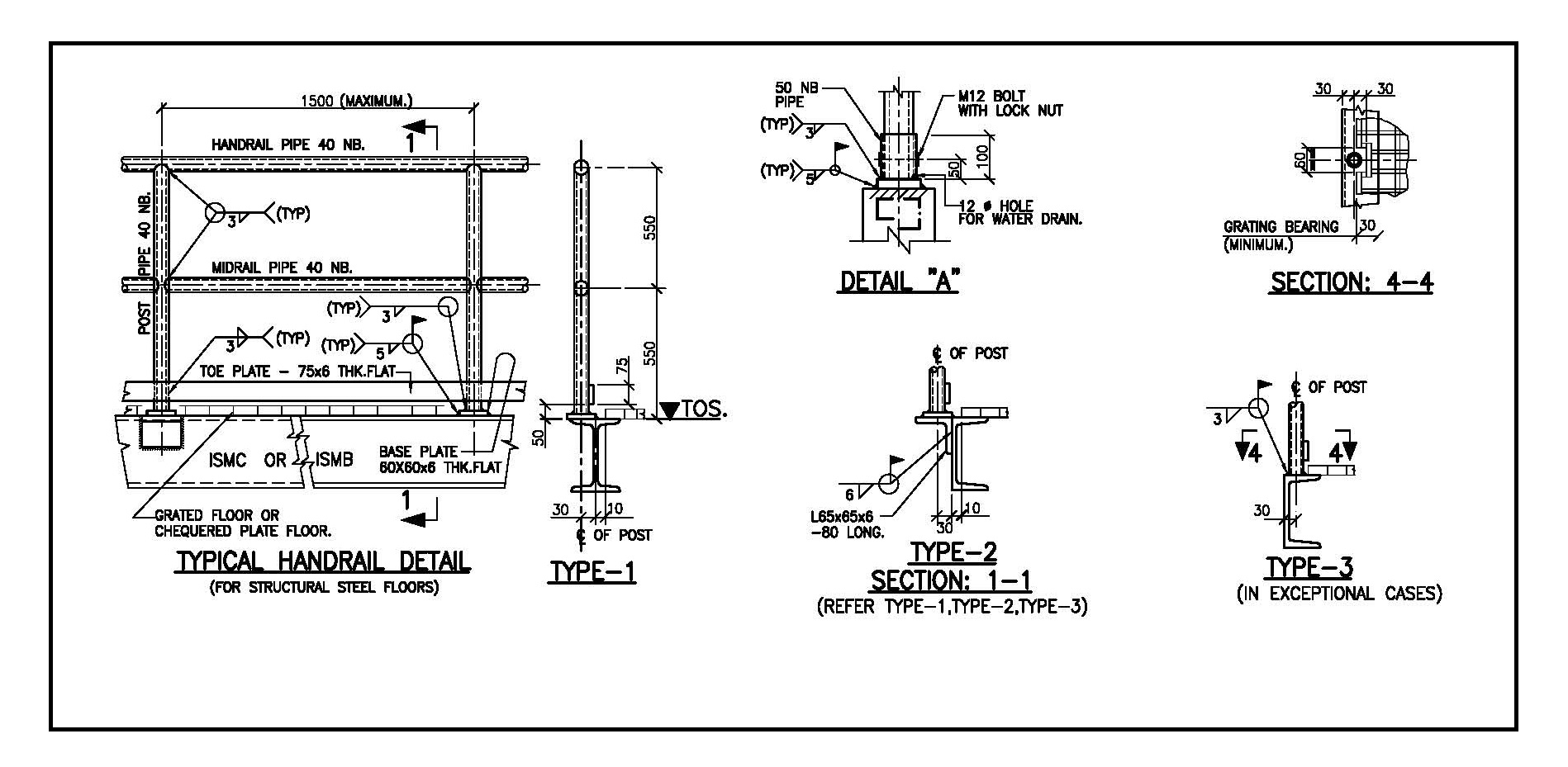
Details and Requirements of Handrails for Steel Structural Floors
Handrails are essential for safety and accessibility in steel structural floors, walkways, platforms, staircases, and industrial structures. They prevent falls, provide support, and must comply with safety standards and regulations like OSHA, ANSI, IS, and Eurocodes.
1. Purpose of Handrails in Steel Structures
✔️ Provides fall protection for workers and users.
✔️ Ensures compliance with building and safety codes.
✔️ Helps with safe movement on platforms, stairs, and walkways.
✔️ Can act as barriers or guardrails in hazardous areas.
✔️ Enhances the structural integrity and durability of steel walkways.

2. Handrail Design Requirements
a. Height Requirements
- OSHA (1910.29): Minimum 42 inches (1067 mm) from the walking surface.
- IS 875 / NBC: Between 900 mm – 1100 mm for general applications.
- BS 6180 / Eurocode: Between 900 mm – 1200 mm for industrial walkways.
b. Load Bearing Capacity
- Must withstand a minimum load of 50-75 kg/m (OSHA).
- Should resist 200 N horizontal force at the top rail (EN 1991-1-1).
- Structural handrails should resist 100 kg impact load (IS 875).
c. Materials Used
| Material | Properties | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel (MS) | Strong, economical, weldable | Industrial walkways, staircases |
| Stainless Steel (SS 304/316) | Corrosion-resistant, durable | Marine, chemical, food industry |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Modular handrails, railing systems |
| Galvanized Steel | Rust-resistant, strong | Outdoor steel structures |
d. Spacing Between Rails & Posts
- Top Rail – At 42 inches (1067 mm) height.
- Intermediate Rail – Midway between floor and top rail.
- Post Spacing – Maximum 1.5 – 2 meters apart.
e. Handrail Diameter & Grip Size
- Circular Handrails: 32 mm to 50 mm diameter.
- Rectangular Handrails: Width 40-50 mm, thickness 10-15 mm.
3. Types of Handrails for Steel Floors
a. Based on Design
| Handrail Type | Description | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Single Rail Handrail | One horizontal rail, simple | Low-traffic areas |
| Double Rail Handrail | Two horizontal rails, more safety | Industrial floors, mezzanines |
| Vertical Bar Handrail | Bars spaced vertically | Public buildings, high-rises |
| Mesh Panel Handrail | Metal mesh infill for added safety | Construction sites, hazardous areas |
| Cable Handrail | Stainless steel cables between posts | Modern buildings, lightweight applications |
b. Based on Application
- Industrial Walkways – Heavy-duty steel or galvanized handrails.
- Mezzanine Floors – Handrails with kickplates for added safety.
- Staircases – Rounded handrails with proper grip size.
- Balconies & Roofs – Corrosion-resistant handrails with glass or mesh infill.
4. Installation & Fixing Methods
a. Mounting Methods
| Mounting Type | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Base Plate Mounted | Fixed using anchor bolts on floor | Walkways, balconies |
| Wall-Mounted Handrails | Attached to walls with brackets | Staircases, corridors |
| Embedded Railings | Installed inside concrete slabs | Permanent structures |
| Clamp-On Handrails | Adjustable, removable clamps | Temporary safety barriers |
b. Welding vs. Bolted Connections
- Welded Handrails – Stronger, permanent, used for industrial structures.
- Bolted Handrails – Modular, easy to install and replace.
c. Kick Plates (Toe Boards)
- Required for industrial applications and elevated platforms.
- Minimum height: 100 mm (OSHA, IS 875).
5. Safety Standards & Compliance
| Standard | Region | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| OSHA 1910.29 | USA | 42-inch height, load-bearing 200 lbs |
| IS 875 / NBC | India | 900-1100 mm height, impact-resistant |
| BS 6180 | UK | 900-1200 mm height, glass infills allowed |
| EN 1991-1-1 | EU | 1 kN/m load capacity, 50 mm max gap |
| AS 1657 | Australia | Industrial walkways require mid-rails |
6. Maintenance & Durability
- Regular inspections for rust, loose fittings, and corrosion.
- Apply protective coatings (galvanizing, powder coating, paint).
- Check for wear and tear in high-traffic areas.
- Replace damaged rails or fittings immediately.
7. Conclusion
Properly designed steel handrails improve safety, stability, and compliance in industrial and commercial buildings. By selecting the right materials, fixing methods, and meeting code requirements, handrails can ensure long-term durability and reliability.

- Catch Basin Types and Details
- Foundation Detail Drawings for Buildings With CAD Files
- Bar Bending Schedule | BBS Calculator For Beam Column and Slab
- Room Paint Calculator | Paint, Primer & Putty Quantity & Cost Estimator
- Brick Wall Construction Calculator | Calculate Bricks & Cost Instantly |
- Unit Converter – Feet, Inches, cm, mm, Yard to Meter and Vice Versa
- Civil Engineering Interview Questions and Important Practical Foundation
- Road Turning Radius as per IS/IRC Codes and International Standards AASHTO BS/DMRB
- Steel Staircase Design
- Steel Shed with Mezzanine Floor
- Structural Masonry Designers Manual
- Water Supply Piping Plan and Plumbing Schematic Diagram
- Sump Pit Drawing
- Cage Ladder Detail Standard Drawing pdf Free Download
- Lintel Slab Layout Details
- PILE CAP Detail Drawing
- Eurocode Load Combinations EN 1990 2002
- Expansion Joint Detail and Specification
- Storm Water Drain Detail Drawing
- Thrust Blocks and Restraints Details
- Octagonal Foundation Reinforcement Details
- Design of Pump Foundation Dynamic and Static Analysis
- Electrical Layout For Residential Building
- Rain Water Gutter and Down Take Systems
- Stormwater Drainage Calculation