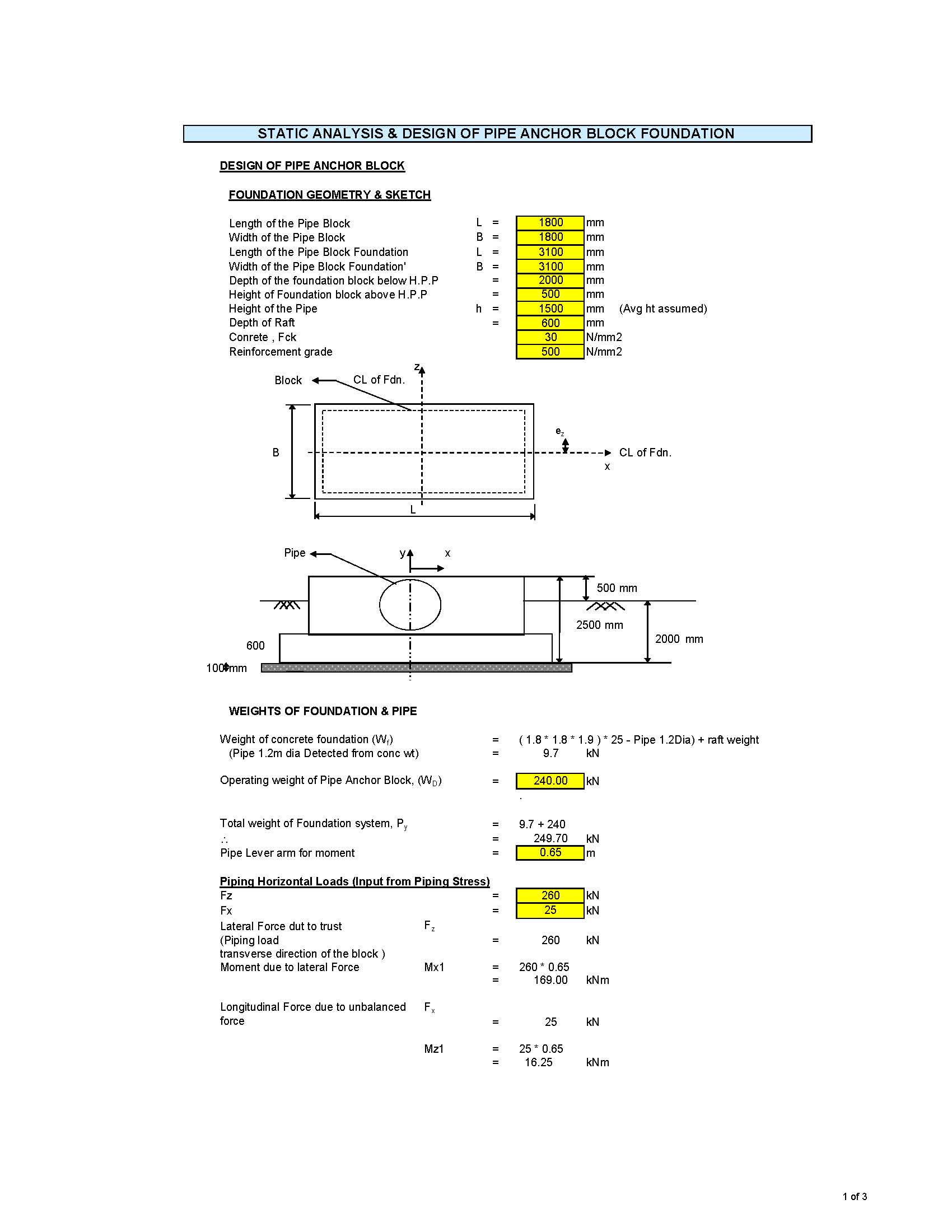
Calculate Eccentricity e = Mu/Pu.
Anchor bolt capacities related to project specific need to be updated in the “PROPERTIES” sheet. The availability of the anchor bolt diameters are also need to be updated in the “PROPERTIES” sheet.
Anchor bolt capacities based on code are calculated and the same is mentioned in the anchor bolt capacities table. For calculating the anchor bolt capacities thread per mm for different bolt diameters are taken from Code ASME B1.13M. Bolt net area is taken from ASME B 1.1. Corrosion allowance need to be given as an input for calculating the bolt net area.
Type of analysis is carried out by comparing eccentricity with base plate length.
If “e< N/6”, then base plate will be in full contact hence pure compression (“PC”) case will be followed.
Maximum bearing stress shall be calculated as fpmax = (Pu/NB)+(Mu/Z)
If “N/6<e<(N/2-Amin/3)” , then base plate will be in partial contact no uplift will be there hence moderate eccentricity(“Eccm”) case will be followed.
Maximum bearing stress shall be calculated as fpmax = (2*Pu/YB) where Y=3(N/2-e).
If “(N/2-Amin/3)<e” then base plate will be in partial contact with uplift hence large eccentricity(“Ecc”) case will be followed.
We have three unknowns namely tension in bolt, length of contact of base plate and bearing stress. Hence Blodgett approach is followed. Cubical equation is taken from Blodgett and solved by “Differential Method”.
Maximum bearing stress shall be calculated as fpmax = (2*(Pu+T)/YB)
Maximum tension per face shall be calculated as Nu = -Pu*(N/2-Y/3-e)/(N/2-Y/3+f)
If e<(N/2-edx) then base plate will be no contact and the case is considered as pure tension ( “PT”) .
Maximum tension per face shall be calculated as Nu = Pu/2+Mu/d1
If e>(N/2-edx) then base plate will be in partial contact and case will be considered as “PTEcc”.
Design of Fixed baseplate 8 bolt.xls – download as Excel Spreadsheet (.xls), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free on our blog spot.
Below files are available for download
- Design of Fixed baseplate 8 bolt.xls – Excel spread sheet
- Design of Fixed baseplate 8 bolt .pdf
Product images are the reference to excel Design of Fixed baseplate 8bolt.
“Do write the details in the Yellow cells only and do not make edit in other cell as the excel sheet is not protected with password and you can edit anywhere in the sheet, accidental edits in the cells may lead to errors in the design sheet due to overriding of formula by values edited by you”




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.