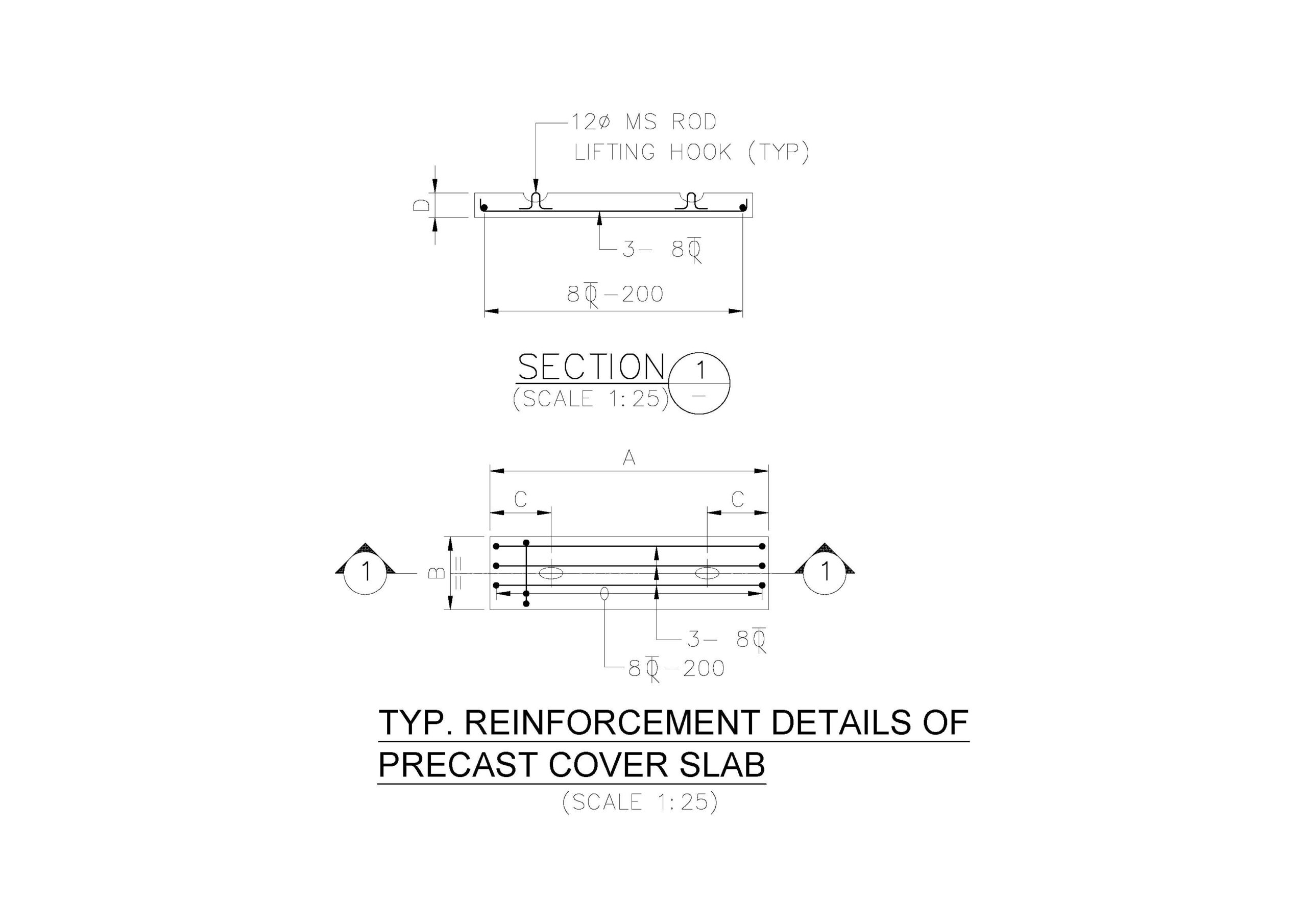
Designing a precast cover slab for a trench involves ensuring the slab can handle expected loads, fits the trench dimensions, and meets relevant safety and durability standards. Below is a detailed guide to designing a precast cover slab for a trench:
Key Design Considerations
- Load Requirements
- Dimensions
- Reinforcement
- Materials
- Manufacturing Tolerances
- Handling and Installation
- Safety Features
- Drainage
Step-by-Step Design Process
1. Load Requirements
- Dead Load: Weight of the slab itself.
- Live Load: Expected loads from vehicles, equipment, or pedestrians.
- Impact Load: Potential dynamic loads from dropped objects or equipment.
- Safety Factors: Apply appropriate safety factors as per design codes (e.g., ACI, Eurocode).
2. Dimensions
- Trench Width and Length: Measure the trench dimensions to ensure the cover slab fits properly.
- Slab Thickness: Typically ranges from 4 to 8 inches depending on load requirements and span.
3. Reinforcement
- Reinforcement Bars (Rebar): Determine the size and spacing of rebar based on structural calculations. Commonly used sizes are #4 or #5 rebar.
- Mesh Reinforcement: Alternatively, use welded wire mesh for additional strength.
- Placement: Ensure rebar is placed in the tension zones (top and bottom thirds of the slab thickness).
4. Materials
- Concrete Mix: Use a mix suitable for outdoor exposure and load requirements. Typical compressive strength is 4000 psi (27.6 MPa).
- Durability: Additives or coatings to improve durability against weather, chemical exposure, and wear.
5. Manufacturing Tolerances
- Precision: Ensure precast slabs are manufactured to precise dimensions to fit the trench without gaps.
- Quality Control: Implement strict quality control measures during manufacturing.
6. Handling and Installation
- Lifting Points: Design lifting hooks or points to facilitate safe handling and placement.
- Installation Method: Plan the installation process to ensure proper alignment and support during placement.
7. Safety Features
- Non-Slip Surface: Apply a non-slip finish on the top surface to prevent accidents.
- Edge Protection: Chamfered edges to reduce chipping and damage.
8. Drainage
- Drain Holes: Incorporate drain holes if the trench is prone to water accumulation.
- Slope: Design the slab with a slight slope for water runoff.
Example Design Calculation for a Precast Cover Slab
Given:
- Trench Dimensions: 2 feet wide, 4 feet long.
- Load Requirement: Vehicle load of 2000 lbs (assuming a safety factor of 1.5).
- Concrete Strength: 4000 psi.
1. Slab Thickness Calculation:
- Span (Width of Trench): 2 feet.
- Assumed Slab Thickness: 6 inches (0.5 feet).
2. Load Calculation:
- Total Load on Slab: 2000 lbs×1.5 (safety factor)=3000 lbs2000 , text{lbs} times 1.5 , text{(safety factor)} = 3000 , text{lbs}2000lbs×1.5(safety factor)=3000lbs.
- Load per Unit Area: 3000 lbs2 ft×4 ft=375 lbs/ft2frac{3000 , text{lbs}}{2 , text{ft} times 4 , text{ft}} = 375 , text{lbs/ft}^22ft×4ft3000lbs=375lbs/ft2.
3. Reinforcement Design:
- Moment Calculation:
- Assume simply supported slab: M=wL28M = frac{wL^2}{8}M=8wL2.
- Where w=375 lbs/ft2w = 375 , text{lbs/ft}^2w=375lbs/ft2 and L=2 ftL = 2 , text{ft}L=2ft.
- M=375×228=187.5 lb-ftM = frac{375 times 2^2}{8} = 187.5 , text{lb-ft}M=8375×22=187.5lb-ft.
- Rebar Requirement:
- Using ACI formula for rebar: As=M0.9fy×dAs = frac{M}{0.9fy times d}As=0.9fy×dM.
- Assume yield strength fy=60,000 psify = 60,000 , text{psi}fy=60,000psi and effective depth d=4.5 ind = 4.5 , text{in}d=4.5in.
- As=187.5×120.9×60,000×4.5=0.001 sq in/inAs = frac{187.5 times 12}{0.9 times 60,000 times 4.5} = 0.001 , text{sq in/in}As=0.9×60,000×4.5187.5×12=0.001sq in/in.
- Use #4 rebar (0.2 sq in per bar), spaced at 12 inches on center.
4. Final Design Specifications:
- Slab Thickness: 6 inches.
- Reinforcement: #4 rebar, spaced at 12 inches on center, both ways.
- Concrete Mix: 4000 psi strength.
- Surface Finish: Broom finish for non-slip surface.
- Drain Holes: 1-inch diameter holes at 12-inch intervals along the centerline.
- Edge Chamfer: 1/2-inch chamfer on all edges.
Conclusion
By following these steps and using appropriate design codes and standards, you can ensure that the precast cover slab will be durable, safe, and capable of handling the expected loads. Proper design and careful consideration of materials, reinforcement, and installation will result in a reliable and effective trench cover solution.
Click here to Download Cover Slab Design