Methods of Typical Handrail Construction in RCC Structures
Handrails in RCC structures are important safety elements used in stairs, ramps, balconies, and walkways. Their construction involves proper design and execution to ensure safety, durability, and compliance with codes. Below are the common methods and details for constructing handrails in RCC structures:
1. Types of Handrails in RCC Structures
a. Cast-in-Situ RCC Handrails
- Fully constructed using reinforced cement concrete.
- Integrated with the main RCC structure (e.g., stairs or ramps).
- Common in industrial or utilitarian settings.
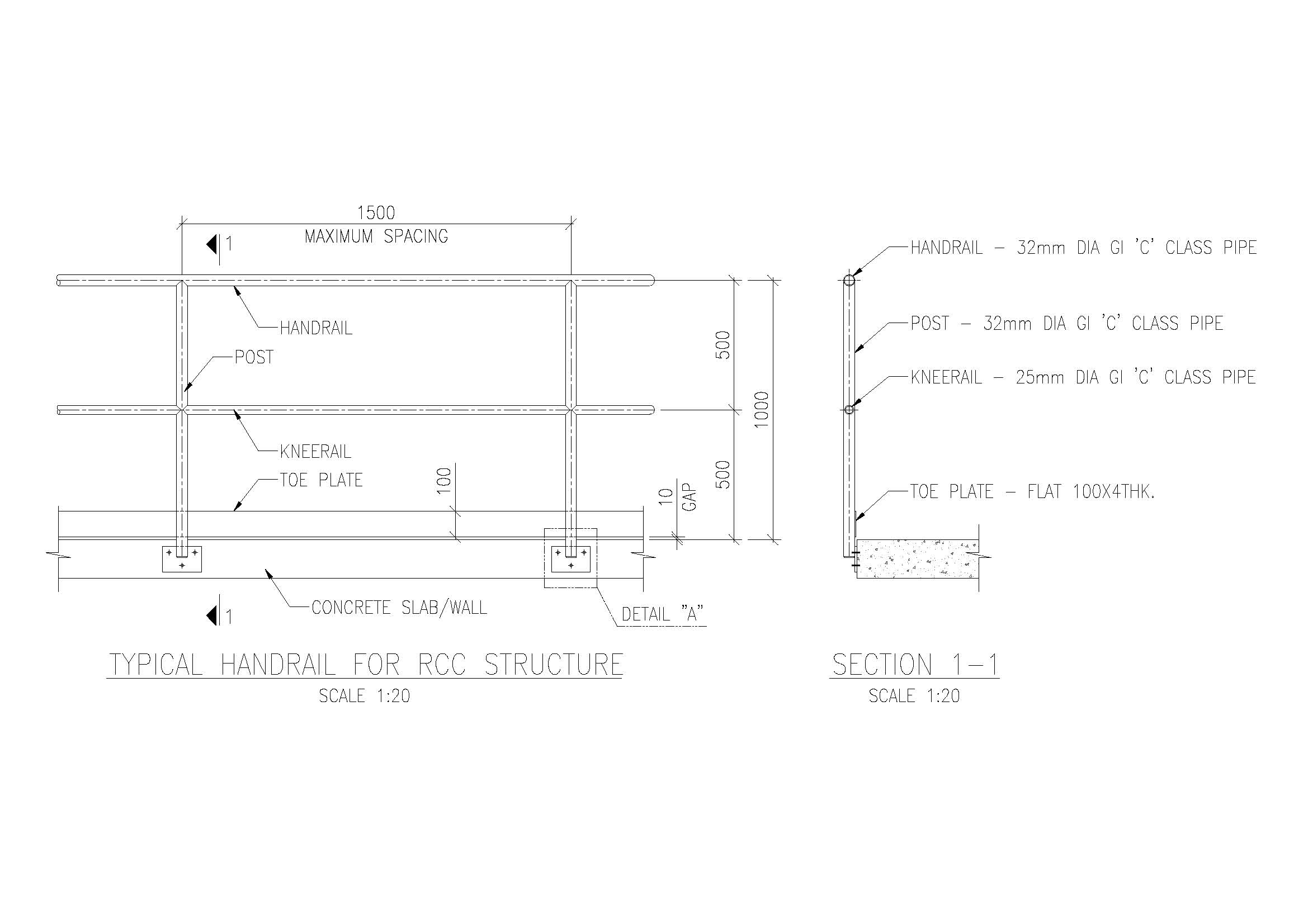
b. RCC Base with Metal Handrails
- RCC upstand beam or wall as the base.
- Steel or aluminum handrails fixed on top using anchor bolts.
- Common for staircases and balconies.
c. RCC Base with Glass Handrails
- RCC structure serves as the base.
- Glass panels fixed using clamps or embedded anchors.
- Common in modern commercial or residential buildings.
d. Precast RCC Handrails
- Handrail elements are precast and installed on-site.
- Suitable for modular or quick construction projects.
2. Methods of RCC Handrail Construction
a. Cast-in-Situ Method
- Design and Formwork:
- Use wooden or steel formwork to shape the handrail.
- Ensure smooth and uniform alignment for aesthetics.
- Reinforcement:
- Provide longitudinal bars (10–12 mm dia) along the length of the handrail.
- Use stirrups or ties (6–8 mm dia) at 150–200 mm spacing.
- Extend reinforcement into adjoining beams, slabs, or columns for continuity.
- Concrete Pouring:
- Use M20 or higher grade concrete for durability.
- Pour concrete carefully to prevent honeycombing.
- Compact using vibrators for a smooth finish.
- Finishing:
- Remove formwork after 7–14 days of curing.
- Apply plaster or polish for a smooth surface.
- Add anti-slip or protective coatings if required.





b. RCC Base with Metal Handrails
- Construct the RCC Base:
- Cast a solid RCC parapet or upstand beam.
- Height: Typically 100–150 mm thick and 800–900 mm high.
- Install Metal Handrails:
- Use stainless steel or mild steel for the handrail structure.
- Anchor the handrail to the RCC base using:
- Anchor bolts (M12 or M16).
- Chemical anchors for strong bonding.
- Finishing:
- Ensure handrail is corrosion-resistant (e.g., powder-coated or galvanized).
- Add decorative caps or covers if needed.
c. RCC Base with Glass Handrails
- Construct the RCC Base:
- Cast a sturdy RCC parapet or low wall.
- Provide embedded steel plates or anchor bolts during concreting.
- Fix Glass Panels:
- Use tempered or laminated glass (10–12 mm thick) for safety.
- Fix glass using clamps, U-channels, or embedded anchors.
- Ensure edges are smooth and polished.
- Reinforce for Stability:
- Add vertical posts or brackets if the glass panels exceed 1.5 m in length.
d. Precast RCC Handrails
- Manufacture Off-Site:
- Cast handrail components (balusters, rails) in molds.
- Include reinforcement for structural stability.
- Transport and Install:
- Fix precast elements onto RCC stairs, ramps, or slabs.
- Use dowels, grouts, or epoxy to secure connections.
- Finishing:
- Apply a uniform plaster finish or paint for aesthetics.
3. Design and Detailing
a. Handrail Height
- Standard height: 800–1000 mm from the floor level.
- Height may vary depending on local building codes.
b. Spacing of Vertical Members (Balusters)
- Maximum spacing: 100–150 mm to prevent accidental falls.
c. Reinforcement Detailing
- Longitudinal bars (handrail): 10–12 mm dia.
- Stirrups (ties): 6–8 mm dia at 150–200 mm spacing.
d. Cross-Section
- Typical handrail dimensions:
- Width: 50–100 mm.
- Depth: 100–150 mm.
4. Finishing Options
- Plain Concrete:
- Apply cement plaster and paint.
- Textured Finish:
- Use stamped patterns or decorative coatings.
- Polished Finish:
- Sand and polish for smooth, reflective surfaces.
5. Maintenance
- Inspection:
- Regularly inspect for cracks, corrosion, or loosening of handrails.
- Repairs:
- Patch cracks with epoxy or cement mortar.
- Repainting:
- Reapply paint or anti-corrosion coatings periodically.
6. Relevant Codes and Standards
- IS 456:2000 – General RCC design guidelines.
- IS 875 (Part 3) – Wind load considerations for outdoor handrails.
- NBC (National Building Code of India) – Handrail height and spacing requirements.
- OSHA – For industrial handrails and safety features.
- 3D HOUSE DESIGN (34)
- Civil and Structural Design Calculations (76)
- Commercial Plans (9)
- East Facing House Plans (14)
- Engineering Concepts – Civil & Structural (224)
- Excel Spreadsheets (37)
- Free Downloads (49)
- House Plans (57)
- Industrial standards (91)
- North Facing House Plans (15)
- South Facing House Plans (15)
- West Facing House Plans (9)