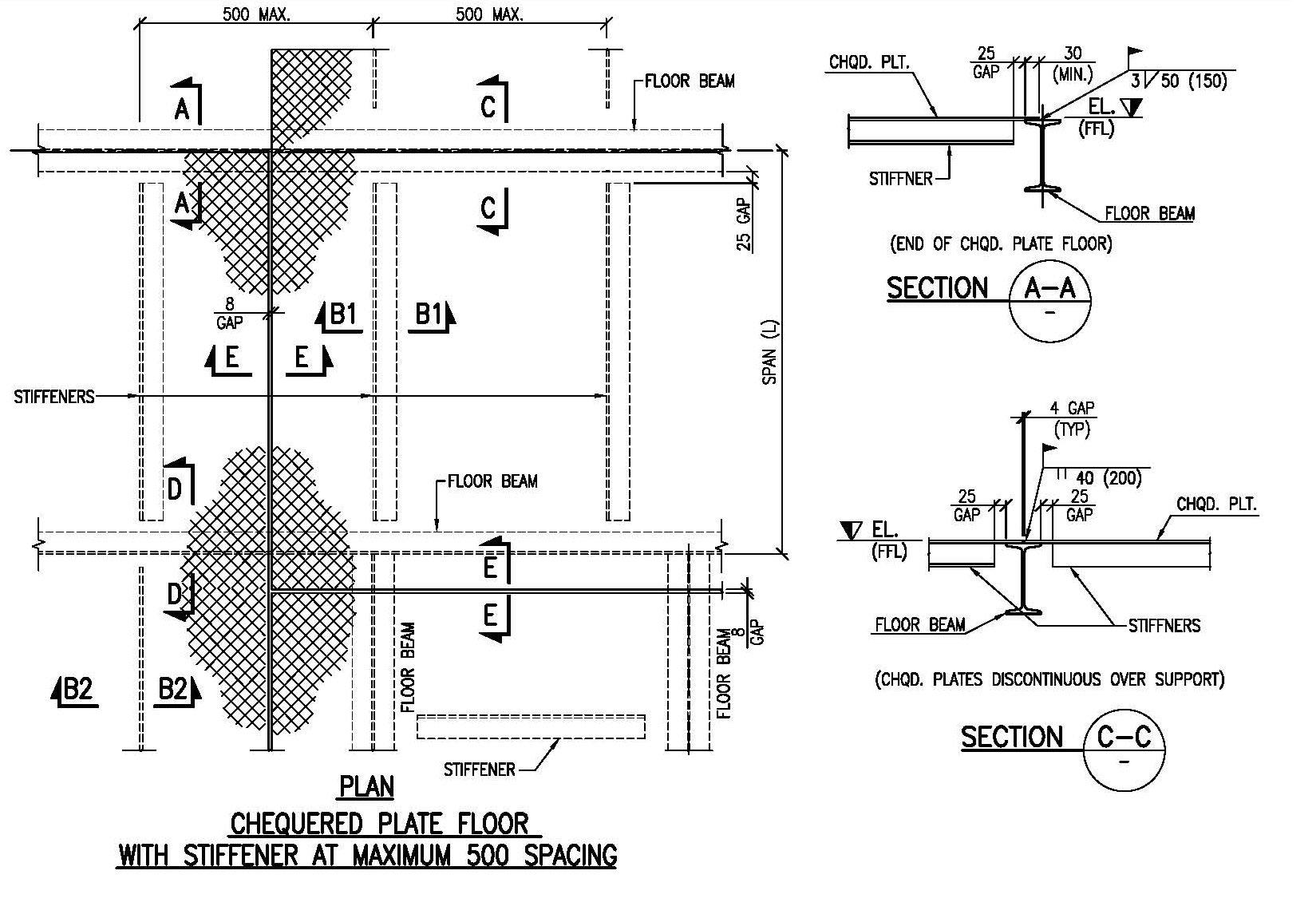
Chequered Plate Standard Details
A chequered plate (also known as a checker plate, tread plate, or diamond plate) is a steel or aluminum plate with a raised pattern for slip resistance and durability. It is widely used in industrial flooring, stair treads, ramps, walkways, and vehicle platforms.
1. Purpose & Benefits of Chequered Plates
✔️ Slip-resistant surface for safety in wet or oily conditions.
✔️ Durable and strong for heavy-duty applications.
✔️ Corrosion-resistant (especially stainless steel & aluminum variants).
✔️ Aesthetic appeal for decorative and architectural use.
✔️ Easy maintenance and long service life.
2. Standard Specifications for Chequered Plates
a. Common Standards for Chequered Plates
| Standard | Region | Material Grades |
|---|---|---|
| IS 3502 | India | Mild Steel (MS) |
| ASTM A786 | USA | Carbon Steel |
| EN 10025-2 | Europe | Structural Steel (S235JR, S275JR) |
| BS 1449 | UK | Stainless Steel |
| JIS G3193 | Japan | Hot-Rolled Steel |
| AS/NZS 3678 | Australia | Steel Plates for Structural Use |
b. Standard Chequered Plate Thickness & Weight
| Thickness (mm) | Weight (kg/m²) – MS | Weight (kg/m²) – SS |
|---|---|---|
| 2.0 | 16.3 | 15.7 |
| 3.0 | 23.5 | 22.5 |
| 4.5 | 34.2 | 32.8 |
| 6.0 | 45.9 | 44.1 |
| 8.0 | 61.2 | 58.8 |
| 10.0 | 76.5 | 73.5 |
Note: Weight varies by material type and pattern depth.
3. Chequered Plate Materials & Applications
| Material | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel (MS) | Cost-effective, strong | Industrial flooring, stair treads |
| Stainless Steel (SS 304/316) | Corrosion-resistant, aesthetic | Marine, food industry, hospitals |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, rustproof | Vehicle ramps, decorative panels |
| Galvanized Steel | Corrosion-resistant, heavy-duty | Outdoor platforms, scaffolding |








4. Common Patterns & Surface Types
a. Types of Patterns
- 5-Bar Pattern – Most common for anti-slip surfaces.
- Diamond Pattern – Provides aesthetic appeal and grip.
- Lentil Pattern – Used in architectural applications.
- Round Studs – High grip for vehicle flooring.
b. Surface Finishes
- Hot-Rolled (HR) – Strong, industrial-grade finish.
- Cold-Rolled (CR) – Smoother, precise dimensions.
- Brushed or Polished – Used for stainless steel or decorative use.
5. Manufacturing Process of Chequered Plates
- Hot Rolling – Steel plates are heated and rolled to the required thickness.
- Pattern Rolling – Raised patterns are added using rollers.
- Cutting & Finishing – Plates are cut into standard or custom sizes.
- Coating (Optional) – Galvanization or powder coating for corrosion resistance.
6. Applications of Chequered Plates
✔ Industrial Flooring – Anti-slip surfaces in factories.
✔ Stair Treads & Ramps – For safe footing in staircases and walkways.
✔ Vehicle Flooring – Truck beds, trailer floors, bus steps.
✔ Marine & Offshore Platforms – Corrosion-resistant surfaces for docks and ships.
✔ Railway Stations & Bridges – High-strength flooring for public spaces.
✔ Decorative & Architectural Use – Wall panels, partitions, and facades.
7. Installation & Maintenance
a. Fixing Methods
- Welding – For permanent installations.
- Bolting – For removable and replaceable flooring.
- Adhesive Bonding – For lightweight applications.
b. Maintenance Tips
- Regular cleaning to remove dirt and debris.
- Anti-rust coatings for steel chequered plates.
- Periodic inspection for wear and tear in high-traffic areas.
8. Conclusion
Chequered plates are essential for safety and durability in industrial and commercial applications. By choosing the right material, thickness, and pattern, they can enhance flooring strength, aesthetics, and corrosion resistance.
- Octagonal Foundation Reinforcement Details
- Design of Pump Foundation Dynamic and Static Analysis
- Electrical Layout For Residential Building
- Rain Water Gutter and Down Take Systems
- Stormwater Drainage Calculation
- Structural Engineering Design Criteria – American Codes and Standards
- Insert Plate Details & Drawing – Embedded in Concrete Structures
- Anchor Bolt Details and Drawing – Embedded in Concrete
- Staircase Layout and Details
- Guard House Layout and Details
- Pump Shed Structural Steel Drawing
- Column Buckling
- Moody Chart | Moment Reactions for Rectangular Plates |
- Standard Road Details
- DG Building Architectural Plan & Finishing Schedule
- Technical Details for Wash Basin Section and Elevation
- Tender Technical Specification for Plumbing and Sanitary works
- Fencing Gate Details and Requirements
- Fencing Layout and Details For Transformer Area
- Fencing with Angle Post and Pipe Post Details & Arrangements
- Civil Engineering Formula Book | Pocket Guide pdf Free download |
- Transformer Foundation with Soak Pit Layout and Details
- Grating Standard Details and Specifications
- Chequered Plate Standard Details
- Handrail Details for Steel Structural Floors
- Cable Pull Pit Requirements and Details
- Laboratory Building Plan and Architecture Details
- Structural Bolt Details Types Grades and Applications
- Finishing Schedule Drawing for Doors, Windows, and Rolling Shutters
- Workshop Building Architectural Layout
- Calculation of Foundation Bearing Capacity as per IS 6403 – 1981
- Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity Calculation For Foundations
- DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHOD OF MULTISTORY CONCRETE BUILDINGS
- Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions pdf Free Download
- Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions
- SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT DIAGRAMS WITH FORMULA
- Weathering Course in RCC Roof
- Rolling Shutter Fixing Detail with RCC Beam
- Duct Bank Details and Pipe Sleeves Details
- Handrail Details | Construction Methods and Types of Handrail |
- Details of Ramp
- Design Calculation of Steel Shelter – AISC 360
- Cage Ladder Specification and Detail Drawing
- Concrete Beam Design as per Canadian Code (CSA A23.3-19)
- Fencing Detail Drawing
- RCC Fencing Post Details
- Gypsum Board False Ceiling Installation
- Design of Anchor Reinforcement in Concrete Pedestals
- Wind Load Calculation as per IS 875 Part 3 2015
- DESIGN BASIS FOR CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL