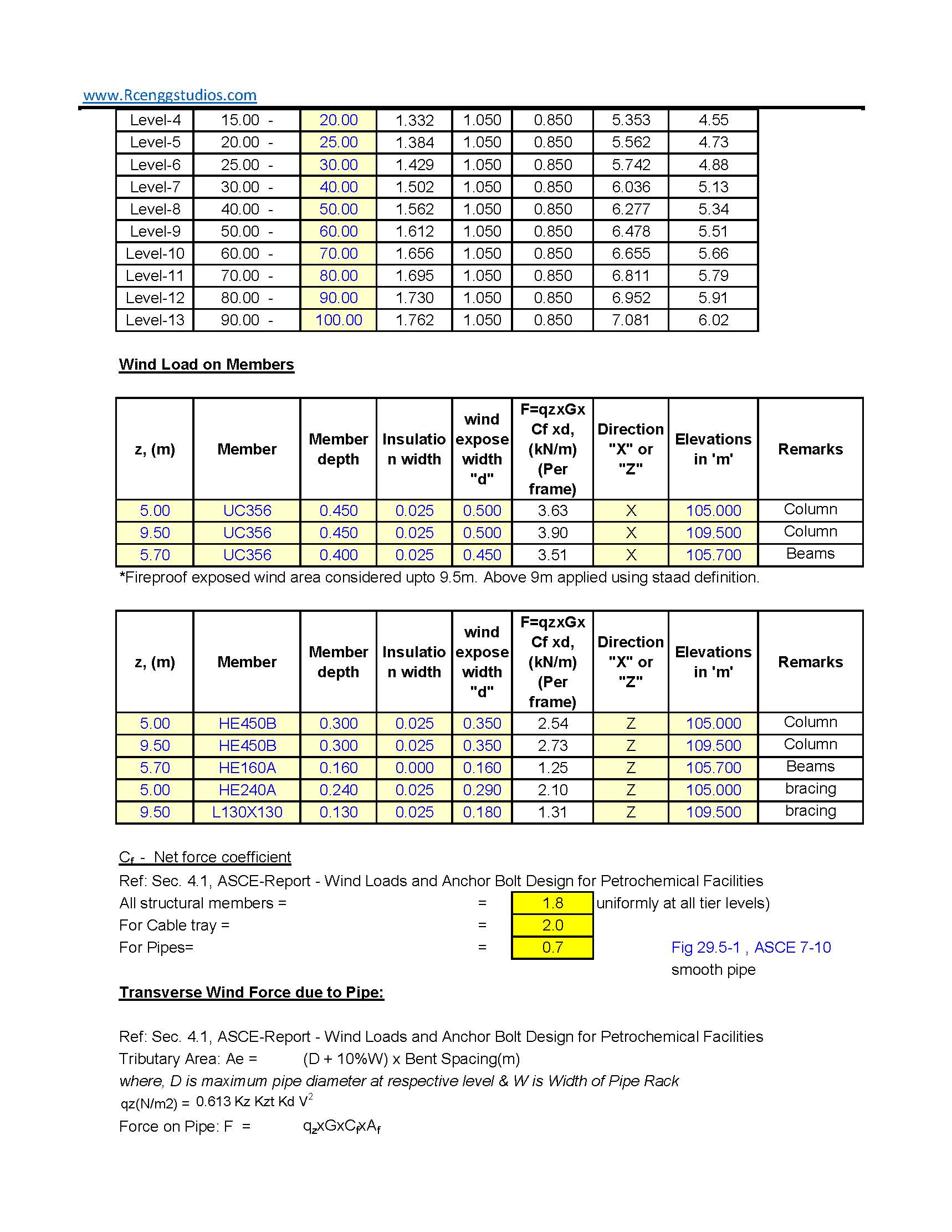
To calculate wind load on Pipe racks, open structures, cable trays and pipes as per ASCE 7-10, use the following approach, accounting for the cylindrical shape and exposure to wind.
For wind load calculations in metric units as per ASCE 7-10, the primary difference lies in the units for wind speed and pressure. Here’s how to calculate wind load using metric conversions:
1. Determine Basic Wind Speed (V)
- Obtain wind speed (V) in meters per second (m/s) from ASCE 7-10 maps, converting as needed.
2. Calculate Velocity Pressure (q)
- The velocity pressure q(z) at a height z in kPa (kiloPascal) can be calculated as: q(z)=0.613×Kz×Kzt×Kd×V2
where:
- 0.613 = conversion factor to metric (in kPa) for air density,
- V = basic wind speed in m/s,
- Kz = velocity pressure exposure coefficient (from ASCE 7-10 Table 27.3-1),
- Kzt = topographic factor,
- Kd = wind directionality factor.
3. Exposure Category
- Define Exposure Category (B, C, or D) based on the surrounding terrain, as this influences Kz values.
4. Calculate Projected Area (A)
- Use the projected area per unit length of the cable tray or pipe:
A=D×L
where:
- D = outer diameter of the pipe or effective width of the cable tray (m or ft),
- L = length of the pipe or cable tray (m or ft).
5. Calculate Wind Load (F)
- The wind force per unit length on the pipe or cable tray can be calculated as: F=q(z)×Cd×A
where:
- F = wind load per unit length (kN/m or lb/ft),
- q(z) = velocity pressure at height zzz,
- Cd = drag coefficient,
- A = projected area per unit length.
6. Consider Combined Effects
- For long runs of cable trays or pipes, consider gust factors and structural sway, especially if elevated.
Example Calculation
For a pipe of 0.5m diameter at 10m above ground, in an exposure category C with a basic wind speed of 40 m/s:
- q(z)=0.613×Kz×V2
- A=D×L (D = 0.5 m)
- F=q(z)×Cd×A



Electrical Layout For Residential Building
Creating an electrical layout for a house involves planning the placement of: Lighting fixtures Power…
HOUSE PLAN 29 X 56 | SOUTH FACING |
House Plan ground floors, the floors are completely utilized without wastage. The plot size is…
Rain Water Gutter and Down Take Systems
Typical Gutter and Downpipe Systems: An Overview Understanding Rain Water Gutter and Down Take Systems:…
Stormwater Drainage Calculation
Designing 🌧️ Stormwater Drainage systems is essential to ensure the efficient collection and disposal of…
Structural Engineering Design Criteria – American Codes and Standards
In the United States, structural engineering design is governed by a robust framework of codes,…
Anchor Bolts Length as per ACI 318-14
In ACI 318-14 (“Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete”), the length of anchor bolts embedded…