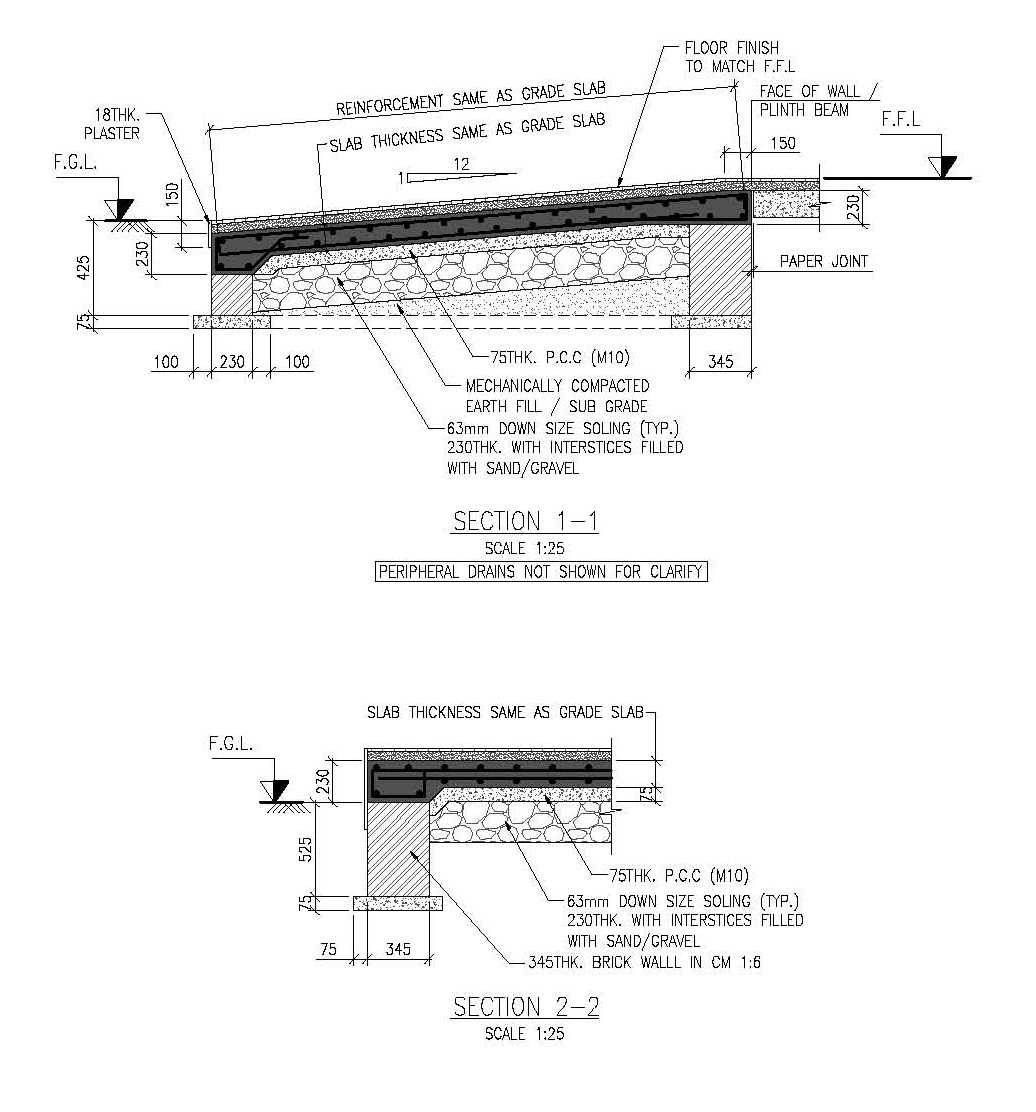
Methods and Details of Ramp Construction
Ramps are inclined surfaces designed to provide smooth access between different levels for pedestrians, vehicles, or equipment. Proper design and construction ensure safety, usability, and durability. Below are the methods and details of ramp construction, categorized by type and purpose:
1. Types of Ramps
- Pedestrian Ramps:
- Used for wheelchair access (e.g., hospitals, public buildings).
- Designed as per accessibility standards like ADA or NBC.
- Vehicle Ramps:
- Used in parking structures, driveways, and industrial facilities.
- Designed to handle vehicular loads.
- Industrial Ramps:
- Used for loading/unloading equipment or materials.
- Typically made of steel or reinforced concrete.
- Temporary Ramps:
- Portable ramps made from lightweight materials like aluminum or wood.
- Common for construction sites or short-term use.


2. Methods of Ramp Construction
a. Cast-In-Situ Concrete Ramps
- Most common method for permanent ramps.
- Steps:
- Excavate and prepare the base with proper compaction.
- Lay formwork along the slope of the ramp.
- Provide reinforcement as per design.
- Pour concrete in layers and compact it.
- Add a non-slip finish to the surface (broom finish or stamped concrete).
b. Precast Concrete Ramps
- Precast panels are manufactured off-site and assembled on-site.
- Suitable for modular and quick construction projects.
- Joints are sealed with grouts or flexible sealants.
c. Steel Ramps
- Common in industrial applications.
- Fabricated from structural steel with anti-slip gratings.
- Installed by welding or bolting onto supports.
d. Asphalt Ramps
- Used for roadways, driveways, and parking areas.
- Steps:
- Prepare a compacted base layer.
- Lay and compact asphalt layers using a paver machine.
- Ensure proper slope and drainage.
e. Wooden or Aluminum Ramps
- Lightweight ramps for temporary or residential applications.
- Prefabricated and installed with screws or bolts.
3. Key Design Details
a. Slope:
- Maximum slope depends on the purpose:
- Pedestrian ramps: 1:12 (8.33%) (as per ADA/NBC).
- Vehicle ramps: 1:10 (10%) or 1:8 (12.5%) for parking structures.
- Industrial ramps: Up to 1:6 (16.67%) for forklifts.
b. Width:
- Minimum width depends on the type:
- Pedestrian ramps: Minimum 1.2 m (as per ADA/NBC).
- Vehicle ramps: Varies based on the number of lanes (typically 3–6 m).
c. Landing:
- Provide level landings at the top and bottom of the ramp.
- Minimum length: 1.5 m for pedestrian ramps.
- For long ramps, provide intermediate landings every 9 m.
d. Surface Finish:
- Anti-slip surfaces are mandatory:
- Concrete ramps: Broom finish or textured coating.
- Steel ramps: Serrated treads or anti-slip grating.
- Asphalt ramps: Add friction additives.
e. Handrails and Edge Protection:
- Handrails for pedestrian ramps:
- Height: 850–1000 mm.
- Continuous along the ramp.
- Curbs or barriers to prevent wheelchairs or vehicles from falling off.
f. Drainage:
- Provide proper drainage to prevent water accumulation.
- Install drains at the base or along the edges.
4. Construction Steps
- Site Preparation:
- Clear and level the area.
- Excavate and compact the base.
- Lay a sub-base material (e.g., crushed stone) for stability.
- Formwork:
- Use timber or steel forms to define the slope and edges.
- Ensure the forms are well-secured to avoid movement during concreting.
- Reinforcement:
- Provide mesh or bars as per design.
- Typical reinforcement: 10–12 mm bars at 150–200 mm c/c.
- Concrete Pouring:
- Pour concrete starting from the lower end.
- Use vibrators to ensure compaction.
- Allow curing for at least 7–14 days.
- Finishing:
- Provide the required texture (e.g., broom finish).
- Install anti-skid strips or coatings if necessary.
- Final Installation:
- Add railings, barriers, or curbs as required.
- Paint markings for safety or aesthetic purposes.
5. Materials Used
- Concrete: M25 or higher grade.
- Steel Reinforcement: Fe 500.
- Formwork: Steel, plywood, or aluminum.
- Anti-Slip Coating: Epoxy or polymer-based finishes.
- Handrails: Stainless steel or powder-coated steel.
6. Maintenance
- Regular Inspection:
- Check for cracks, surface wear, or corrosion in steel components.
- Cleaning:
- Remove dirt, debris, or moss for pedestrian ramps.
- Surface Repair:
- Resurface damaged or worn-out sections.
- Repainting:
- Apply fresh anti-slip coating or markings as needed.
Standards and Codes
- IS 456:2000: General concrete design.
- NBC (National Building Code of India): Ramp design guidelines.
- ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act): Accessibility standards.
- OSHA 1910: Ramp safety in industrial applications.
- 3D HOUSE DESIGN (35)
- Civil and Structural Design Calculations (76)
- Commercial Plans (9)
- East Facing House Plans (14)
- Engineering Concepts – Civil & Structural (226)
- Excel Spreadsheets (37)
- Free Downloads (49)
- House Plans (57)
- Industrial standards (92)
- North Facing House Plans (15)
- South Facing House Plans (15)
- West Facing House Plans (9)
Related Posts: