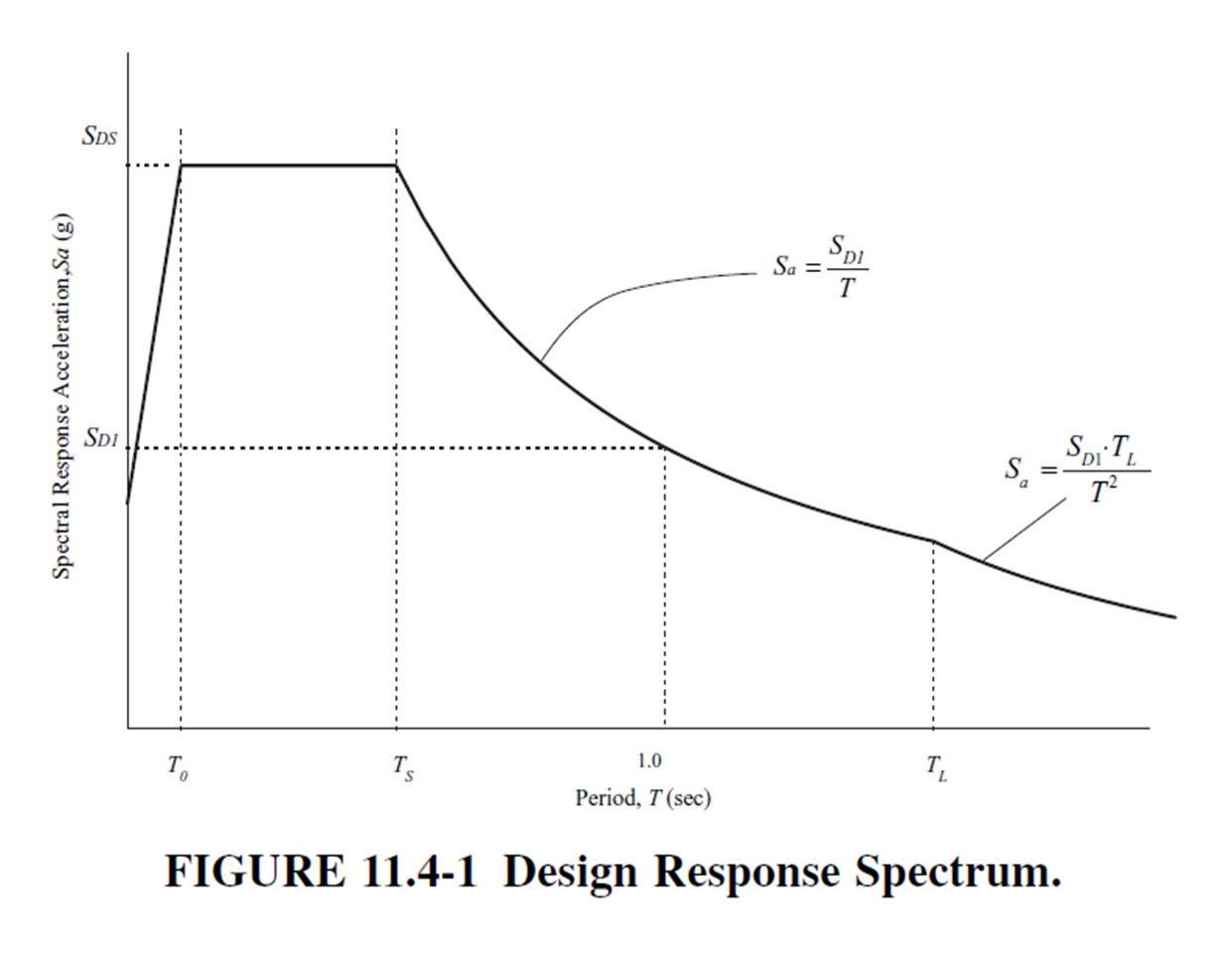
Calculating the design spectral acceleration at short periods (SDS) as per the AISC 07-16 (American Institute of Steel Construction) involves several steps, including understanding and applying provisions from the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) 7-16. Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculate SDS:
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Determine the Site Class
Site class is based on the soil properties at the site. It ranges from A (hard rock) to F (special soil). The site class can be determined through geotechnical investigations or predefined values based on soil type and seismicity.
2. Obtain the Mapped Spectral Acceleration Values
The mapped spectral acceleration values are typically provided by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) or local building codes. You need two values:
- SS: The mapped spectral acceleration for short periods (0.2 seconds).
- S1: The mapped spectral acceleration for 1-second periods.
These values can be found using the USGS Seismic Design Maps Tool or local building codes.
3. Determine the Site Coefficients (Fa and Fv)
Site coefficients Fa and Fv modify the spectral acceleration values based on the site class. They are provided in tables within the ASCE 7-16 code. Fa is used for SS, and Fv is used for S1.
4. Calculate the Adjusted Spectral Acceleration Values
Adjust the spectral acceleration values using the site coefficients:
- SMS=Fa×SSSMS = Fa \times SSSMS=Fa×SS
- SM1=Fv×S1SM1 = Fv \times S1SM1=Fv×S1
Where:
- SMSSMSSMS = Site-modified spectral acceleration for short periods.
- SM1SM1SM1 = Site-modified spectral acceleration for 1-second periods.
5. Calculate the Design Spectral Acceleration Values
The design spectral acceleration values are calculated by reducing the adjusted values:
- SDS=23×SMSSDS = \frac{2}{3} \times SMSSDS=32×SMS
- SD1=23×SM1SD1 = \frac{2}{3} \times SM1SD1=32×SM1
Where:
- SDSSDSSDS = Design spectral acceleration at short periods.
- SD1SD1SD1 = Design spectral acceleration at 1-second periods.
Example Calculation
Given:
- Site Class: D
- SS: 1.0g (mapped spectral acceleration for short periods)
- S1: 0.4g (mapped spectral acceleration for 1-second periods)
1. Determine Site Coefficients (From ASCE 7-16 Tables):
For Site Class D:
- Fa: 1.2 (for SS = 1.0g)
- Fv: 1.6 (for S1 = 0.4g)
2. Calculate Adjusted Spectral Accelerations:
- SMS= Fa × SS
- SMS=1.2×1.0g=1.2g
- SM1=Fv×S1
- SM1=1.6×0.4g=0.64g
3. Calculate Design Spectral Accelerations:
- SDS=2/3×SMS
- SDS=2/3×1.2g=0.8g
- SDS=2/3×SM1
- SDS=2/3×0.64g=0.427g
Summary
- SDS (Design spectral acceleration at short periods) = 0.8g
- SD1 (Design spectral acceleration at 1-second periods) = 0.427g
These values are used in the seismic design and analysis of structures to ensure they can withstand anticipated earthquake forces as per AISC 07-16 standards.
Symbols
Cs = The seismic response coefficient
W = The effective seismic weight
SDS = The design spectral response acceleration parameter in the short period range
R = The response modification factor in Table 12.2-1
Ie = The Importance Factor
SD1 = the design spectral response acceleration parameter at a period of 1.0 s
T = The fundamental period of the structure(s)
TL = The long-period transition period(s)
S1 = The mapped maximum considered earthquake spectral response acceleration parameter
The base shear force is calculated by the above equation. The mass and Cs used in this calculation and the base shear force determined as a result of the calculation are tabulated in the Dynamic Analysis report.
The seismic response coefficient, Cs, is determined by the following equation.
The value of Cs computed with Eq. (12.8-2) need not exceed the following:
for T ≤ TL
for T > TL
Cs should not be less than
Structures located where S1 ≥ 0.6g, Cs shall not be less than
Recent Posts
- Electrical Layout For Residential Building
- HOUSE PLAN 29 X 56 | SOUTH FACING |
- Rain Water Gutter and Down Take Systems
- Stormwater Drainage Calculation
- Structural Engineering Design Criteria – American Codes and Standards
- Anchor Bolts Length as per ACI 318-14
- Insert Plate Details & Drawing – Embedded in Concrete Structures
- JOURNAL PAPER GUIDELINES FOR ACSE
- Anchor Bolt Details and Drawing – Embedded in Concrete
- Staircase Layout and Details
- Guard House Layout and Details
- Pump Shed Structural Steel Drawing
- ASCE 7-16 Wind Load on Buildings and Structures
- Column Buckling
- Moody Chart | Moment Reactions for Rectangular Plates |
- Test Pile Drawing Calculation & Guidelines
- Commercial Shop Plan
- Shop Floor Plan
- HOUSE PLAN WITH SHOP 40 x 60 | SOUTH FACING |
- Wind Load Calculation as per Australian Code (AS/NZS 1170.2:2021)
- HOUSE PLAN 30 X 45 | EAST FACING | INTERIOR HOUSE DESIGN |
- HOUSE PLAN 60 x 40 | EAST FACING | APARTMENT TYPE |
- Standard Road Details
- DG Building Architectural Plan & Finishing Schedule
- AMAZING TV UNIT IDEAS 90+ MODELS
- HOUSE PLAN 60 x 50 | EAST FACING |
- Technical Details for Wash Basin Section and Elevation
- Tender Technical Specification for Plumbing and Sanitary works
- HOUSE PLAN 25 x 50 | SOUTH FACING |
- HOUSE PLAN 60 x 45 | SOUTH FACING |
- Fencing Gate Details and Requirements
- Fencing Layout and Details For Transformer Area
- Fencing with Angle Post and Pipe Post Details & Arrangements
- Civil Engineering Formula Book | Pocket Guide pdf Free download |
- HOUSE PLAN 35 x 60 | WEST FACING |
- Transformer Foundation with Soak Pit Layout and Details
- Grating Standard Details and Specifications
- Chequered Plate Standard Details
- Handrail Details for Steel Structural Floors
- Cable Pull Pit Requirements and Details
- Laboratory Building Plan and Architecture Details
- Structural Bolt Details Types Grades and Applications
- HOUSE PLAN 40 x 60 | NORTH FACING |
- Finishing Schedule Drawing for Doors, Windows, and Rolling Shutters
- Workshop Building Architectural Layout
- Calculation of Foundation Bearing Capacity as per IS 6403 – 1981
- Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity Calculation For Foundations
- DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHOD OF MULTISTORY CONCRETE BUILDINGS
- HOUSE PLAN 60 x 60 | SOUTH FACING |
- Civil Structural Engineering Interview Questions pdf Free Download