Category: Civil and Structural Design Calculations
-
Eurocode Base Plate Calculator – EN 1993-1-8
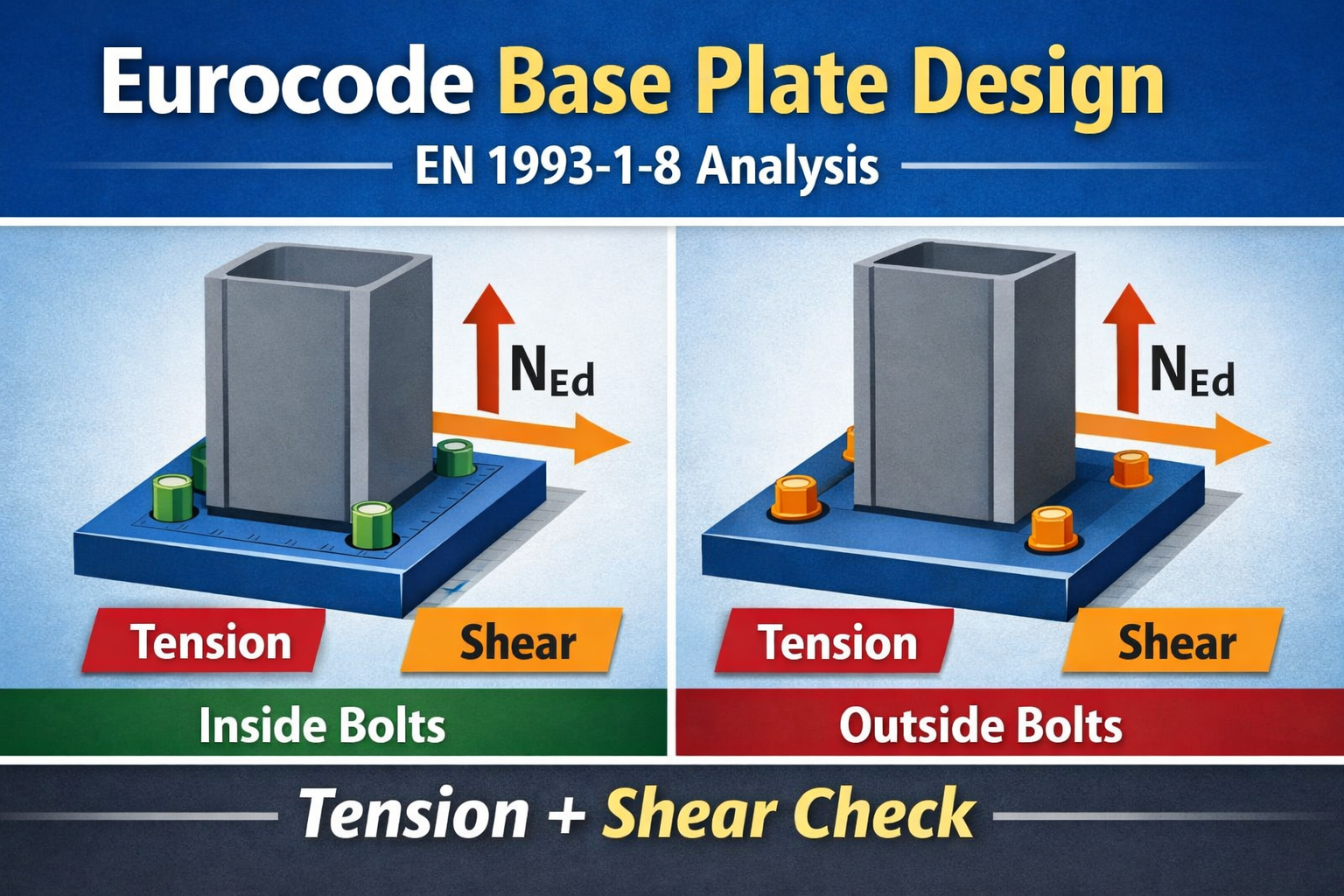
Introduction Base plates are critical components in steel structures, transferring column loads safely to concrete foundations. Correct sizing of the plate and anchor bolts ensures both structural safety and serviceability. This tool uses Eurocode EN 1993-1-8 to calculate: You can also visualize bolt layouts for inside or outside column positions, helping engineers check proper spacing Read more
-
Base Plate Design Calculation AS 4100

Introduction In structural steel design, the base plate is a critical component that ensures the proper transfer of axial loads and moments from a column to its foundation. Accurate design of base plates with proper bolt layout is essential to prevent excessive bending, tension, or compression in steel connections. To simplify this process, our AS Read more
-
Base Plate Design Calculator CSA A23.3

Introduction Steel column base plates transfer loads from the column to the concrete foundation. Designing base plates correctly ensures safety against excessive bearing, bending, and bolt tension. This CSA Base Plate Calculator simplifies preliminary design, following Canadian codes: The calculator supports metric and imperial units, allowing engineers to select their preferred system. CSA Base Plate Read more
-
Base Plate Design Calculator ACI 318
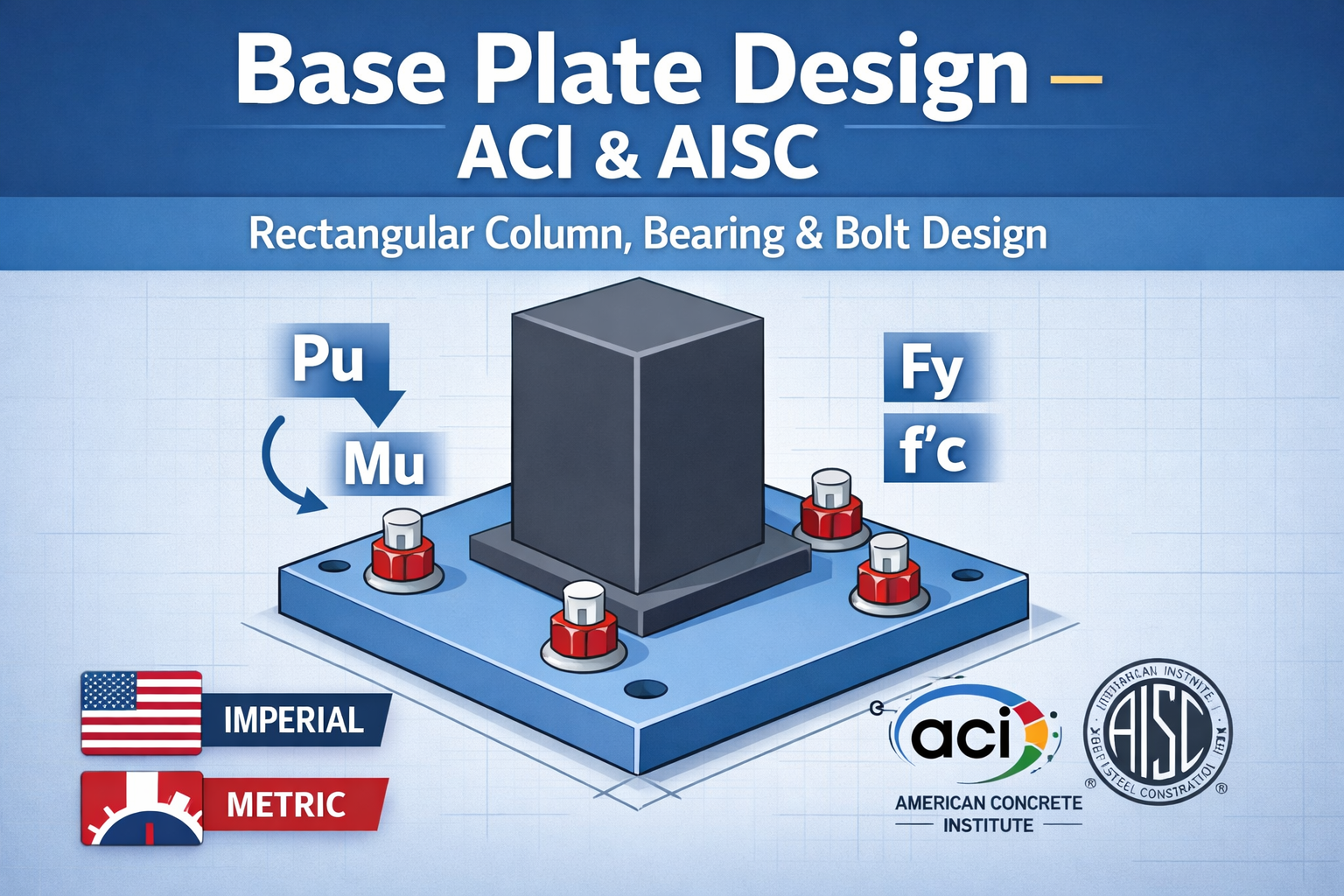
Introduction Designing a steel column base plate is a critical step in structural engineering, ensuring that loads from the column are safely transferred to the concrete foundation. Engineers need to calculate the plate thickness, bearing pressure, and anchor bolt tension to meet design standards. Our interactive Base Plate Design Calculator allows you to perform this Read more
-
Base Plate Design as per IS 800 2007

Introduction (Anchor Bolts Outside & Inside Column Flange) Base plates are critical steel connection elements used to safely transfer axial load, bending moment, and shear force from a steel column to the concrete foundation.As per IS 800:2007 – General Construction in Steel, base plate design ensures adequate bearing, bending resistance, and anchorage safety. This article Read more
-
Room Paint Calculator | Paint, Primer & Putty Quantity & Cost Estimator

Looking to renovate your room? Our Room Paint, Primer & Putty Calculator helps you instantly estimate the exact quantity of paint, primer, and wall putty you need. Simply enter your room dimensions, select interior or exterior painting, specify the number of coats, and input the costs per liter or kilogram. The calculator automatically computes: Perfect Read more
-
Load Conversion & Stress Calculator | kN to kg, ton, N, MPa Online
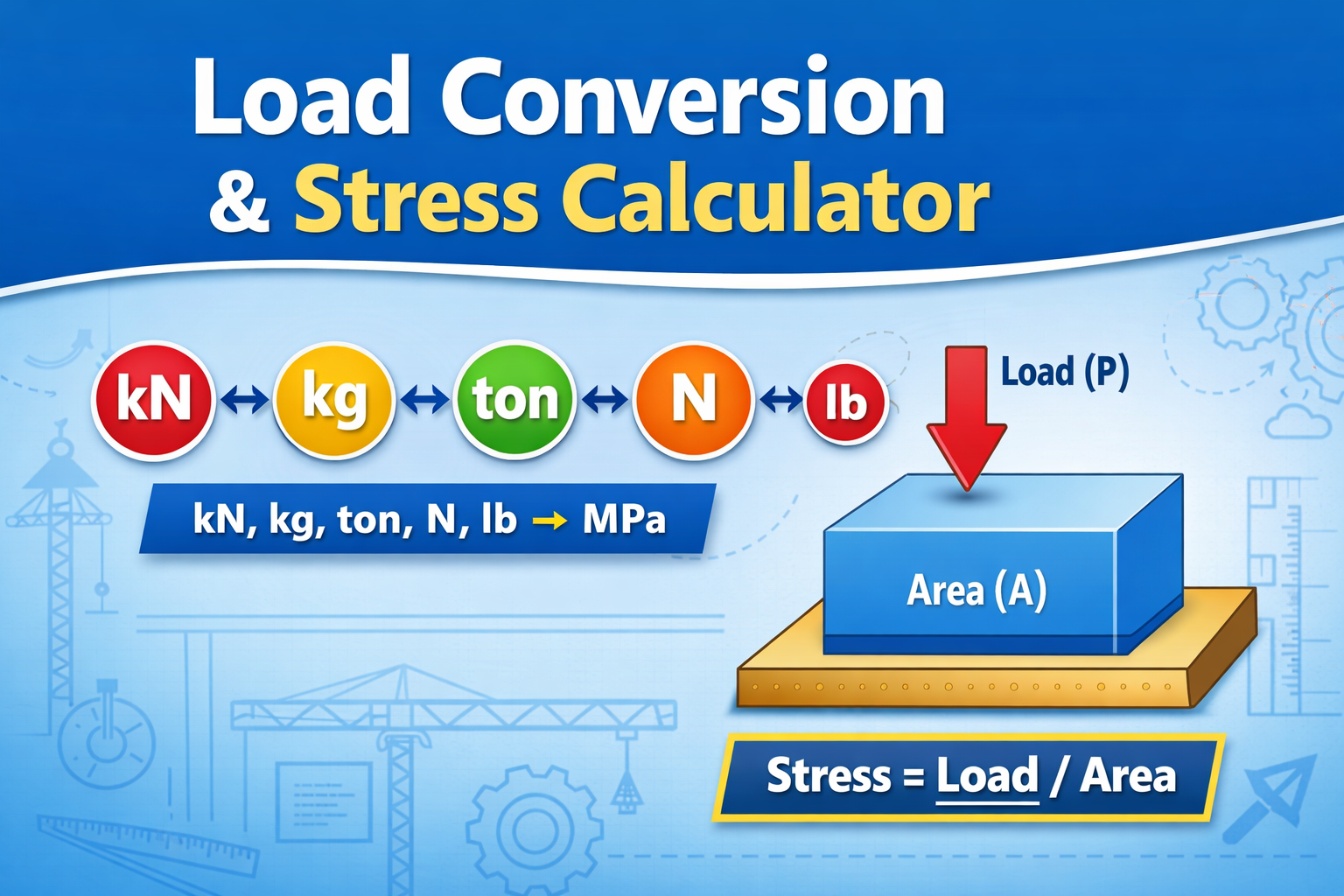
Load Conversion & Stress Calculator for Civil and Structural Engineers In civil and structural engineering, accurate load conversion and stress calculation are critical for safe and economical design. Engineers frequently need to convert loads between kN, kg, ton, Newton (N), and pound (lb) and evaluate the resulting stress on structural elements such as slabs, footings, Read more
-
Water Tank Capacity Calculator – Feet & Meter Conversion (Litres & Gallons)

Water Tank Capacity Calculator with Unit Conversion Accurate water storage is critical for residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. This Water Tank Capacity Calculator lets you calculate tank capacity quickly and easily using Length, Width, and Height in Feet (ft) or Meter (m). Recommended Tank Sizes (India) Usage Type Typical Capacity Small House 1000 – 2000 Read more
-
Brick Wall Construction Calculator | Calculate Bricks & Cost Instantly |

Introduction Building a brick wall requires accurate planning to avoid extra costs and material wastage. Our Brick Wall Construction Calculator helps you quickly estimate the number of bricks required and the total construction cost including labour and mortar. It’s perfect for builders, engineers, and DIY enthusiasts. Brick Wall Calculator – Brick Quantity & Construction Cost Read more
-
Unit Converter – Feet, Inches, cm, mm, Yard to Meter and Vice Versa

Length Unit Converter 🌙 Toggle Dark Mode Length Unit Converter Convert Feet, Inches, cm, mm, and Yard to Meters and vice versa instantly. Feet & Inches → Meter Feet Inches Meter: 0 Meter → Feet, Inches, cm, mm, Yard Meter Feet: 0 Inches: 0 cm: 0 mm: 0 Yard: 0 Features Instant conversion while typing Read more
-
Lifting Analysis of Skid Using Spreader Beam 4-Point
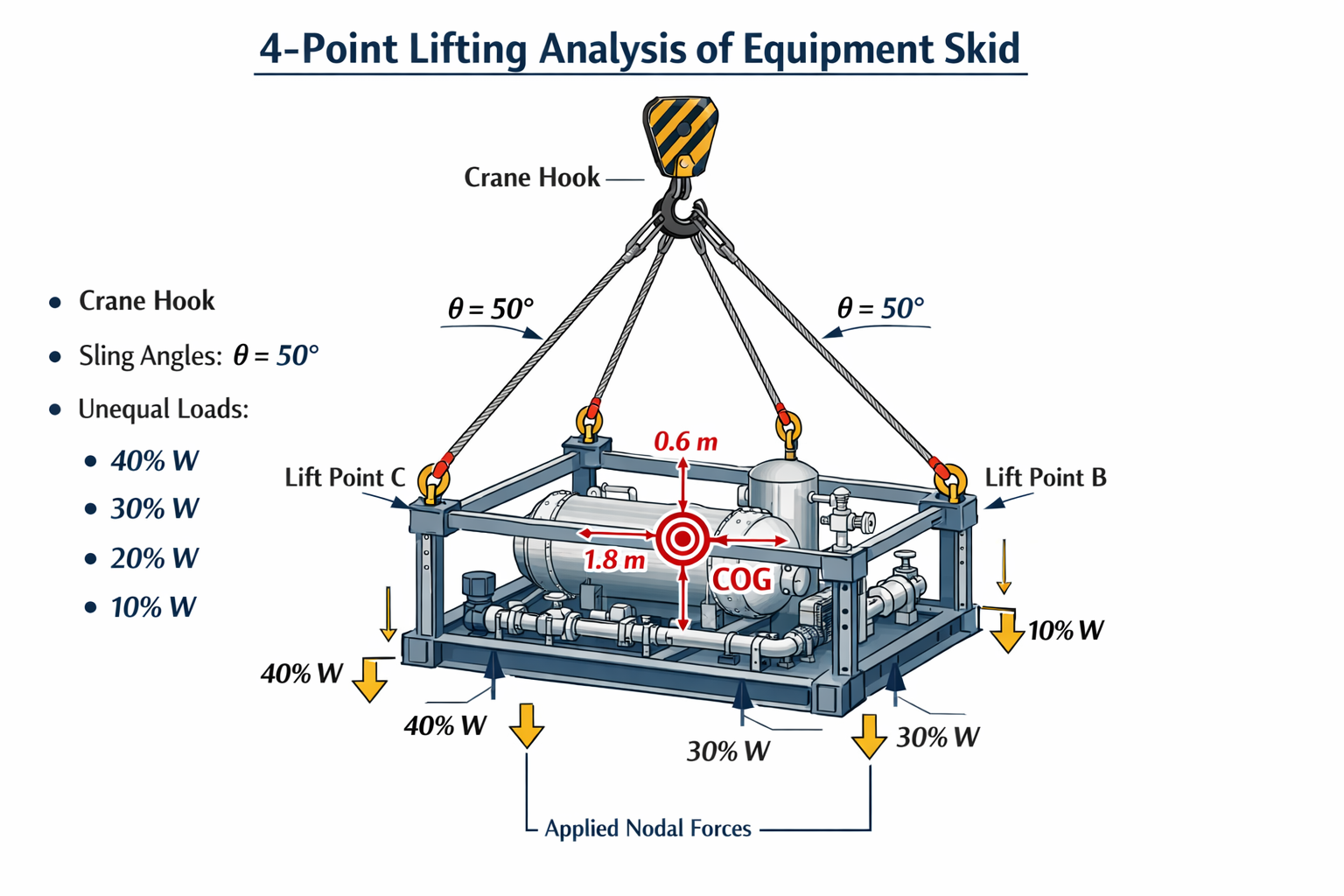
COG Shift, Moment Calculation & Sling Forces for STAAD Pro In heavy equipment skids, direct 4-point lifting without a spreader beam often results in high sling forces, torsional effects, and uneven load sharing due to Centre of Gravity (COG) shift.A spreader beam is commonly introduced to control sling angles, redistribute loads, and improve structural stability Read more
-
Base Plate Design as per IS Code | IS 800:2007 Steel Column Base |

Introduction In steel structures, the base plate is a critical element that transfers load from the steel column to the concrete foundation safely. A properly designed base plate ensures uniform load distribution, prevents excessive bearing stress in concrete, and provides stability against shear and overturning. In India, base plate design is mainly governed by IS Read more
-
Wind Load Calculation IS 875 Part 3 2015

Below is a compact, practical guide you can use on a blog or for quick design checks. I cite the code and explanatory notes so you can check the clauses. Check Below for Free Pdf Download of Wind Load Calculation & Nominal Payable Calculation Excel Spread Sheet Wind load Calculation Design wind speed at height Read more
-
Road Turning Radius as per IS/IRC Codes and International Standards AASHTO BS/DMRB

1. Turning Radius as per Indian Standards (IRC/IS Codes) In India, road geometric standards are given mainly by IRC, not IS.Relevant codes: A. IRC Standard Vehicle Turning Radius Vehicle Type Standard Turning Radius (IRC) Passenger Car 6.0 m Light Commercial Vehicle (LCV) 7.5 m Bus 12.0 m Single-Unit Truck 12.5 m Semi-Trailer (Articulated Truck) 14–15 Read more
-
Design of Steel Silo

1. Introduction Steel silo is, typical uses (grain, cement, powders), and the scope of this design procedure (static structural design of cylindrical shell with conical hopper, supports and foundation). Mention that design must follow the relevant national/regional codes and that the procedure below is a general engineering workflow (not a legal substitute for code compliance). Read more
-
Design of Beam to Beam End Plate Connection

Beam end-to-end connections (splices) ensure continuity and safe transfer of shear, axial, and moment forces between beam segments. They are commonly achieved using bolted cover plates, welded butt joints, or end plates. Design focuses on bolt and weld strength, plate thickness, and detailing to ensure structural safety, ease of erection, and economy. Types of end-to-end Read more
-
DESIGN OF FLAT SLAB pdf Free Download

🔹 What is a Flat Slab? A flat slab is a reinforced concrete slab directly supported by columns without the use of beams. The load transfer is from slab → column → foundation. It is commonly used in: 🔹 Types of Flat Slabs 🔹 Design Procedure (as per IS 456:2000 & IS 875) 1. Preliminary Read more
-
Design of Thrust Block

Thrust blocks are one of the most important structural components in underground piping systems. They are designed to resist the unbalanced forces generated at pipe bends, tees, reducers, and valves due to internal fluid pressure. Without proper thrust restraint, these forces can cause pipe joint failure, movement, or leakage. What is a Thrust Block? A Read more
-
Analysis and Design of Drain Sump Pit

Introduction A sump pit, commonly used in buildings, industrial plants, and utility areas, serves as an underground water collection tank designed to temporarily store rainwater, wastewater, or stormwater. Proper structural and RCC design of a sump pit is crucial to withstand soil pressure, groundwater uplift, and water-retaining conditions. This document outlines the structural analysis, RCC Read more
-
Design of Steel Shelter as per IS 800

Designing a steel shelter requires a clear understanding of structural stability, safety, and economy. In India, the IS 800:2007 – General Construction in Steel Code of Practice serves as the primary standard for the design and construction of steel structures, including shelters, sheds, canopies, and industrial buildings. This code lays down the requirements for both Read more
-
Hydrodynamic Load on Tanks | Convective and Impulsive |
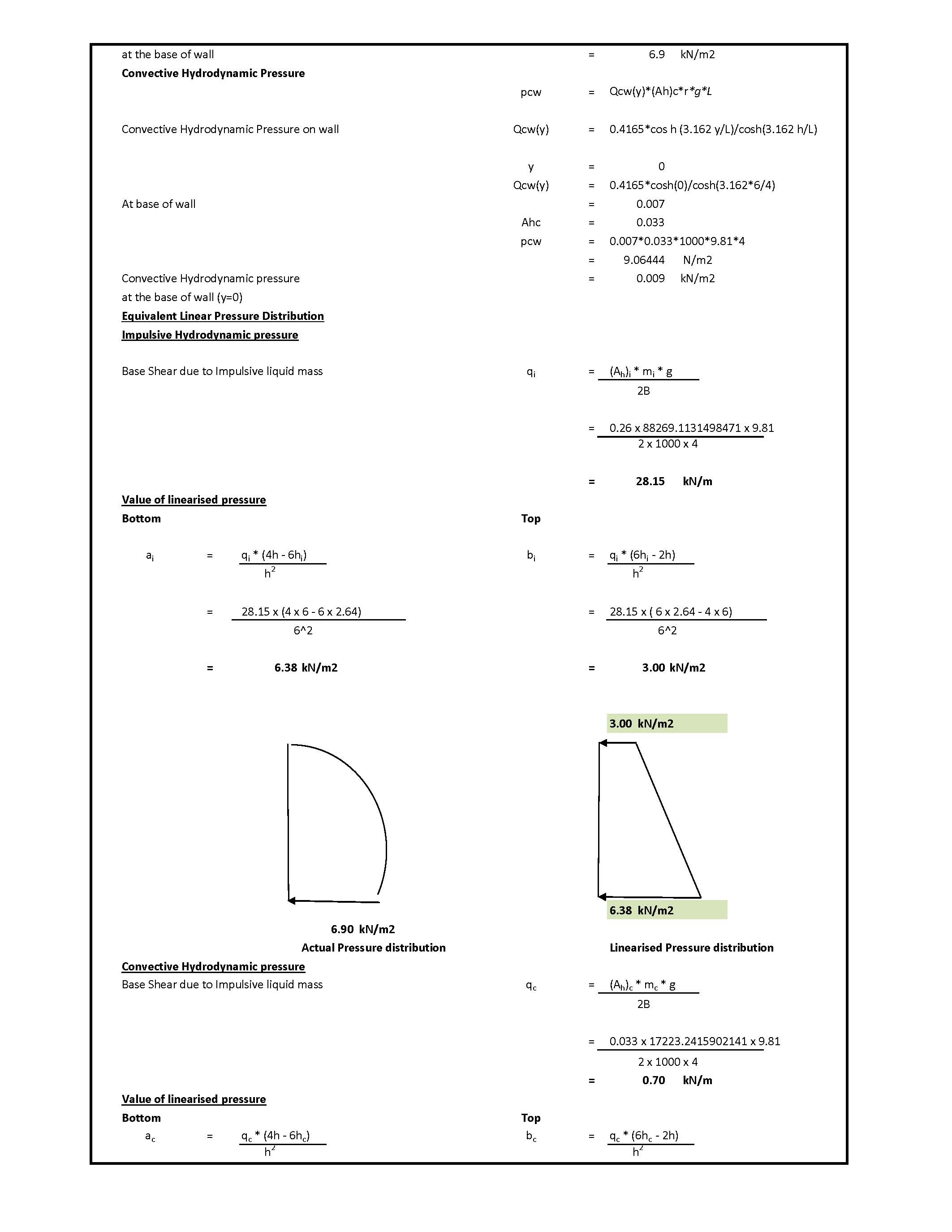
Hydrodynamic loads for tanks refer to the forces exerted on the tank and its internal or external components due to fluid motion, especially during dynamic events like earthquakes, wave action, or fluid sloshing. These loads are critical in designing tanks (such as water tanks, oil tanks, or storage reservoirs) to ensure structural safety and stability. Read more
-
PILE STIFFNESS CALCULATION

STAAD INPUT FOR SUPPORT CONDITION VERTICAL STIFFNESSAllowable vertical settlement = 12 mmAllowable vertical load (2000*1.5) = 3000 kN Cl. 6.1.5, IS:2911 (Part 4)-1985 Vertical stiffness = 3000×103/12= 250000 kN/m Horizontal STIFFNESSAllowable lateral deflection = 5 mmAllowable lateral force = 120 kN Cl. 7.4, IS:2911 (Part 4)-1985Horizontal stiffness = 120×103/5= 24000 kN/m Error! Filename not specified. Read more
-
Loads and Load Combinations as per AS/NZS 1170.0 2002

Designing Piperacks (pipe support structures) in compliance with Australian Standards involves determining appropriate loads and load combinations. These ensure structural safety and serviceability under expected operating conditions. 📘 Relevant Australian Standards 🔩 Typical Loads on Piperacks 1. Dead Load (G) 2. Live Load (Q) 3. Pipe Contents Load (Fluid Load) 4. Thermal Loads 5. Wind Read more
-
Design of Pump Foundation Dynamic and Static Analysis

Design workflow (step-by-step) 2) Loads you must consider (typical) 3) Bearing capacity & foundation size (quick formulas) Areq=Wtotal / qallow where Wtotal = vertical load + self weight of foundation, qallow – allowable soil bearing pressure (kN/m²). 4) Natural frequency / dynamic criteria (must check) fn=1/2π(sqrt(k/m) )where k= effective stiffness of foundation system (N/m), m Read more
-
Stormwater Drainage Calculation
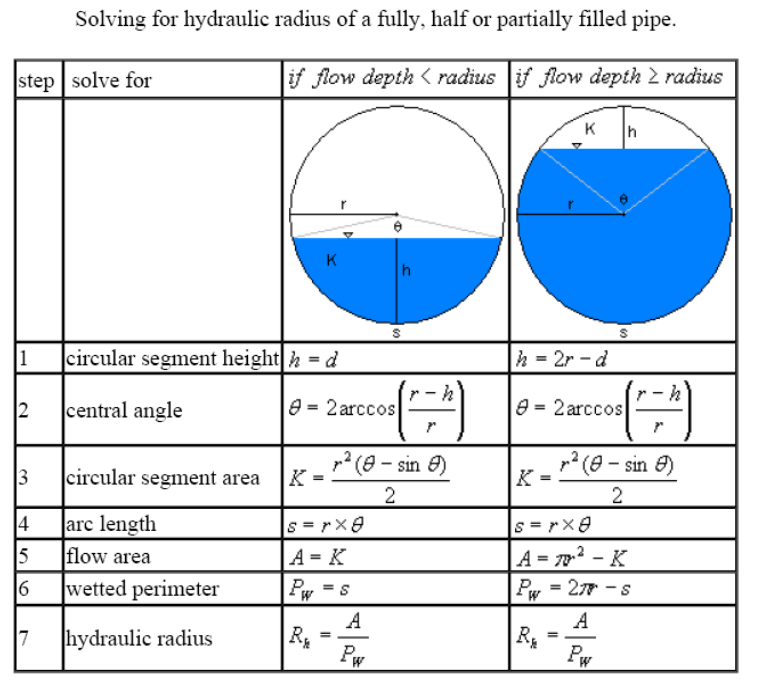
Designing 🌧️ Stormwater Drainage systems is essential to ensure the efficient collection and disposal of surface runoff from rainfall. Proper pipe sizing ensures that the stormwater is carried safely without causing flooding, ponding, or structural damage. 📘 1. Key Formula: Rational Method The Rational Method is widely used for stormwater pipe sizing in small urban Read more
-
Structural Engineering Design Criteria – American Codes and Standards

In the United States, structural engineering design is governed by a robust framework of codes, standards, and guidelines to ensure safety, functionality, and durability of buildings and infrastructure. Understanding and applying the right standards is essential for engineers to deliver code-compliant and efficient designs. B.1 INTRODUCTION This appendix summari zes the codes, standards, criteri a, Read more
-
Wind Load Calculations ASCE 7-16 Pdf Free Download

Wind Speed Calculation as per ASCE 7-16 (“Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures”) provides a systematic approach to determining wind loads on buildings and structures. The calculation involves determining wind speed, exposure categories, wind pressure, and applying appropriate load factors. Step 1: Determine Basic Wind Speed (V) Step 2: Identify Read more
-
Wind Load Calculation as per Australian Code (AS/NZS 1170.2:2021)
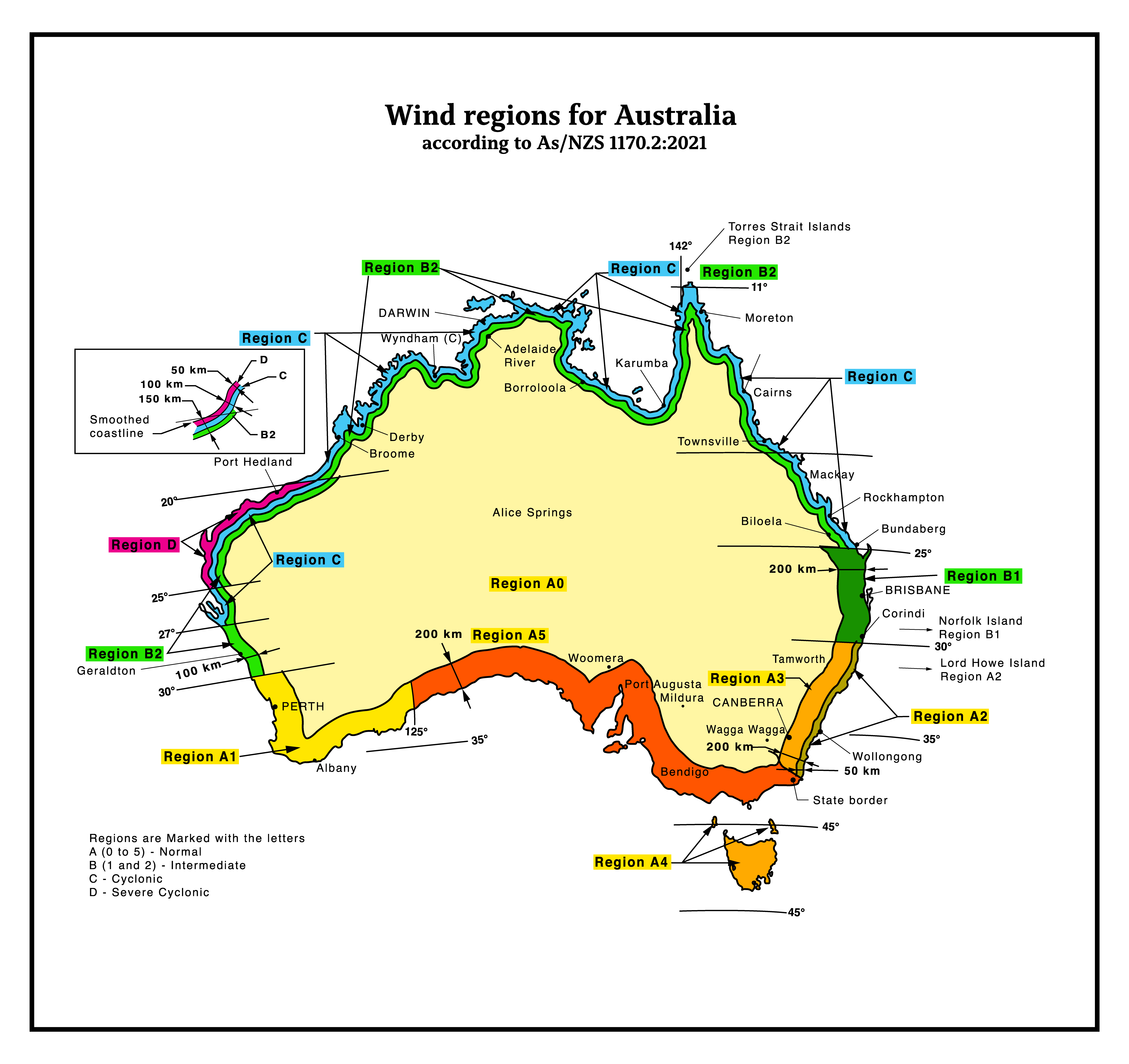
Wind loads in Australia are calculated based on AS/NZS 1170.2:2021 – Structural Design Actions, Part 2: Wind Actions. This standard provides guidelines for determining wind loads on buildings and structures based on wind regions, terrain categories, building height, and shape factors. AS/NZ 1170.2 (2021) is the Australian and New Zealand Standard that specifically addresses wind loads Read more
-
Standard Road Details
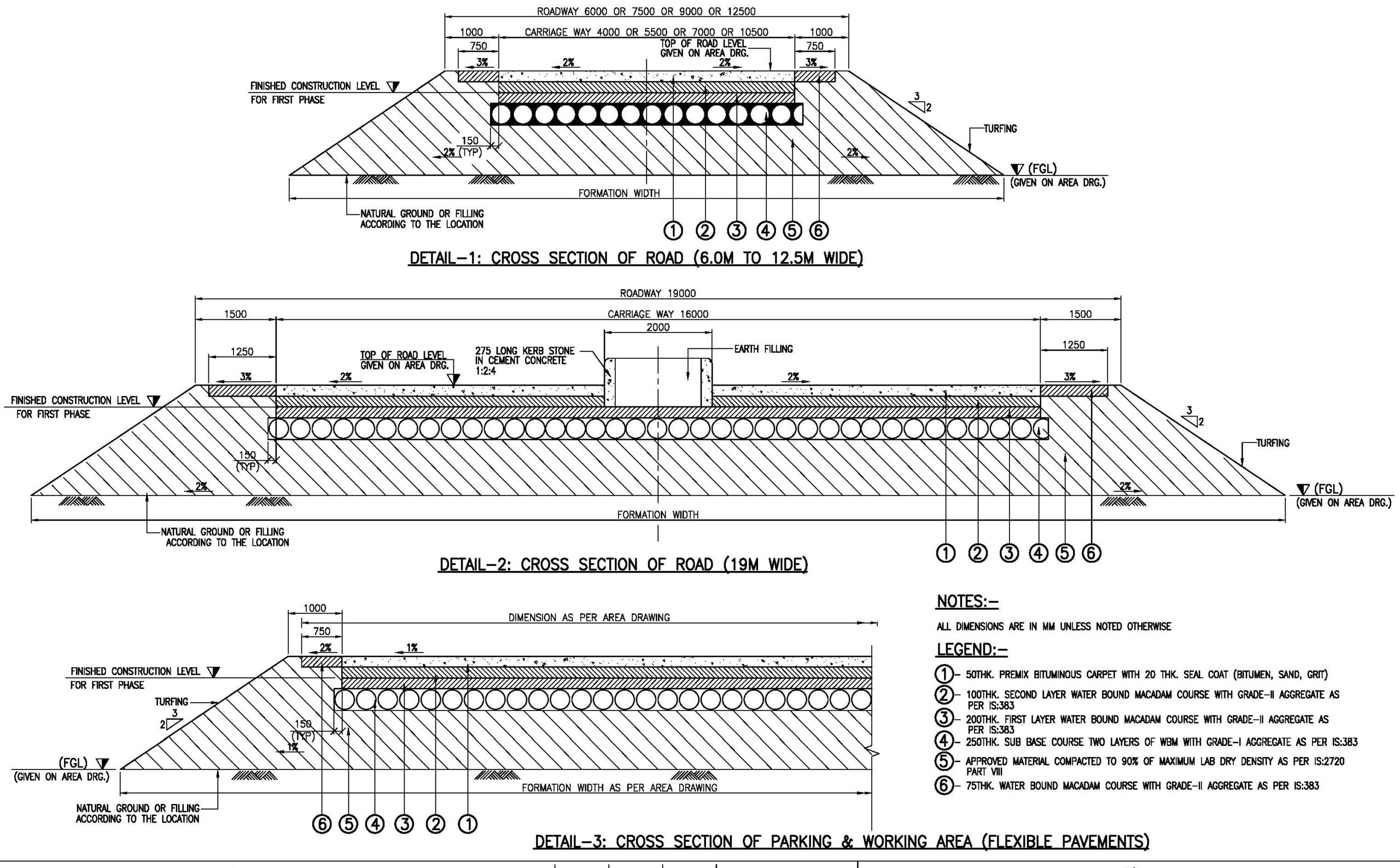
Rigid & Flexible Road Details – Drawings & Requirements Road construction is broadly classified into rigid pavement and flexible pavement based on the material used and load distribution characteristics. A rigid road consists of concrete pavement, while a flexible road is primarily made of bituminous (asphalt) layers. Both have unique structural designs, materials, and applications. Read more
-
SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAMS WITH FORMULA
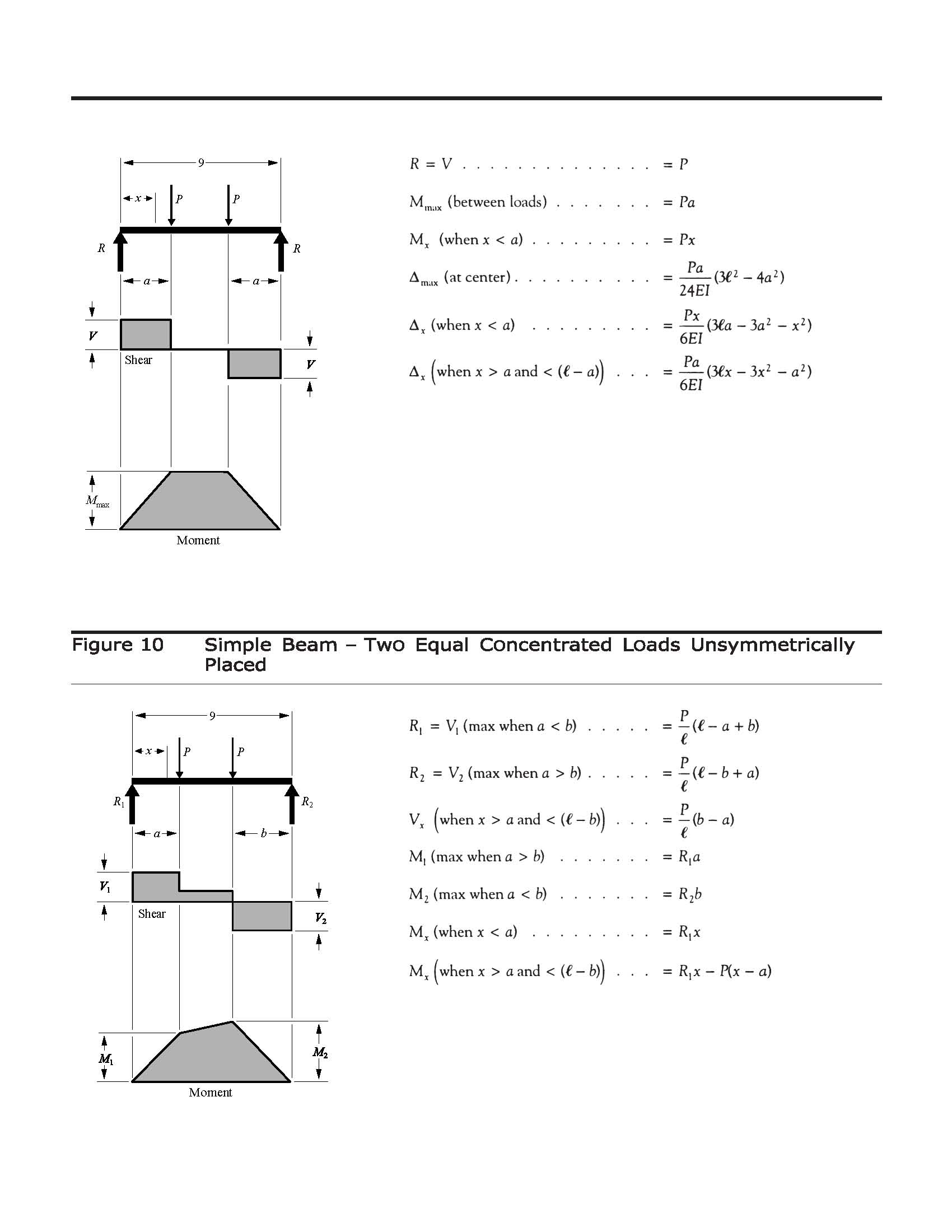
Introduction Figures 1 through 32 provides a series of shear and moment diagrams with accompanying formulas for design of beams under various static loading conditions. Notations Relative to “Shear and Moment Diagrams E = modulus of elasticity, psi I = moment of inertia, in.4 L = span length of the bending member, ft. R = Read more
-
Canadian Code Seismic Calculation Example

The National Building Code of Canada (NBC) 2020 provides the latest guidelines for seismic design, ensuring structures can withstand seismic events. Here’s an overview of the seismic calculation procedure as per NBC 2020: 1. Determine Seismic Hazard Values Utilize the 2020 National Building Code of Canada Seismic Hazard Tool to obtain site-specific seismic hazard values. Read more
-
Design Calculation of Steel Shelter – AISC 360
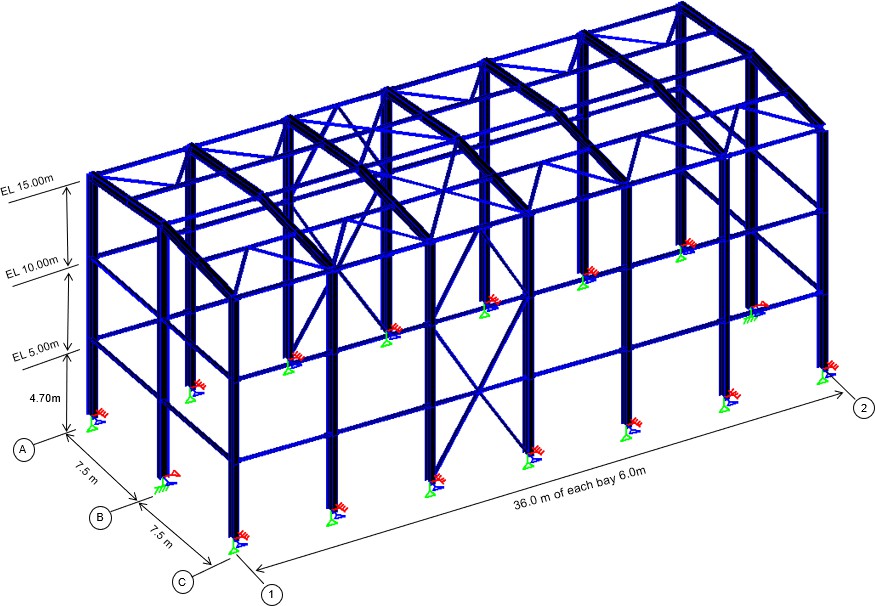
PURPOSE AND SCOPE The scope of this document is to provide the calculations for the Analysis and Design of Steel Shelter. The software used for structural analysis and design is STAAD Pro Connect Edition. .A three-dimensional model of shelter structure is created in STAAD and all relevant loads are applied in accordance with ASCE 7-10 Read more
-
Vertical Vessel Foundation Design
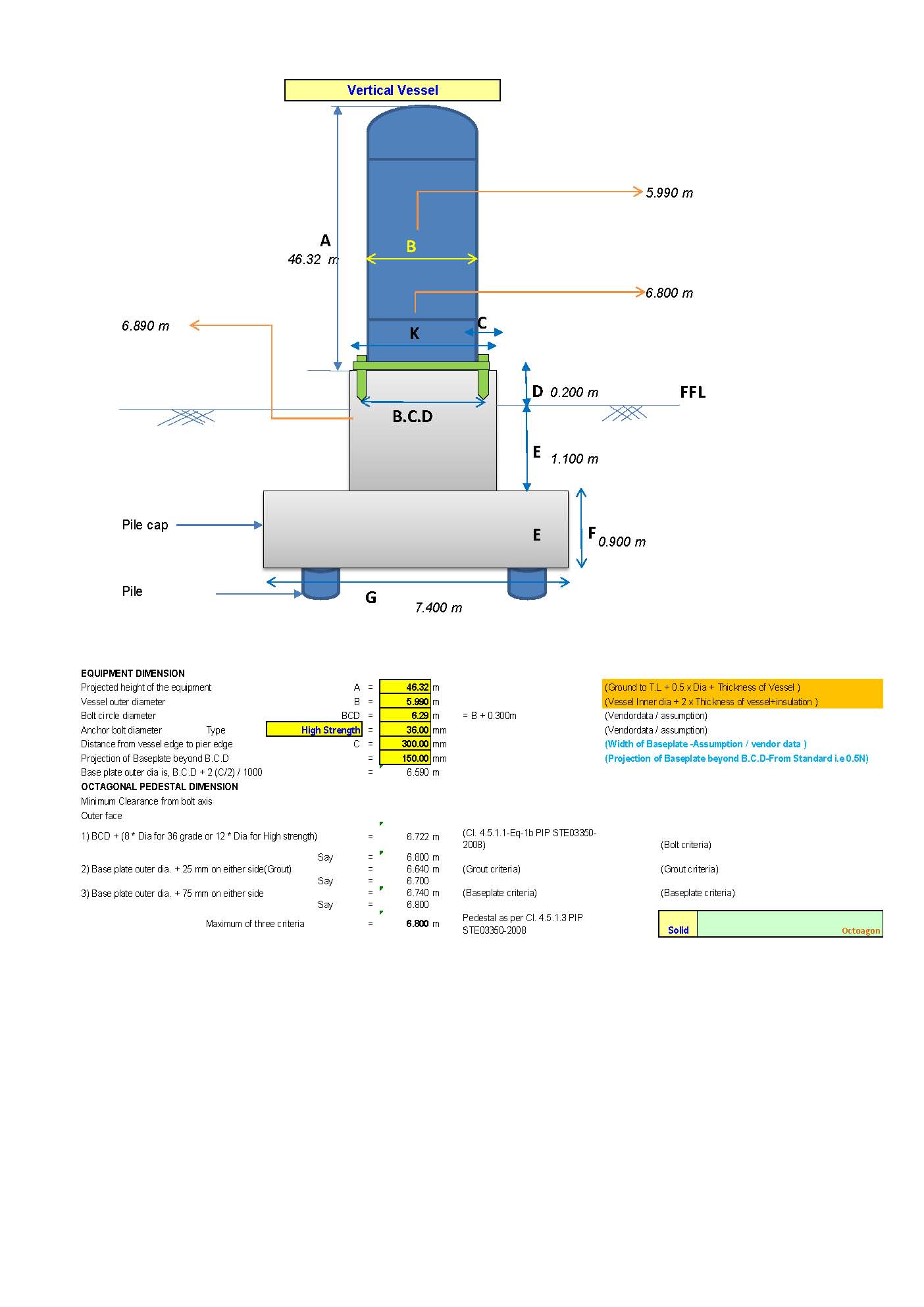
Vertical Vessel foundation design The design of a foundation for a vertical vessel involves ensuring the stability, strength, and serviceability of the foundation under various loads (dead load, live load, wind, seismic, etc.). Vertical vessels are typically supported on circular ring foundations, annular plates, or pedestal-type foundations. Here’s a step-by-step process for designing a vertical Read more
-
Effective Length for RCC Columns
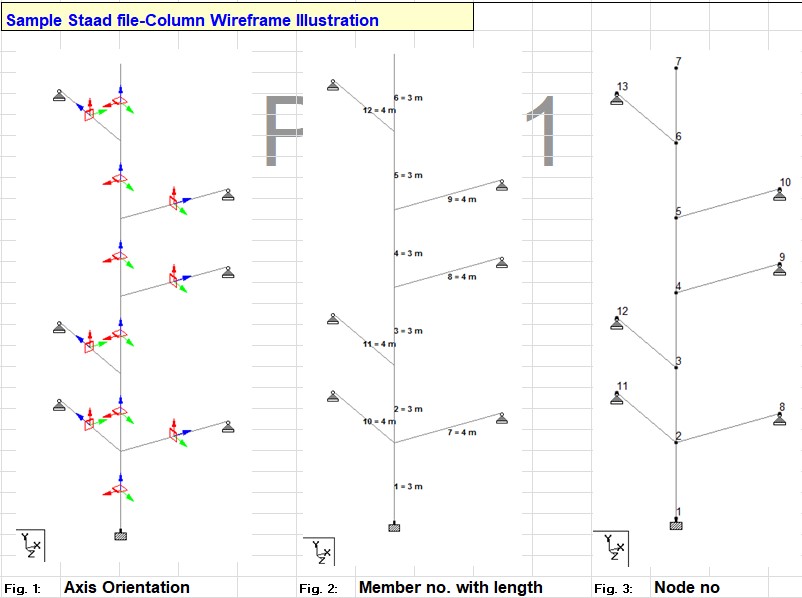
In STAAD.Pro, ELY and ELZ are parameters used to define the effective length factors of a column in the major axis (local Y-axis) and minor axis (local Z-axis), respectively. These parameters are essential when designing RCC columns to account for buckling in different directions as per the relevant design code, such as IS 456:2000. How Read more
-
DESIGN OF SLABS AS PER IS456
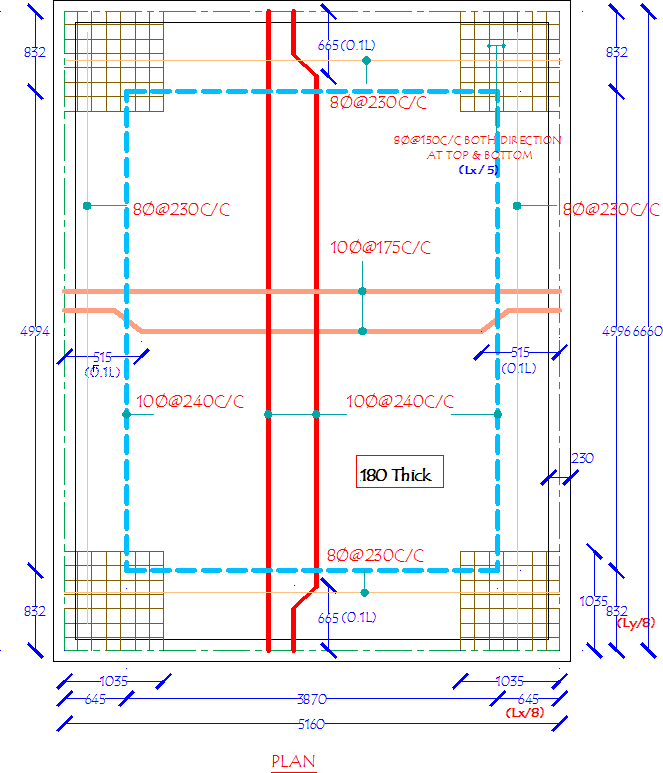
DESIGN OF SLABS AS PER IS456 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional planar structural element having thickness small compared to its other two dimensions. It provides a working flat surface or a covering shelter in buildings. It primarily transfers the load by bending in one or two directions. Reinforced concrete slabs are Read more
-
Design of Staircase Waist Slab
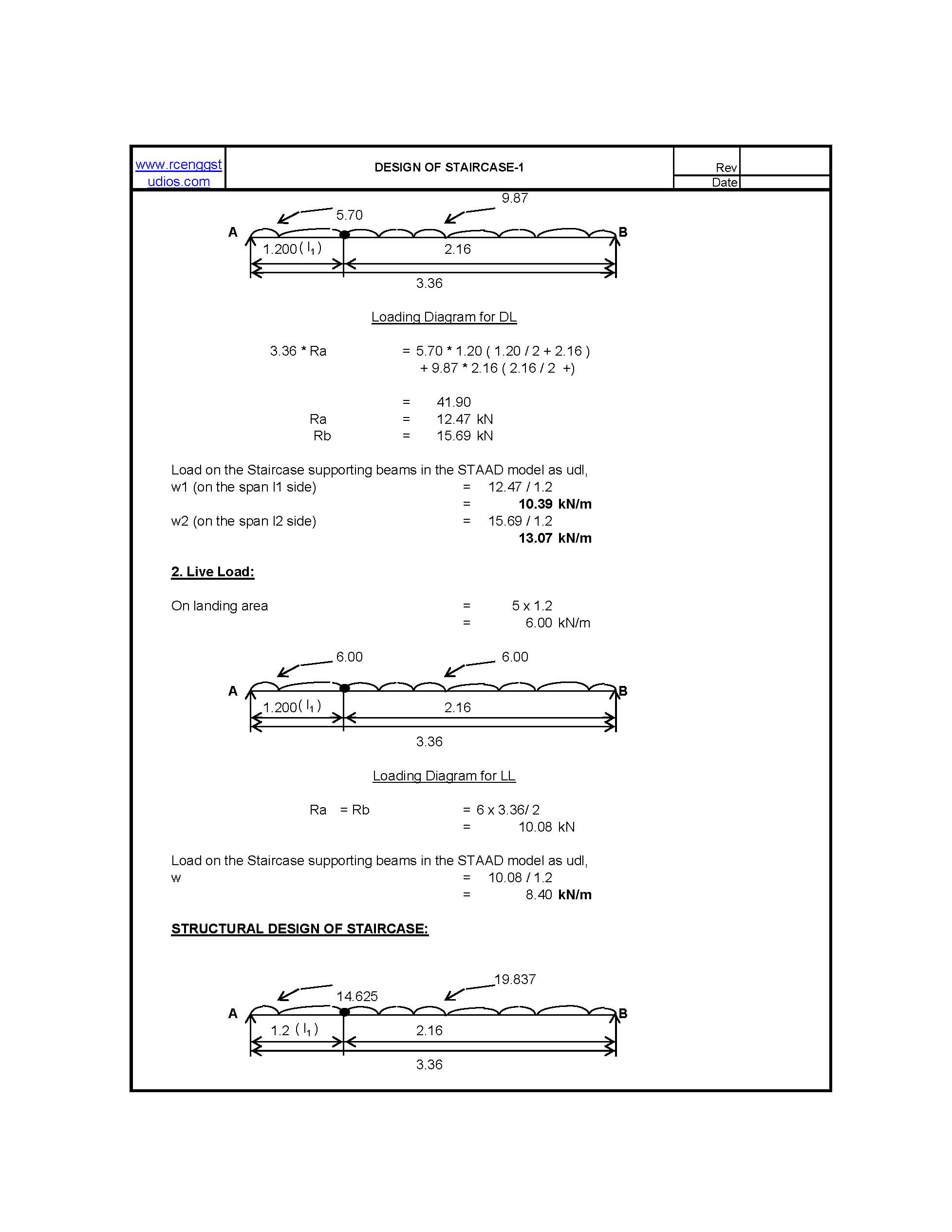
Design of Staircase Waist Slab A waist slab is the inclined structural element of a staircase that supports steps and transfers the loads to supporting beams or walls. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide for designing a waist slab as per IS 456:2000: Given Parameters: “Do write the details in the Yellow cells only and do Read more
-
Monorail Beam Design

Designing a monorail beam as per IS 800:2007 (General Construction in Steel – Code of Practice) involves several steps to ensure that the structure is capable of supporting the loads applied during its operation. Monorails are commonly used in material handling systems and typically consist of a steel beam supporting a trolley or hoist for Read more
-
Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19)
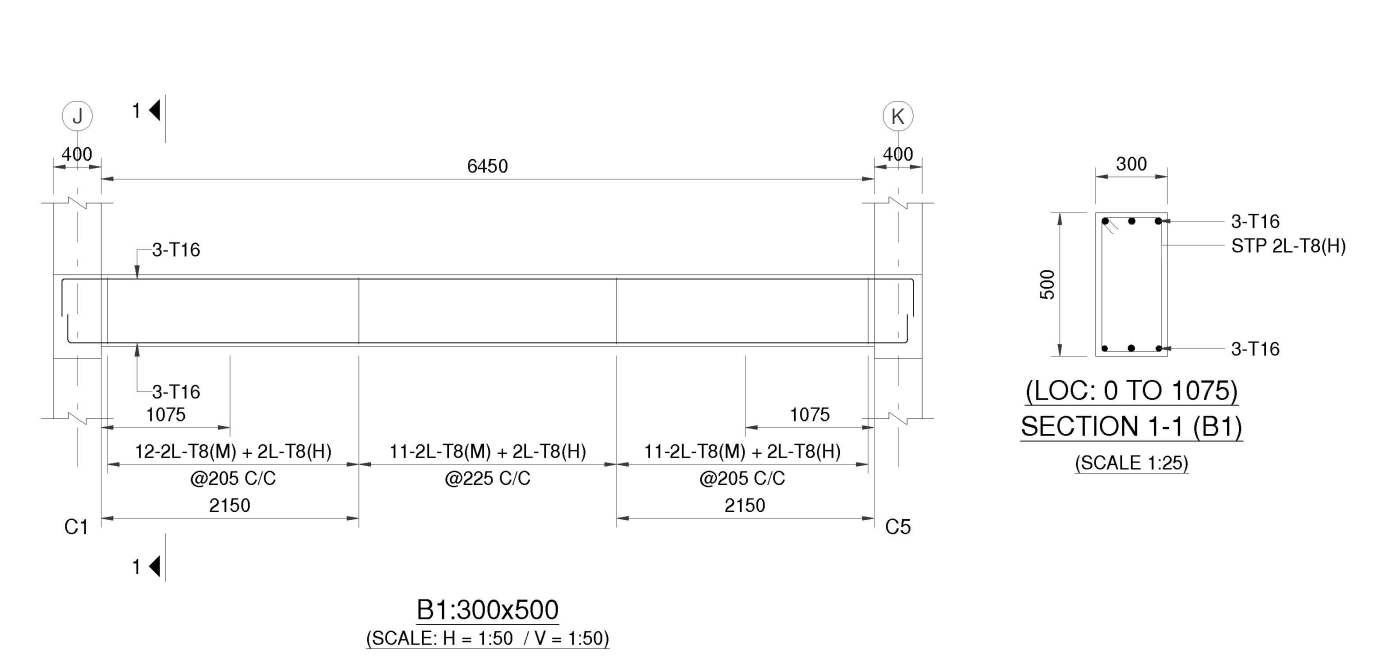
Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19) The design of concrete beams in Canada is governed by CSA A23.3-19: Design of Concrete Structures, which provides guidelines for strength, serviceability, and durability of reinforced concrete elements. Below is a step-by-step approach to designing a concrete beam according to the Canadian code. 1. Key Parameters Read more
-
Wind Load Calculation as per Canadian Code | NBCC 2020 |
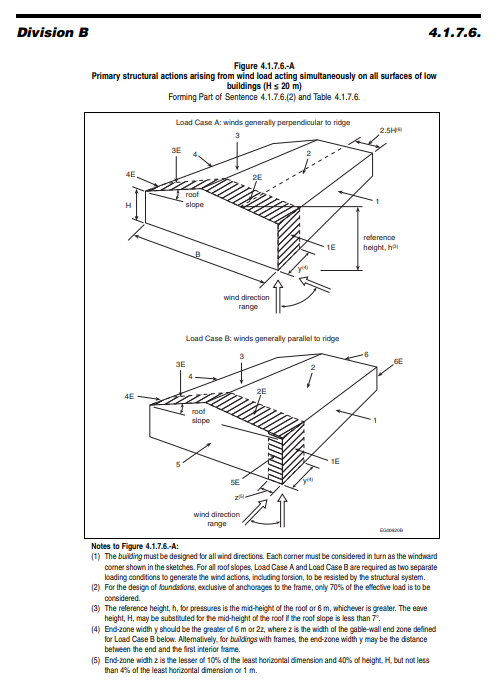
To calculate wind load as per the National Building Code of Canada (NBCC) 2020, the following steps summarize the process: 1. Reference Code and Formula Wind load calculation is governed by NBC 2020, specifically the provisions in Part 4, Section 4.1.7 (Wind Loads). The wind pressure (q) is calculated using: q=Iw⋅Ce⋅Cg⋅Cp⋅p Where: Iw: Importance factor Read more
-
Transformer Foundation Design
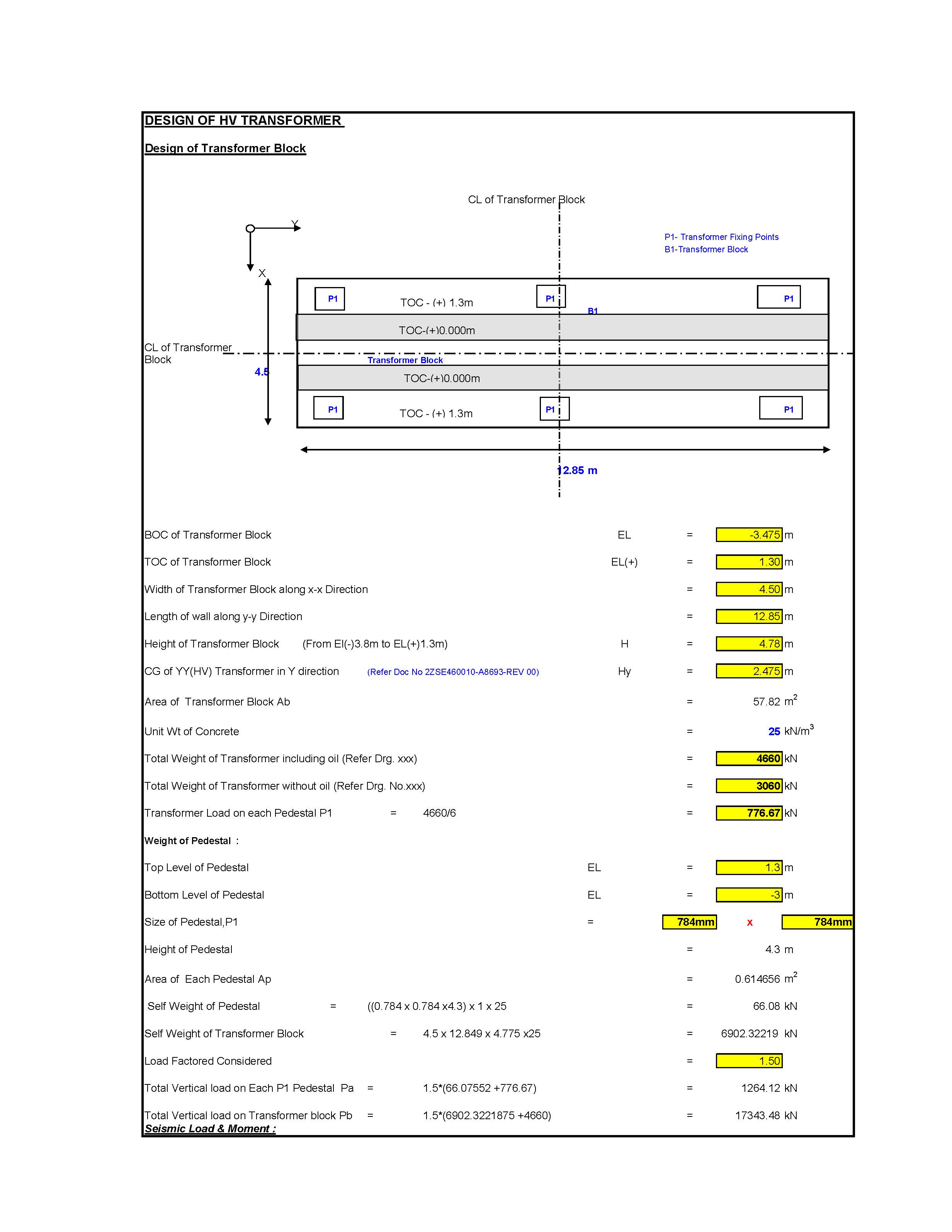
Designing a transformer foundation involves considering the transformer’s size, weight, dynamic forces, and environmental conditions to ensure safety and stability. Here’s a step-by-step guide to designing a transformer foundation: Transformer Foundation Design 1. Understand the Design Requirements 2. Determine Foundation Type 3. Structural Design A=Wqallowable Where W is the total load and q allowable Read more
-
Box Culvert Design
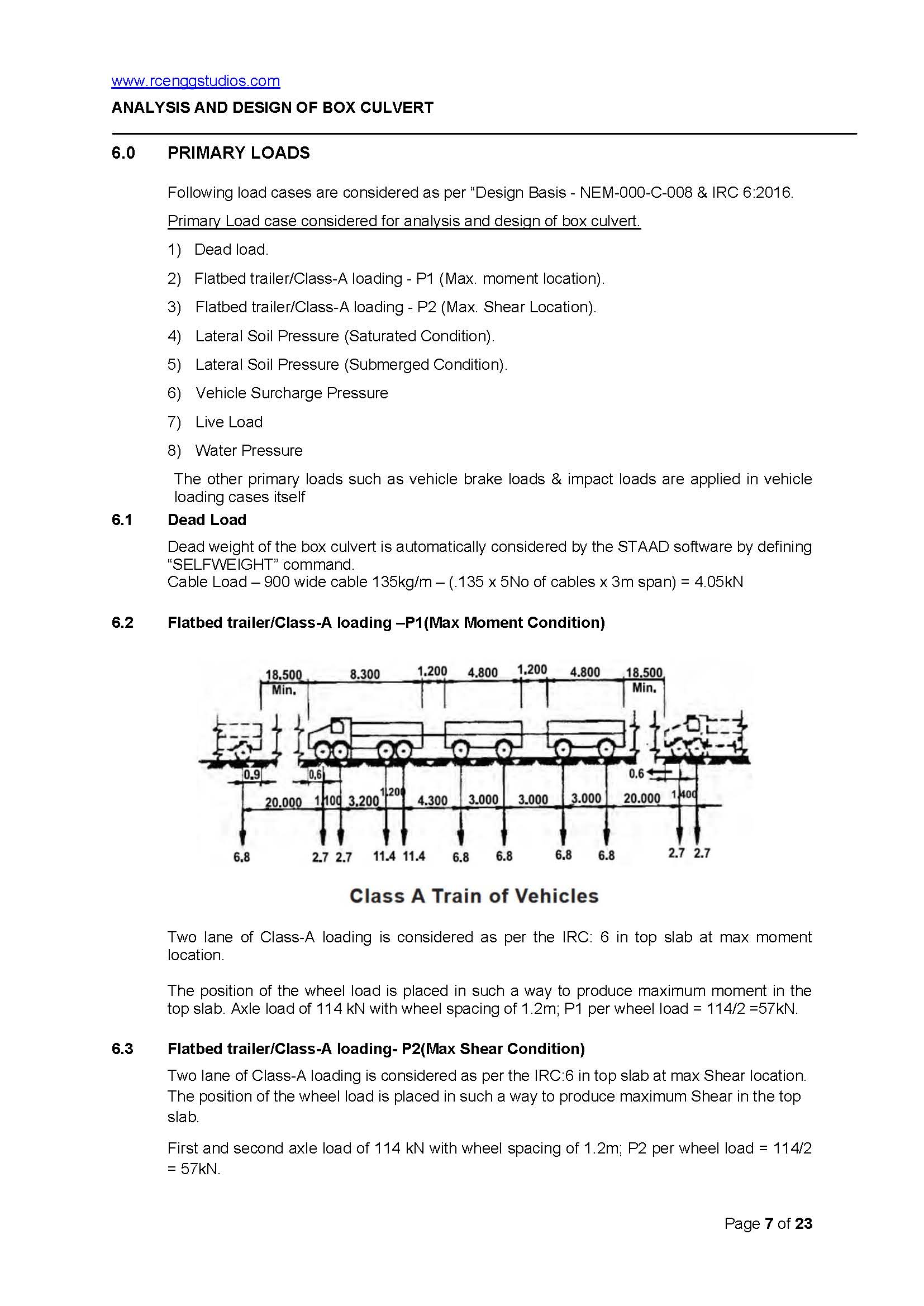
Box culvert design according to IRC 6 (Standard Specifications and Code of Practice for Road Bridges, Section II) involves several considerations for structural strength, stability, and durability. Here are the main design bases to consider: 1. Load Considerations Dead Load: Weight of the box culvert, including the self-weight of the concrete, parapets, and other permanent Read more
-
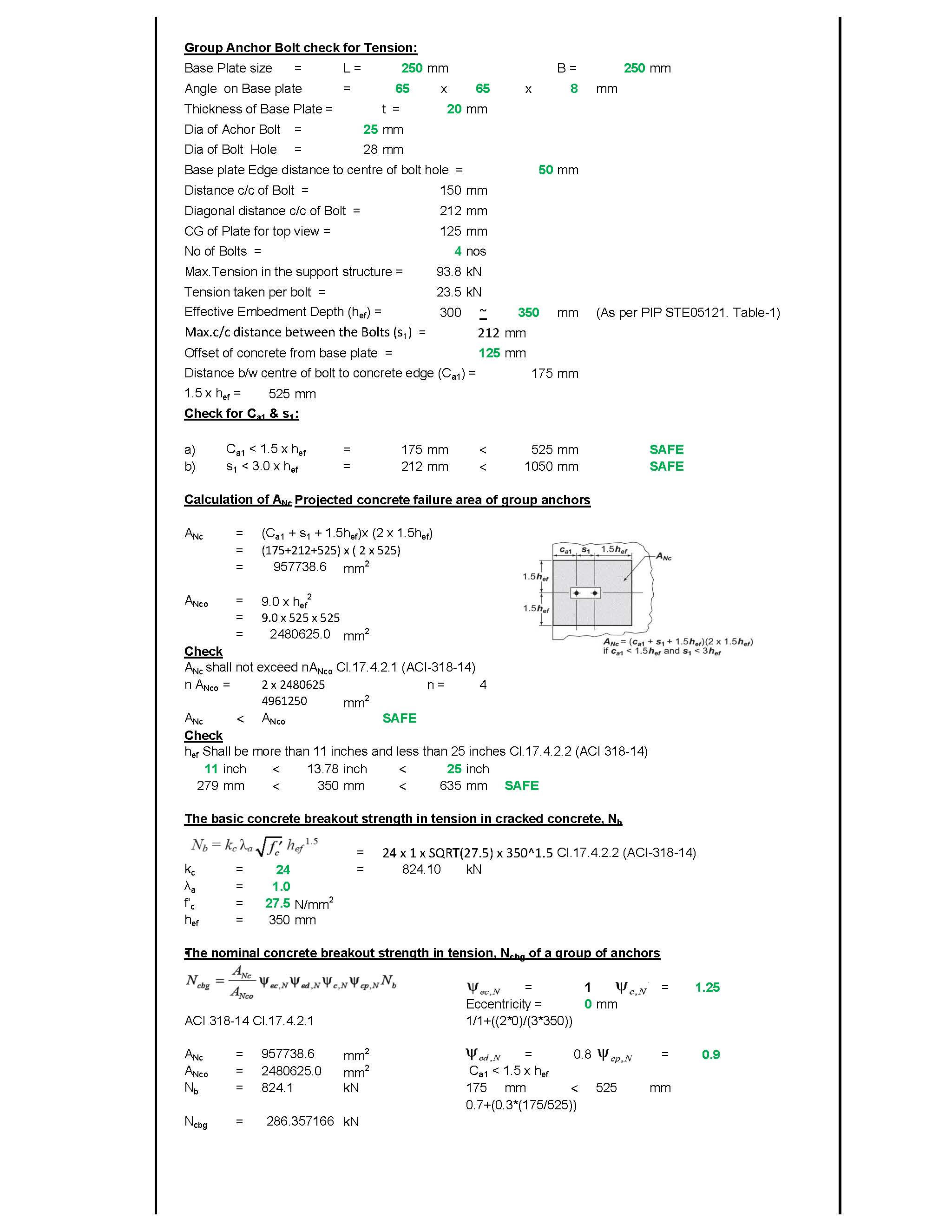
Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals
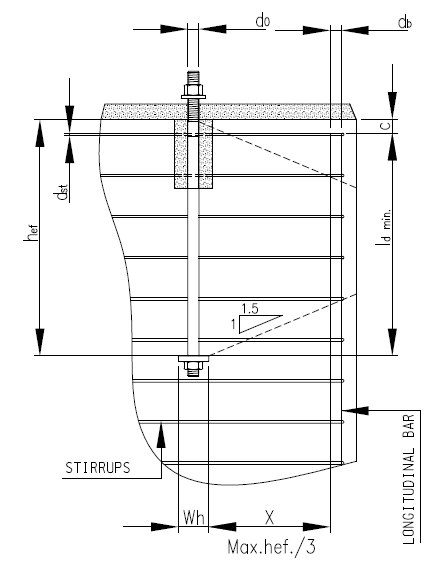
Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals Pedestal rebars parallel to anchor bolts have been checked in order to verify their capability to absorb the tensile force transferred by the anchor bolts. Stirrups have been checked to verify their capability to tranfer to concrete the shear force transmitted by the anchor bolts. The value of Read more
-
Wind Load Calculation for Pipe Rack
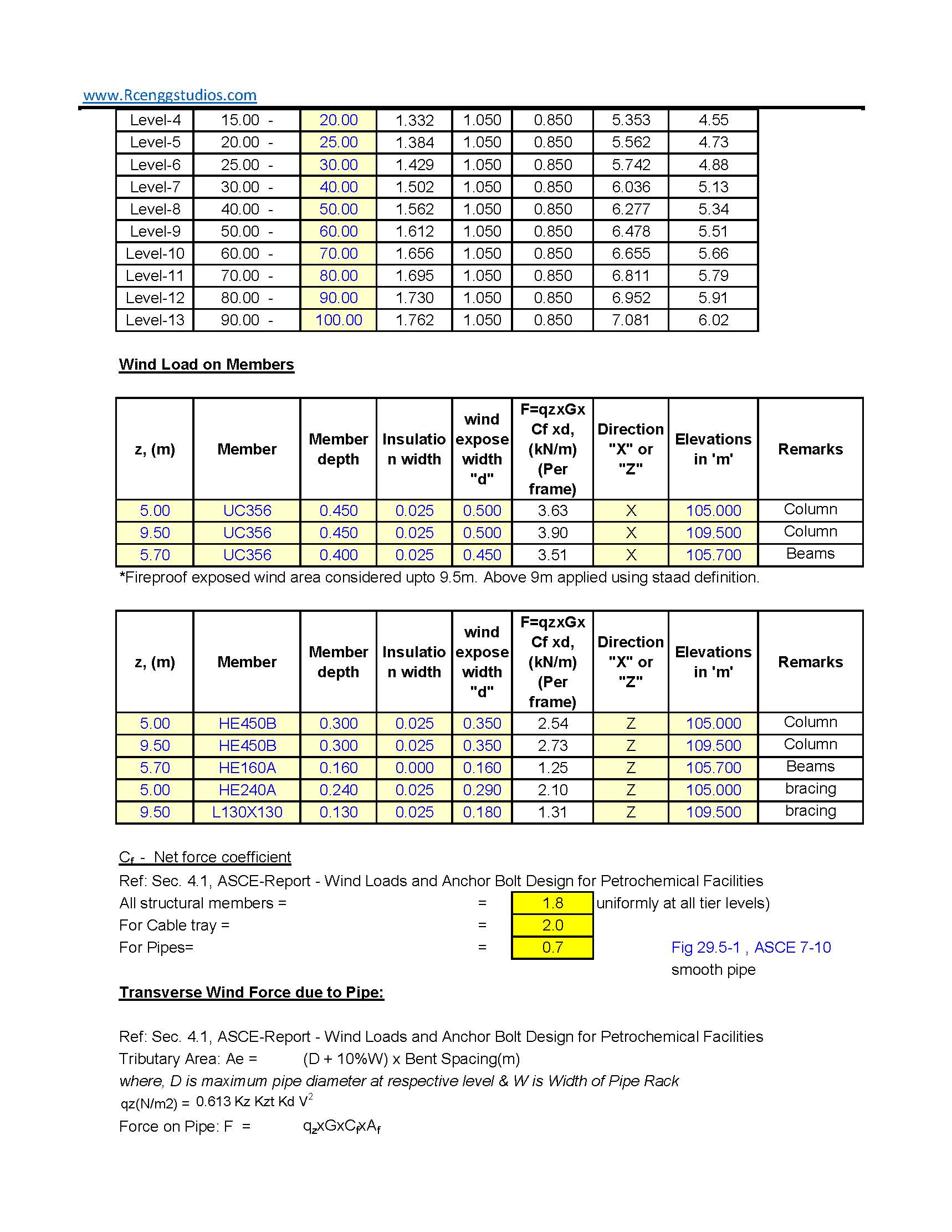
To calculate wind load on Pipe racks, open structures, cable trays and pipes as per ASCE 7-10, use the following approach, accounting for the cylindrical shape and exposure to wind. For wind load calculations in metric units as per ASCE 7-10, the primary difference lies in the units for wind speed and pressure. Here’s how to calculate wind Read more
-
Wind Load Calculation as Per Indian Code

Wind Load Calculation Wind speed -33m/sec From Ground floor to Slab level – 14.675m SLAB LEVEL to NEXT Slab level – 9.0 m Horizontal support interval – 1.55m Height of the building = 27.725m say 28m Length = 39.450m Width = 22.195m Dead load = self weight of beam Wind load WIND SPEED – 42M/SEC Read more
-
Response Spectrum Analysis in STAAD pro
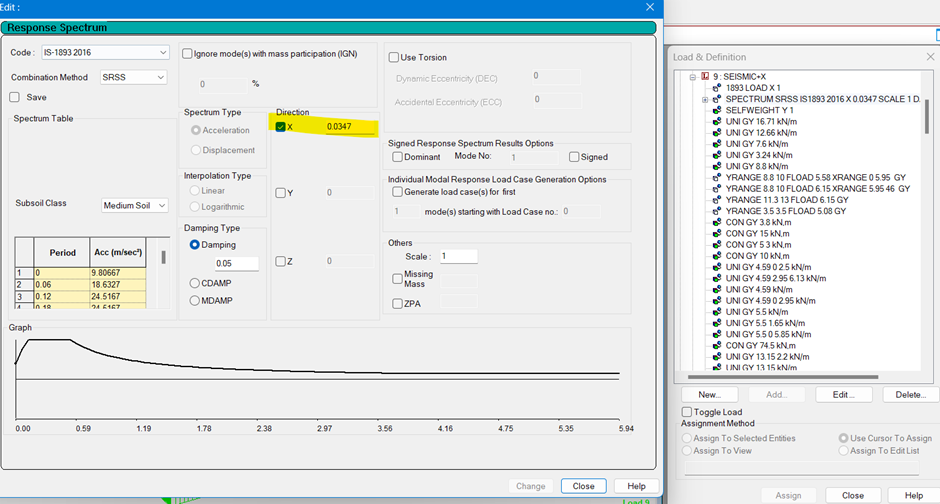
In STAAD.Pro, combining loads using the SRSS (Square Root of the Sum of the Squares) method is not directly available as a load combination type. However, you can implement it through a workaround in the STAAD Editor by writing load combinations for the relevant seismic or lateral loads and then manually applying the SRSS method Read more
-
Side Face Reinforcement as per ACI & IS code
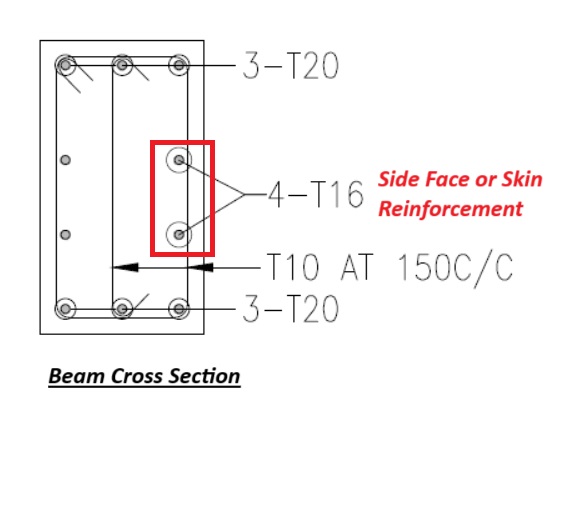
Side face reinforcement – IS 456:2000 (Indian Standard) The side face reinforcement in structural elements, particularly beams, is required to control crack widths due to lateral shear forces and to prevent the sides from cracking under load. The provision of side face reinforcement is mandatory when the depth of the beam exceeds a certain limit, Read more
-
Lifting Padeye Design
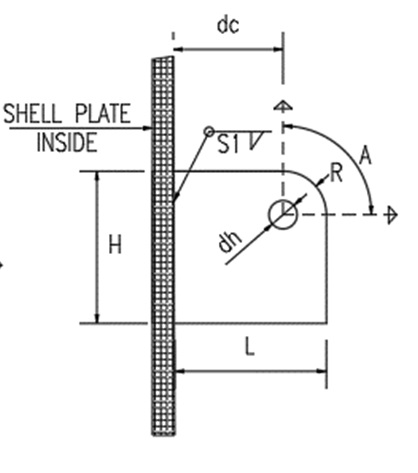
Padeye is a plate or attachment point commonly used in lifting and rigging operations to connect slings, shackles, or other lifting equipment. Proper design and calculation of a padeye are essential to ensure safe lifting operations. The calculation is based on factors such as load capacity, thickness of the plate, material properties, and hole size Read more
-
Corbel Design and Details
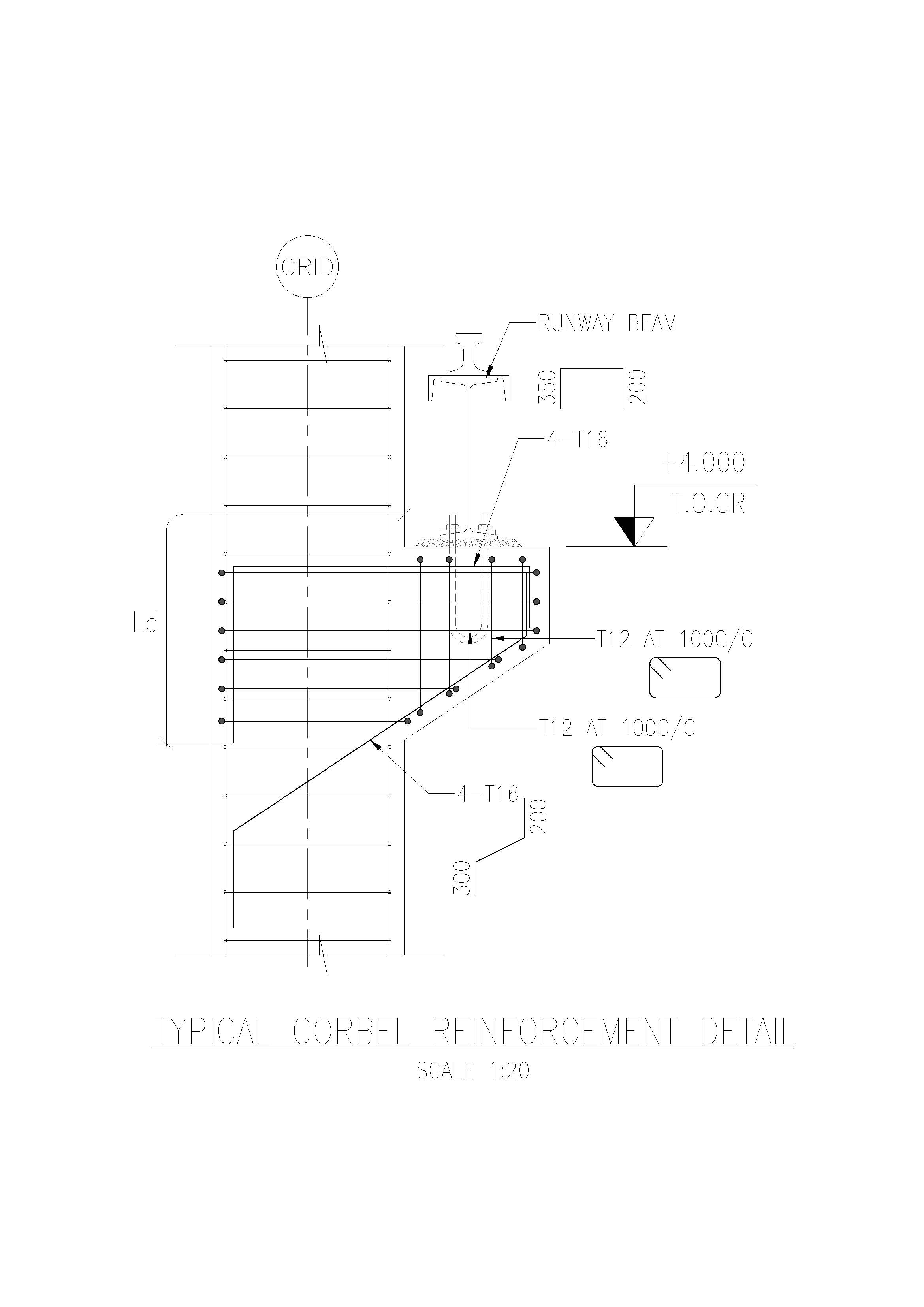
DESIGN OF CORBEL A corbel is a short cantilever used to support structural loads like beams or girders projecting from a column or wall. It is commonly found in reinforced concrete and steel structures. The design of a corbel should ensure that it is capable of safely transferring vertical loads from beams to columns or Read more
-
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS USING RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS
The purpose of this chapter is to summarize the fundamental equations used in the response spectrum method and to point out the many approximations and limitations of the method. For, example it cannot be used to approximate the nonlinear response of a complex three-dimensional structural system. Read more
-
Building Load Calculation
1. INTRODUCTION: The structure is a “Multi-storied building” consisting of Two Basement Floors + Stilts Floor + Thirteen upper floors. The 2 basements are used for two-wheeler parking and one stilt floor for four-wheeler parking and all other floors are Residence area. The Structure is designed as a Reinforced concrete framed structure supported on raft Read more
-
Deep Excavations
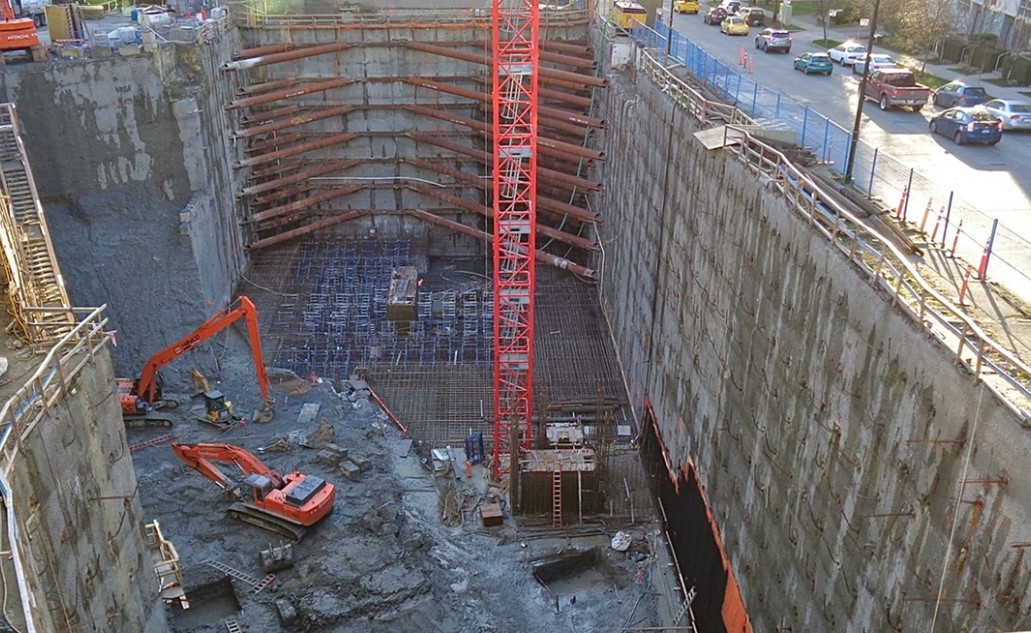

ABSTRACT All major topics in the design of in-situ retaining systems for deep excavations in urban areas are outlined. Type of wall, water related problems and water pressures, lateral earth pressures, type of support, solution to earth retaining walls, types of failure, internal and external stability problems, displacements of walls and adjacent ground, instrumentation Read more
-
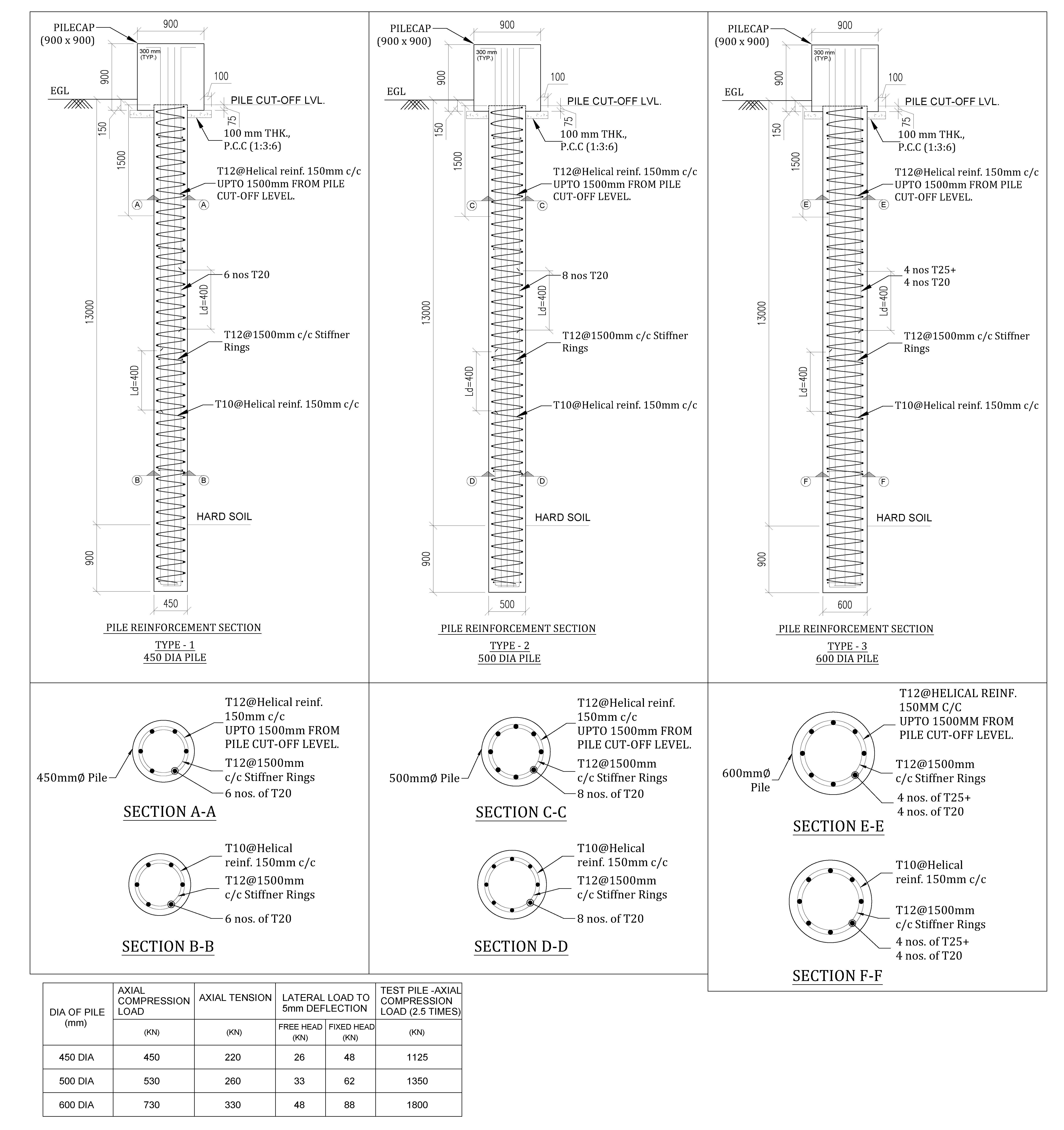
Structural Design of working pile
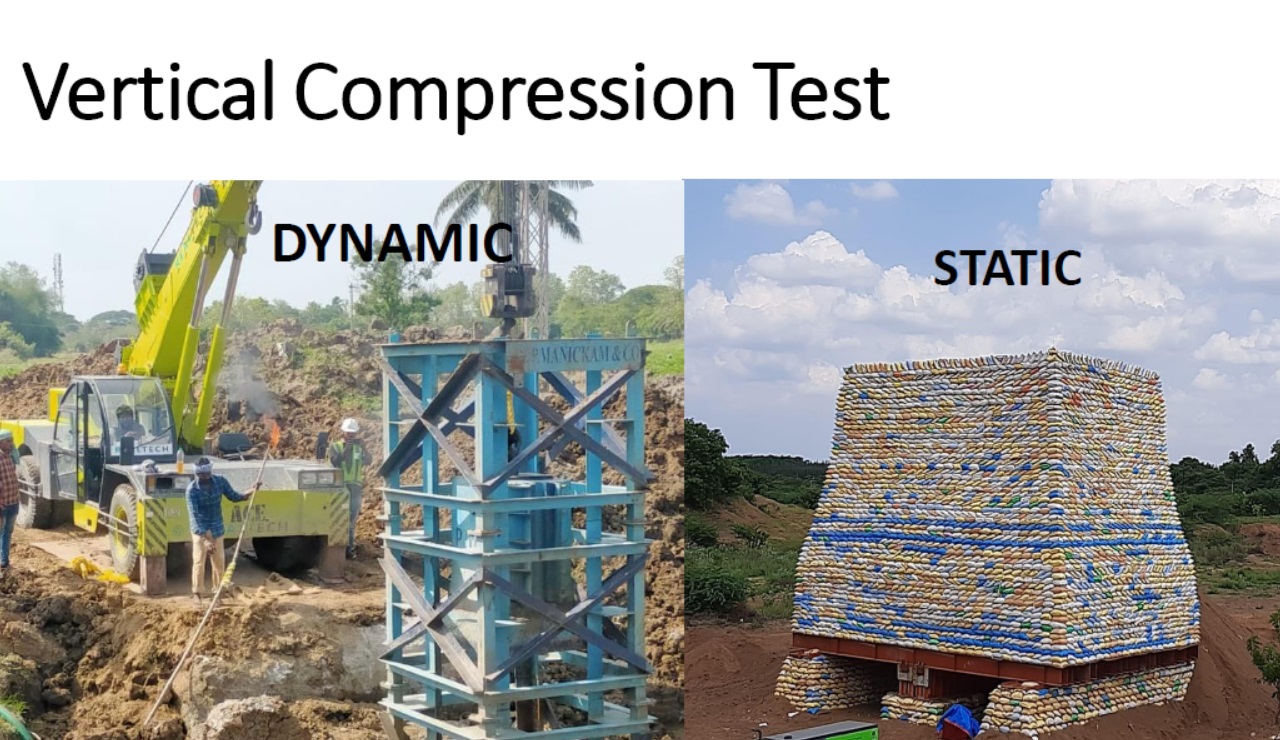
Designing working piles according to IS 2911 (Part 1 to 4) standards involves specific guidelines to ensure the safe and effective construction of piles used as foundations for various types of structures. IS 2911 is the Indian Standard for the design and construction of pile foundations. The standard is divided into multiple parts, each addressing Read more
-
Design of Gantry Girder
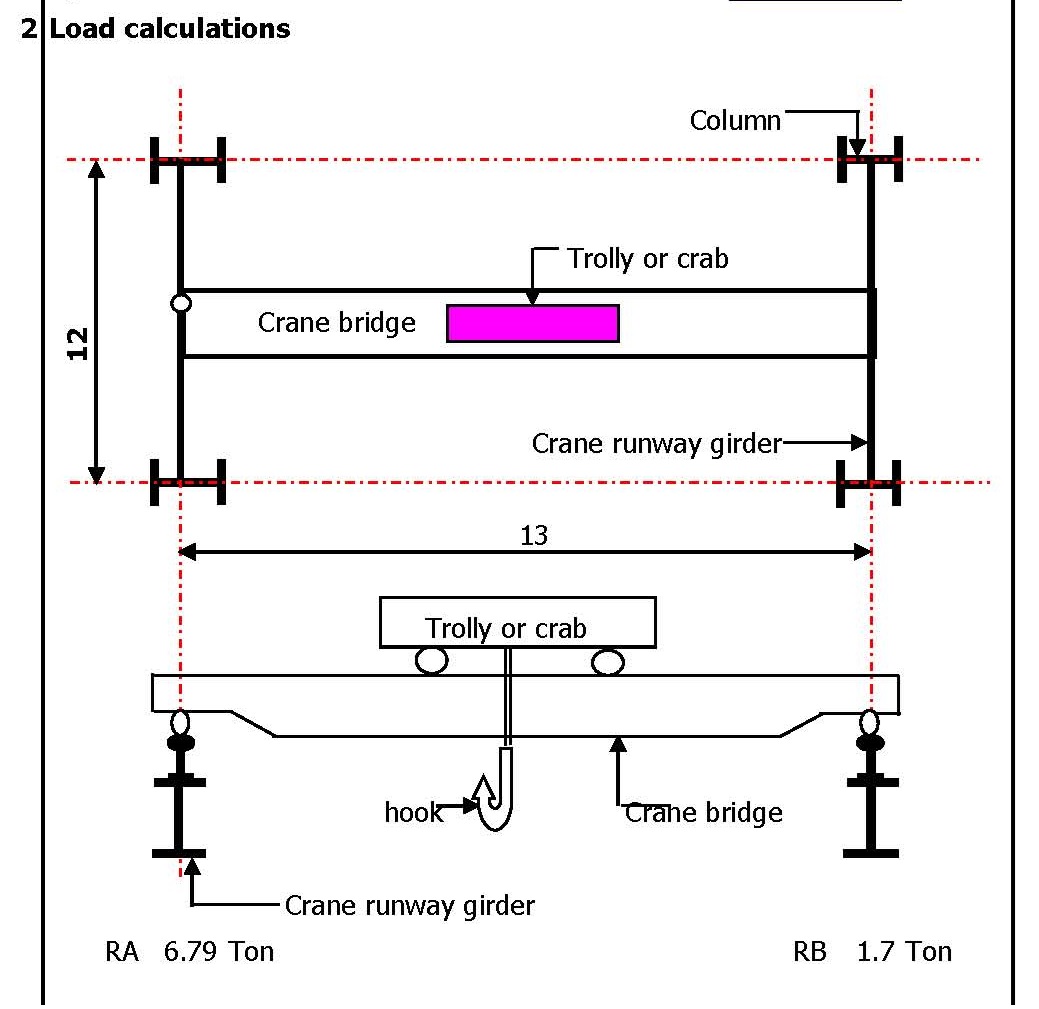
Designing a crane girder, which is a key structural component used in overhead cranes, involves careful consideration of loads, material properties, structural analysis, and adherence to relevant standards and codes. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to design a crane girder Step 1: Determine Design Parameters Step 2: Calculate Loads Step 3: Select Material Step Read more
-
Seismic Load Calculation as per ASCE 7-16
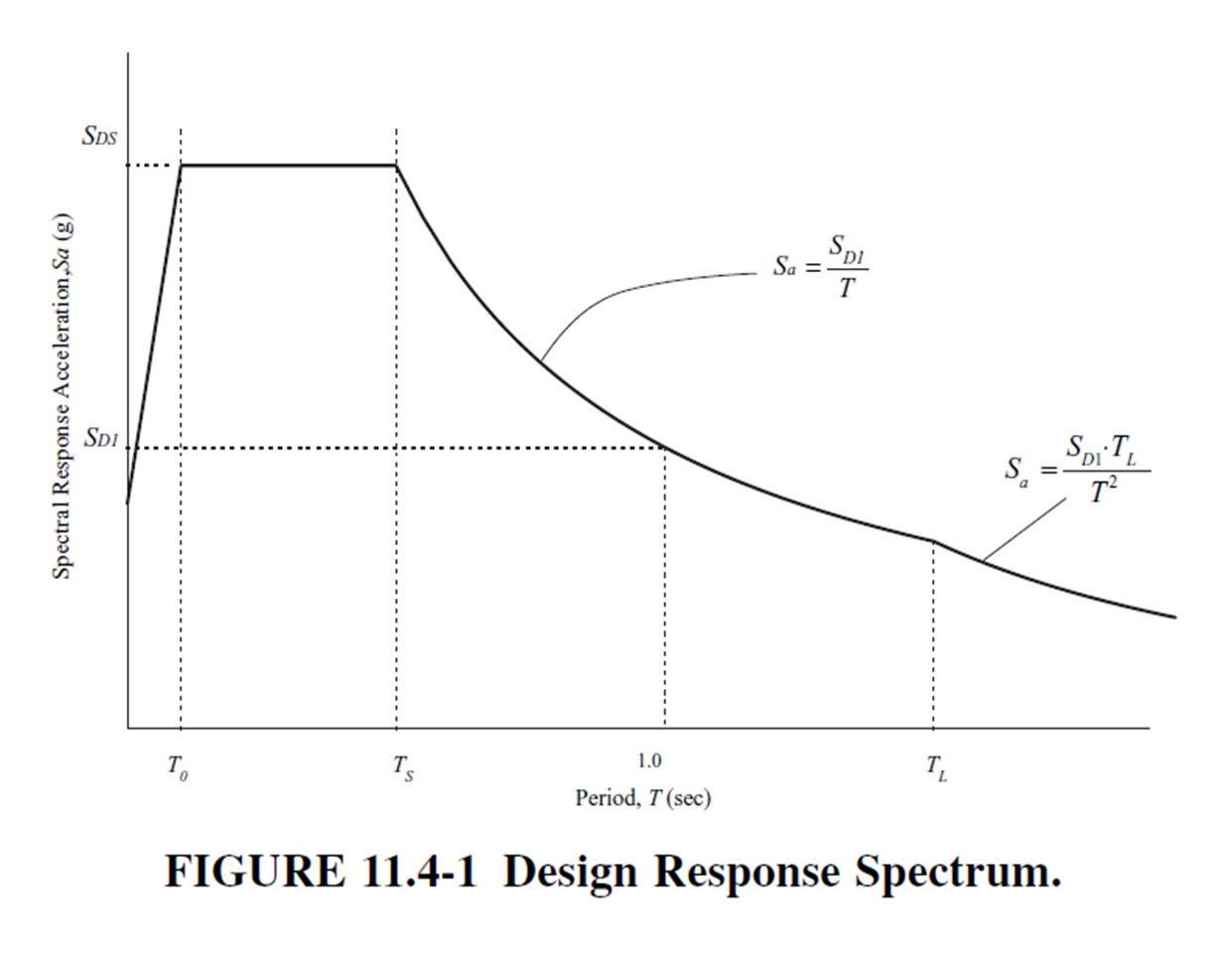
The summary of the process to calculate the Design Spectral Acceleration at Short Periods (SDS) as per AISC 07-16 involves five steps: determining the site class, obtaining mapped spectral acceleration values, determining site coefficients (Fa and Fv), calculating adjusted spectral accelerations, and lastly, calculating the design spectral values (SDS and SD1). These values ensure structures… Read more
-
DESIGN OF WIND PRESSURE AS PER EN 1991-1-4

The calculation for wind load as per EN 1991-1-4 for a gas plant located in a terrain category I includes parameters such as a fundamental basic wind velocity of 32.30 m/s, a directional factor and season factor of 1.00 each, and various terrain factors and roughness lengths. Wind turbulence intensity and peak velocity pressure vary… Read more
-
Trench Details
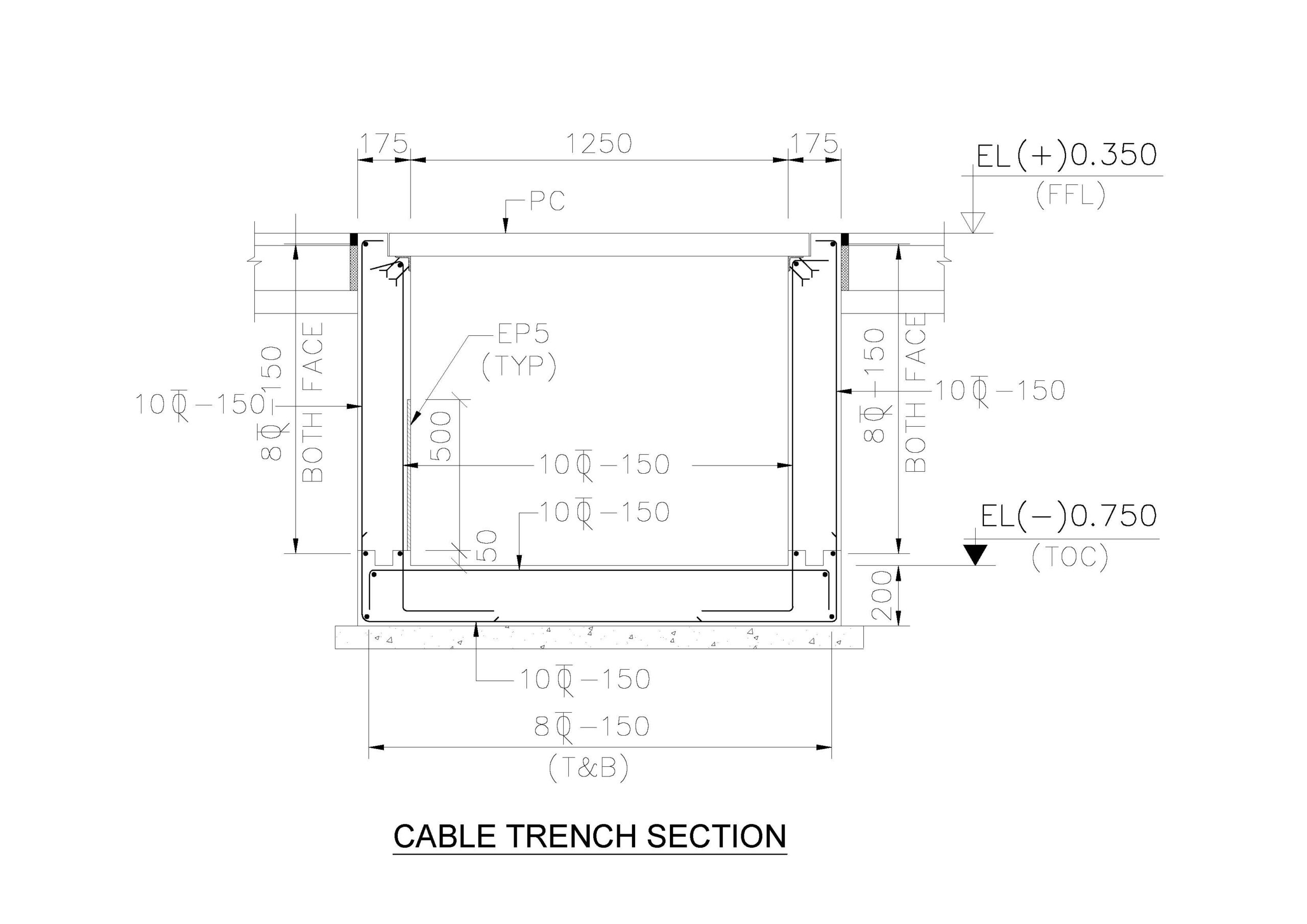
Designing a reinforced concrete (RCC) trench involves several steps to ensure it can handle the intended loads and environmental conditions. Here’s a detailed guide on designing an RCC trench, including structural design considerations, reinforcement details, and construction steps. Key Design Considerations Purpose and Use Dimensions Load Requirements Material Specifications Reinforcement Details Drainage Provisions Construction Steps Read more
-
PRECAST COVER SLAB DETAILS
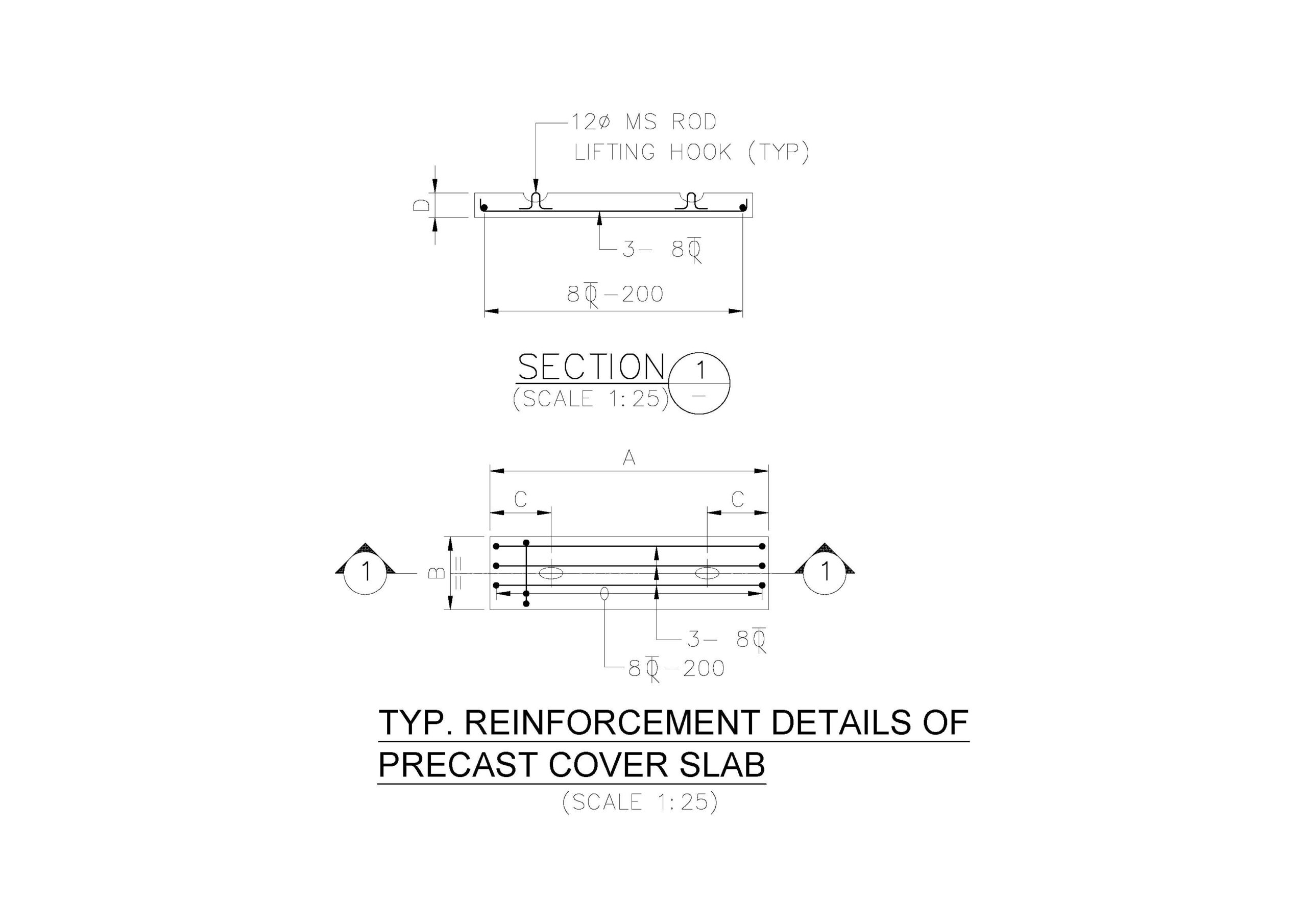
Designing a precast cover slab for a trench involves ensuring the slab can handle expected loads, fits the trench dimensions, and meets relevant safety and durability standards. Below is a detailed guide to designing a precast cover slab for a trench: Key Design Considerations Load Requirements Dimensions Reinforcement Materials Manufacturing Tolerances Handling and Installation Safety Read more
-
Grade Slab Details
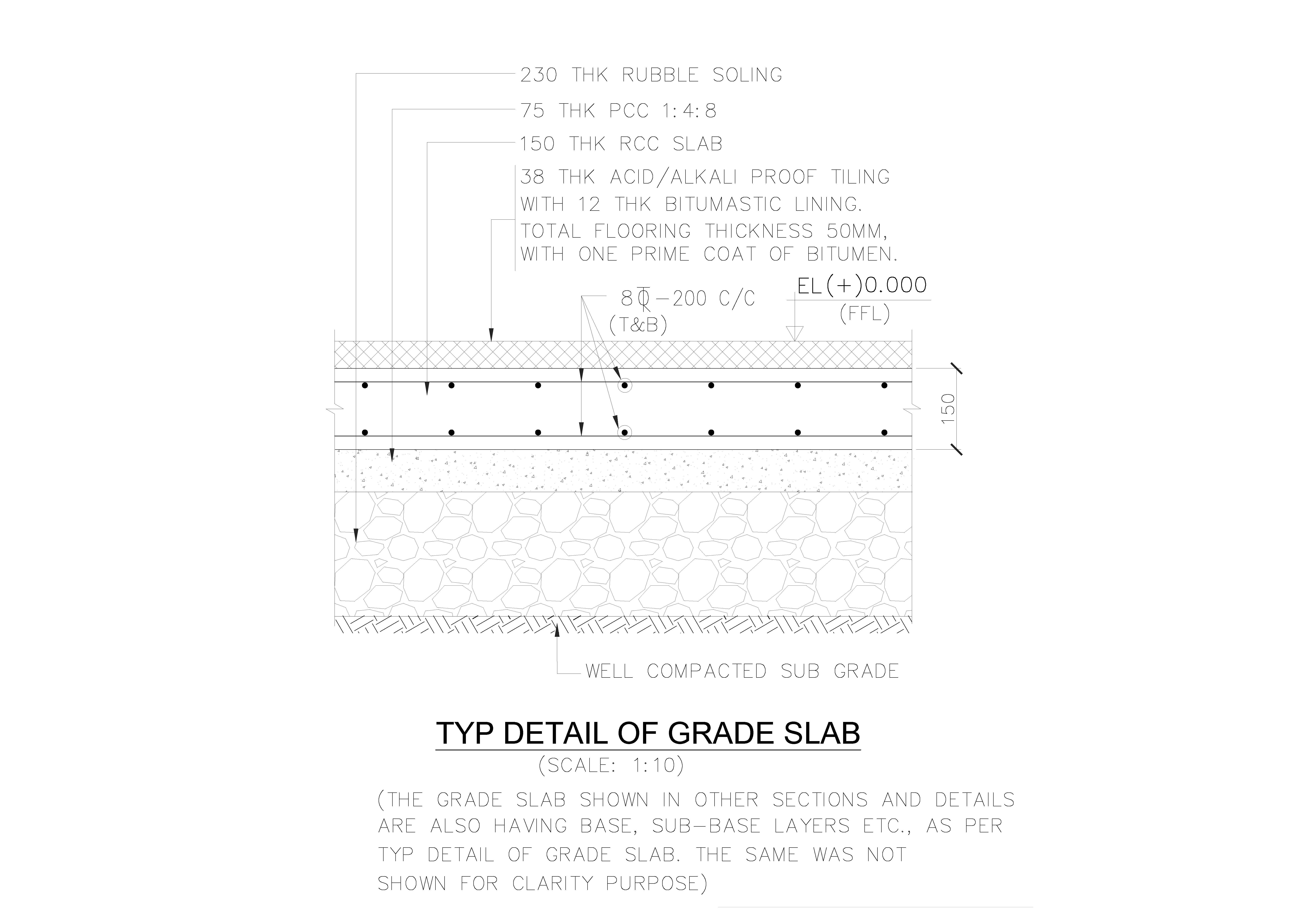
Paving or Grade slab Details A grade slab, also known as a ground-bearing slab, is a type of concrete slab that is directly supported by the ground and typically used as the foundation for buildings and other structures. Here are the details for designing and constructing a grade slab: Components and Structure Subgrade Preparation Read more
-
CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT ARRANGEMENT
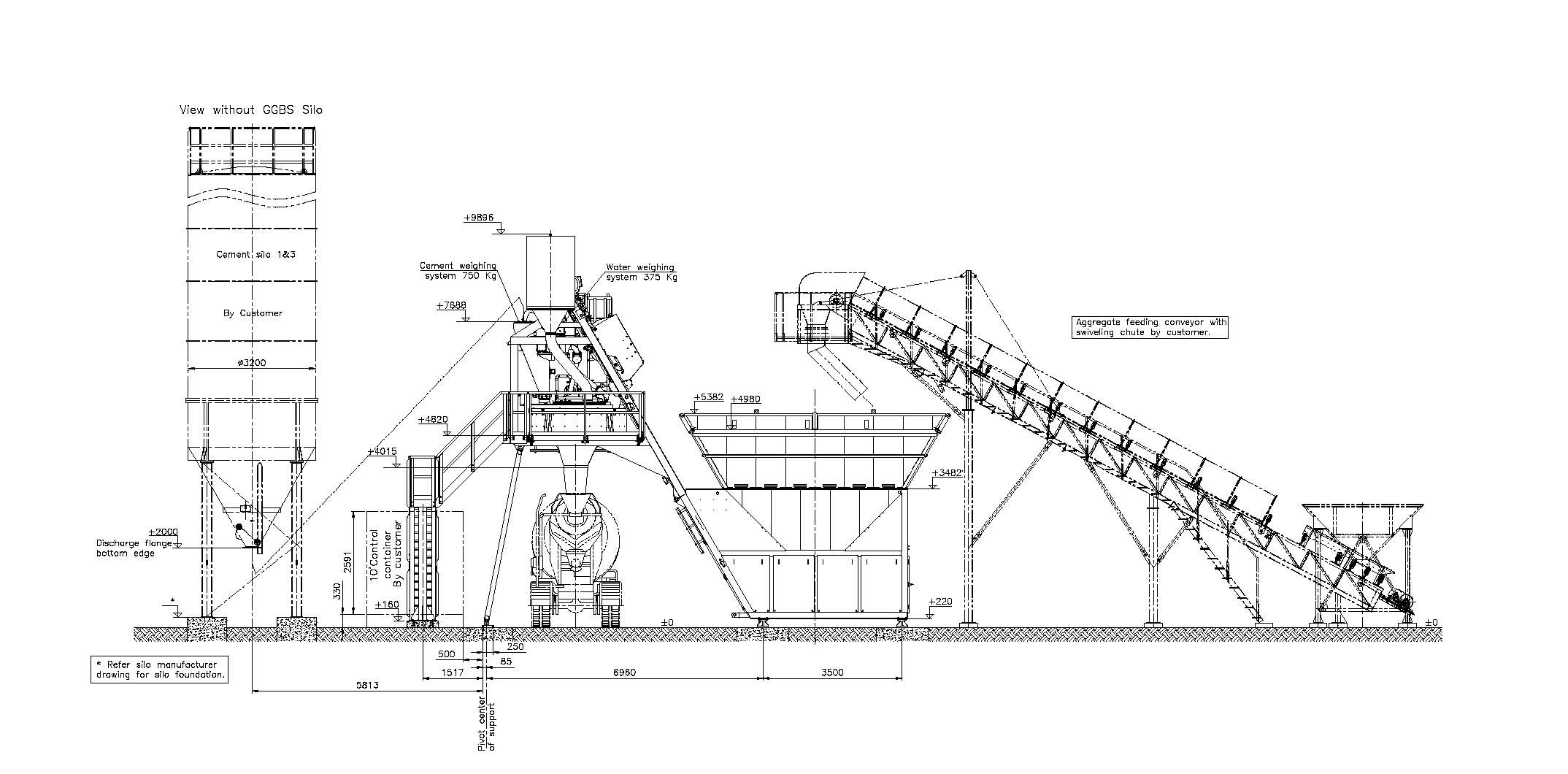
A well-designed batching plant arrangement ensures efficient concrete production, safety, and ease of maintenance. The arrangement typically includes several key components: aggregate storage bins, conveyor belts, cement silos, water and admixture tanks, the mixer, and control systems. Here’s a detailed guide to arranging a batching plant: Key Components of a Batching Plant Aggregate Storage Bins Read more
-
LOAD COMBINATIONS NBCC 2023

LOAD COMBINATIONS CANADIAN CODE NBCC 2023 The National Building Code of Canada (NBCC) 2023 provides updated guidelines for load combinations used in the design of structures. These combinations ensure that buildings can safely withstand various types of loads they may encounter, including dead loads, live loads, wind loads, snow loads, and earthquake loads. Below are Read more
-
STEEL SHED DRAWING
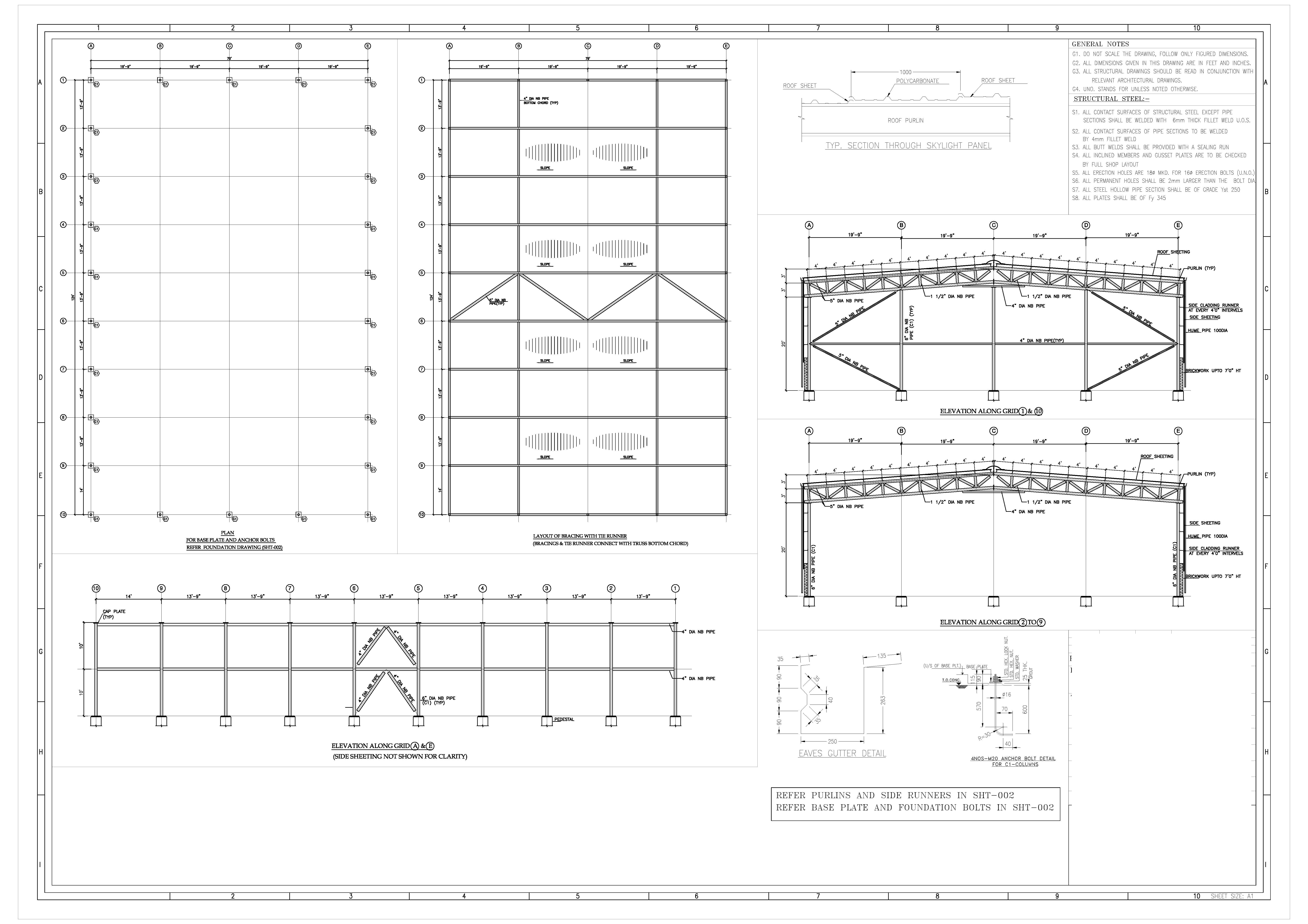
1. Plan View (Top View): Outline of the Shed: Show the overall dimensions of the shed. Columns and Supports: Indicate the positions of steel columns and any internal supports. Doors and Windows: Mark the locations and dimensions of doors and windows. Roof Plan: If the roof has a particular shape (e.g., gable, sloped), indicate the Read more
-
Plumbing Drawing
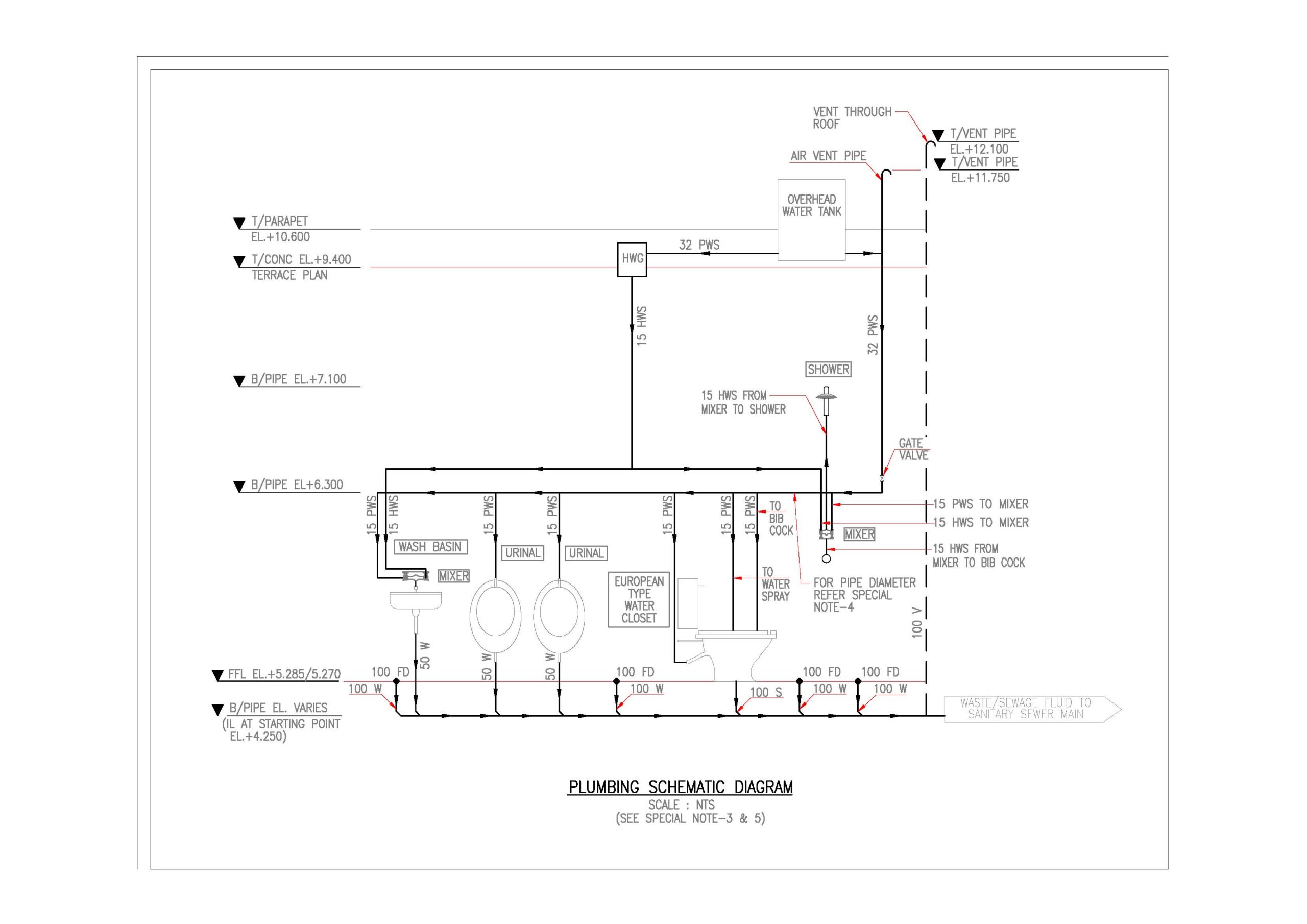
Creating a plumbing scheme drawing involves outlining the entire plumbing system of a building, showing the connections between different fixtures, pipes, valves, and other components. Here are the steps to create a comprehensive plumbing scheme drawing: Steps to Create a Plumbing Scheme Drawing: Gather Building Plans: Obtain architectural plans that include floor layouts, elevations, and Read more
-
Pre Engineered Building Design Specification IS Code
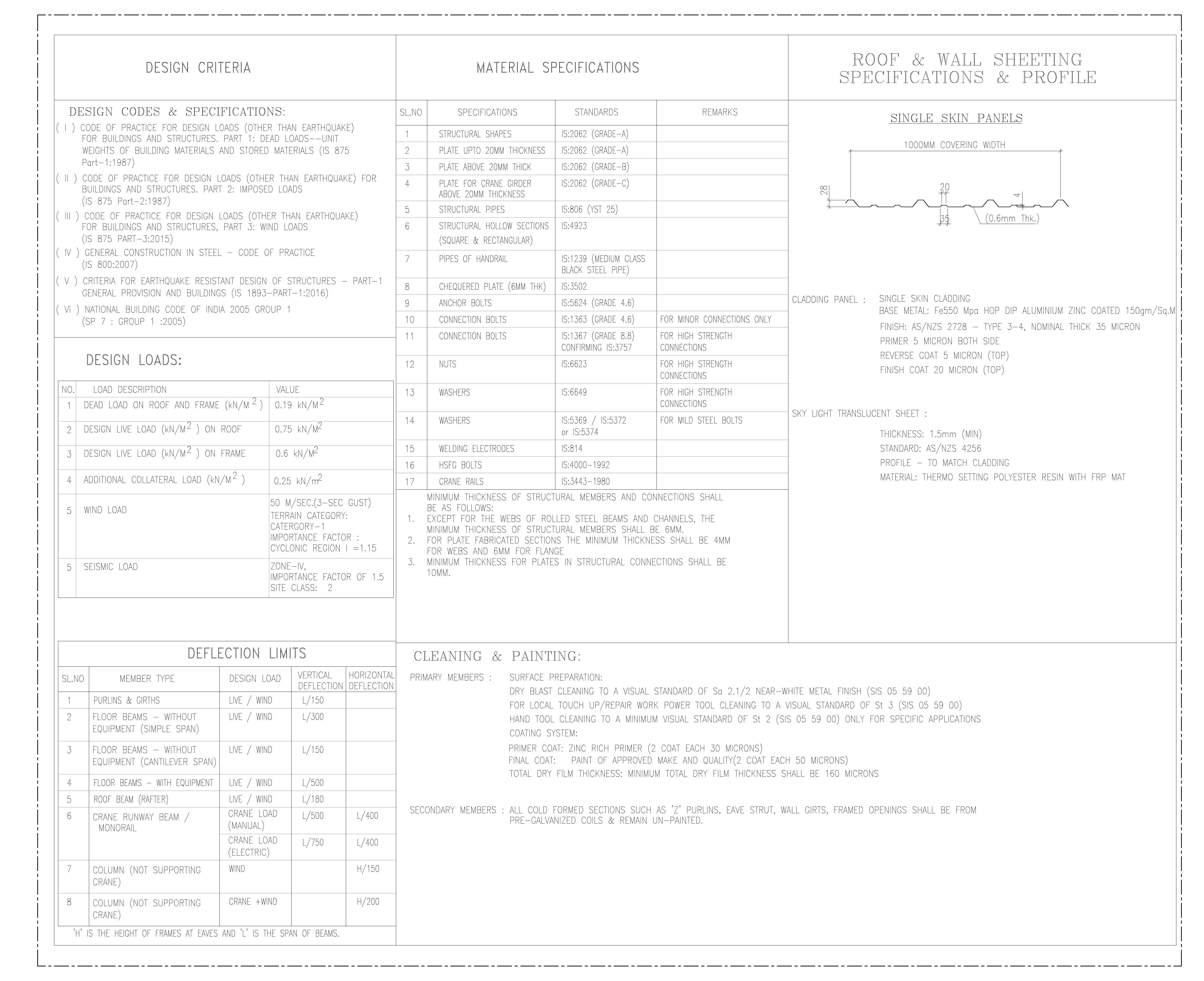
Pre-Engineered Building PEB PEB stands for Pre-Engineered Building. It refers to a building system where components are designed and fabricated in a factory, then transported to the site for assembly. This method is widely used in the construction of industrial buildings, warehouses, commercial complexes, and other structures requiring large open spaces. Key Features of PEB: Read more
-
DESIGN OF PIPERACK STRUCTURE

DESIGN OF PIPERACK STRUCTURE – ASCE 7-10 The length of Pipe rack 42m is considered to avoid forces due to thermal expansion of pipe rack under ambient temperature and free to expand at ends. This is general engineering practice for Pipe rack design with single vertical bracings and mentioned in “Design Specification for Steel Structures” Read more