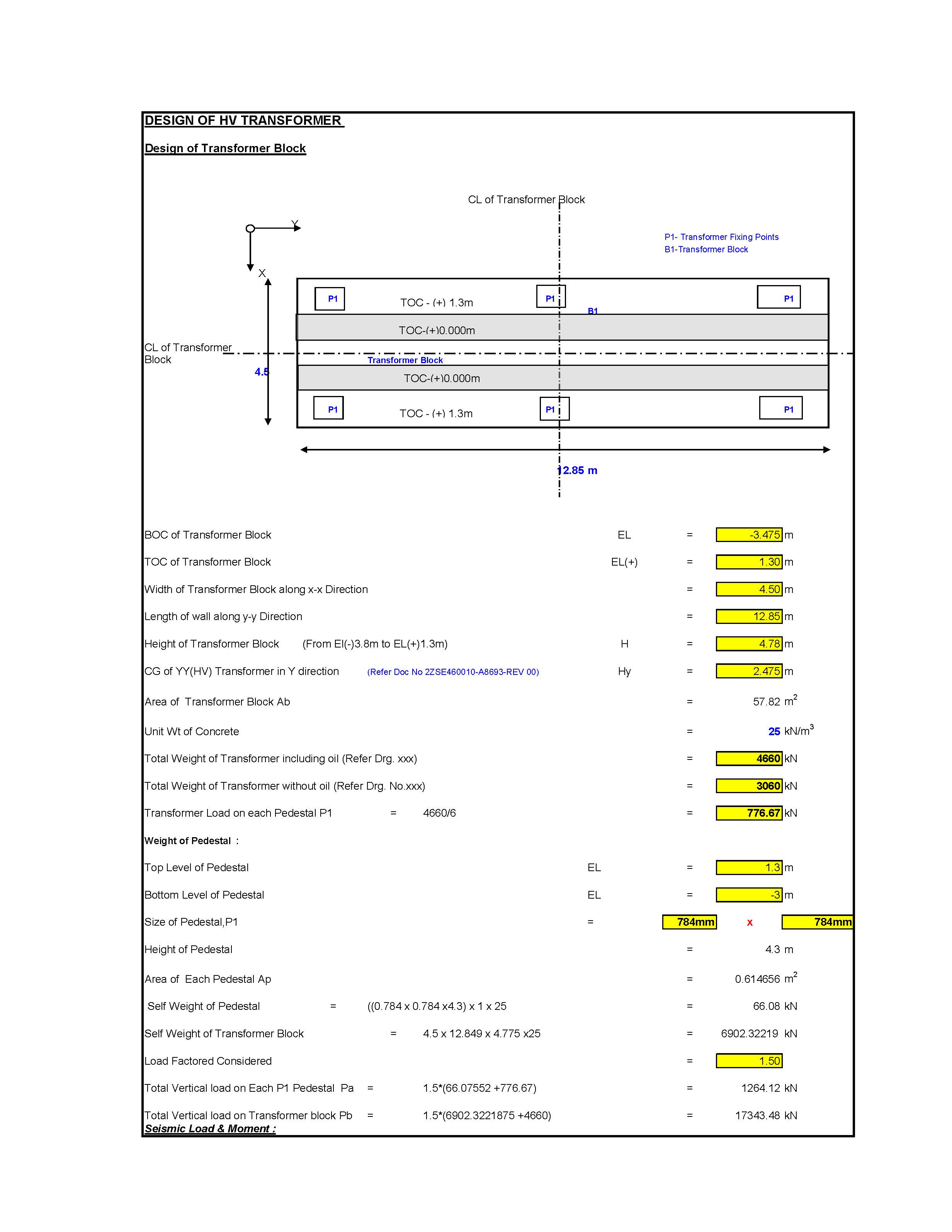
Designing a transformer foundation involves considering the transformer’s size, weight, dynamic forces, and environmental conditions to ensure safety and stability. Here’s a step-by-step guide to designing a transformer foundation:
Transformer Foundation Design
1. Understand the Design Requirements
- Transformer Data: Obtain the dimensions, weight (including oil weight), and base footprint from the manufacturer.
- Static and Dynamic Loads: Include the dead load, live load, wind load, seismic forces, and equipment vibrations.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess soil conditions, groundwater levels, and climate factors.
2. Determine Foundation Type
- Slab-on-Grade: For smaller transformers on solid ground.
- Isolated Footings: For large transformers with heavy loads.
- Pile Foundations: For transformers on weak or compressible soils.
3. Structural Design
- Load Calculations:
- Calculate the total load, including the transformer weight, oil, and ancillary equipment.
- Account for wind and seismic loads as per applicable codes (e.g., IS 1893, ASCE 7).
- Base Area:
- Ensure the foundation base area provides adequate bearing capacity.
A=Wqallowable
Where W is the total load and q allowable is the allowable soil bearing capacity.
- Thickness of Foundation Slab:
- Based on bending moments, shear forces, and punching shear.
- Reinforcement:
- Design based on bending and shears stresses using IS 456 (India), ACI 318 (USA), or similar standards.



4. Dynamic Analysis
- Consider dynamic forces due to vibrations and short-circuit forces.
- Ensure the natural frequency of the foundation system does not resonate with the operational frequency of the transformer.
5. Additional Considerations
- Cable Trenches: Include cable entry/exit points.
- Oil Containment: Provide oil pits or bund walls to contain any leakage.
- Drainage: Ensure proper drainage to prevent water accumulation.
- Earthing: Provide earthing pits or grids as per electrical codes.
6. Applicable Codes and Standards
- IS 456: For RCC design in India.
- ACI 318: For concrete design in the USA.
- IS 1893/ASCE 7: For seismic design.
- IS 875/ASCE 7: For wind load calculations.
- IEC/IEEE Standards: For electrical and equipment-specific design.
7. Safety Factors
- Include factors of safety for materials and loads as per code requirements.
8. Construction Guidelines
- Use high-quality concrete (usually M25 or higher) for durability.
- Ensure proper curing and compaction of the foundation.
- Install anti-vibration pads if required.
This approach ensures a stable, durable, and code-compliant foundation for transformers in any application.
Related Posts: