To calculate wind load as per the National Building Code of Canada (NBCC) 2020, the following steps summarize the process:
1. Reference Code and Formula
Wind load calculation is governed by NBC 2020, specifically the provisions in Part 4, Section 4.1.7 (Wind Loads).
The wind pressure (q) is calculated using:
q=Iw⋅Ce⋅Cg⋅Cp⋅p
Where:
- Iw: Importance factor for wind (from NBC Table 4.1.7.1)
- Ce: Exposure factor (depends on terrain, height, and location)
- Cg: Gust effect factor
- Cp: Pressure coefficient (varies with structure shape)
- p: Reference wind pressure (in Pascals)

2. Steps to Calculate Wind Load
Step 1: Determine Basic Wind Pressure (p)
- Obtain the reference wind velocity (V) from NBC climatic data maps.
- Calculate p using: p=0.613⋅V2(in Pascals)
- Where V is the basic wind speed in m/s.
Step 2: Apply Importance Factor (Iw)
- Based on the building category (e.g., residential, industrial), choose the Importance Factor (Iw) from NBC Table 4.1.7.1.
Step 3: Find the Exposure Factor (Ce)
- Select Ce based on terrain category, building height, and other local factors from NBC Table 4.1.7.4.
Step 4: Calculate Gust Factor (Cg)
- Gust factor (Cg) depends on structural flexibility and can generally range from 0.85 to 1.0 for standard buildings.
Step 5: Pressure Coefficient (Cp)
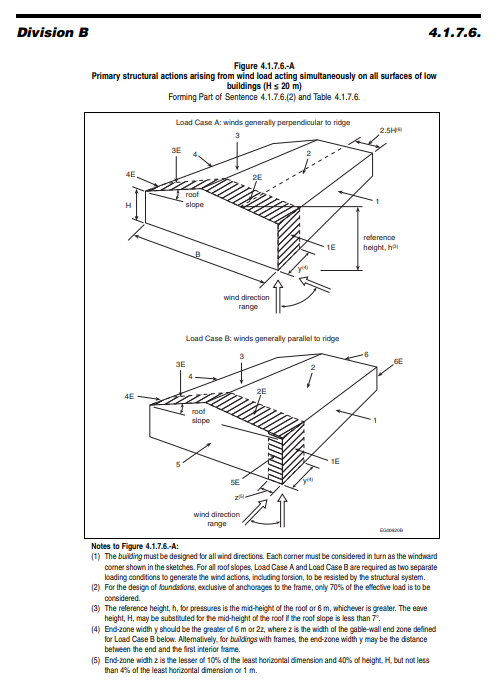
- Obtain the pressure coefficient (Cp) from NBC Figure 4.1.7.6 based on the shape and orientation of the structure.
3. Total Wind Force
The wind force on a surface is given by:
F=q⋅A⋅Cd
Where:
- A: Projected area of the structure (in m²)
- Cd: Drag coefficient (specific to the structure and available in NBC charts)
Example (Hypothetical Calculation):
- Basic wind speed (V): 40 m/s
- Reference wind pressure (p):
p=0.613⋅402 =980Pa
- Assume factors:
- Iw=1.0
- Ce=1.2
- Cg=0.85
- Cp=1.3
- Wind pressure (q):
q=1.0⋅1.2⋅0.85⋅1.3⋅980=1297.8 Pa
- For an area of A=20 m2 the total wind load:
F=1297.8⋅20=25,956 N (25.96 kN)
Notes:
- Always verify site-specific parameters like terrain roughness and local wind speed.
- For complex structures, use wind tunnel testing or CFD analysis for precise calculations.
Let me know if you’d like help with a specific example or additional details!
Wind Load Calculation for a Shelter as per Canadian Code (NBC 2020)
This guide provides a step-by-step example for calculating wind loads for a shelter using the National Building Code of Canada (NBC 2020). The focus will be on Part 4, Section 4.1.7 (Wind Loads).
2. Example Parameters
Assume the following shelter dimensions and site-specific values:
- Shelter Size:
- Width = 10 m
- Length = 20 m
- Height = 5 m
- Site Information:
- Basic wind speed (V): 35 m/s (from NBC climatic maps)
- Terrain Category: Open terrain (Category II)

- Factors:
- Iw=1.0 (standard importance for shelters)
- Ce=1.1 (exposure factor from NBC Table 4.1.7.4)
- Cg=0.85 (gust factor for typical rigid structures)
- Cp=1.3 (pressure coefficient for walls, per NBC Table 4.1.7.6)
3. Step-by-Step Calculation
Step 1: Determine Reference Wind Pressure (p)
The reference wind pressure is calculated using:
p=0.613⋅V2
Substitute V=35 m/s
p=0.613⋅352 = 750.4 Pa

Step 2: Calculate Total Wind Pressure (q)
Using the wind pressure formula:
q=Iw⋅Ce⋅Cg⋅Cp⋅p
Substitute values:
q=1.0⋅1.1⋅0.85⋅1.3⋅750.4
Step 3: Calculate Wind Load (F)
The total wind force is:
F = q ⋅ A
Where:
A=Projected Area of the Shelter

For the windward wall:
A=Width × Height=10 m×5 m=50 m2
F=913.1 Pa⋅50 m2=45,655 N (45.66 kN)
For the leeward wall, use Cp=0.8:
qleeward=1.0⋅1.1⋅0.85⋅0.8⋅750.4=561.3 Pa
qleeward=561.3⋅50=28,065 N (28.07 kN)
4. Total Wind Load on the Shelter
To account for net forces, add windward and subtract leeward pressures, considering their directions. Include roof uplift forces if applicable.
5. Design Checks
- Ensure shelter anchorage and structural members can resist calculated forces.
- For irregular shapes or significant flexibility, consider advanced wind modeling or CFD analysis.
Let me know if you need further assistance with detailed steps or other code provisions!
- 3D HOUSE DESIGN (34)
- Civil and Structural Design Calculations (76)
- Commercial Plans (9)
- East Facing House Plans (14)
- Engineering Concepts – Civil & Structural (224)
- Excel Spreadsheets (37)
- Free Downloads (49)
- House Plans (57)
- Industrial standards (91)
- North Facing House Plans (15)
- South Facing House Plans (15)
- West Facing House Plans (9)